In short, yes, bee feeders are good for bees, but only when used correctly. A feeder is a critical tool for beekeepers to help a colony survive specific periods of stress, not a permanent solution or a substitute for natural forage. Using them improperly or at the wrong time can do more harm than good.
The central purpose of a bee feeder is to act as a temporary life support system. It is not meant to replace a bee's natural foraging behavior, but to prevent starvation when a colony is new or when natural nectar sources are unavailable due to seasonal extremes.

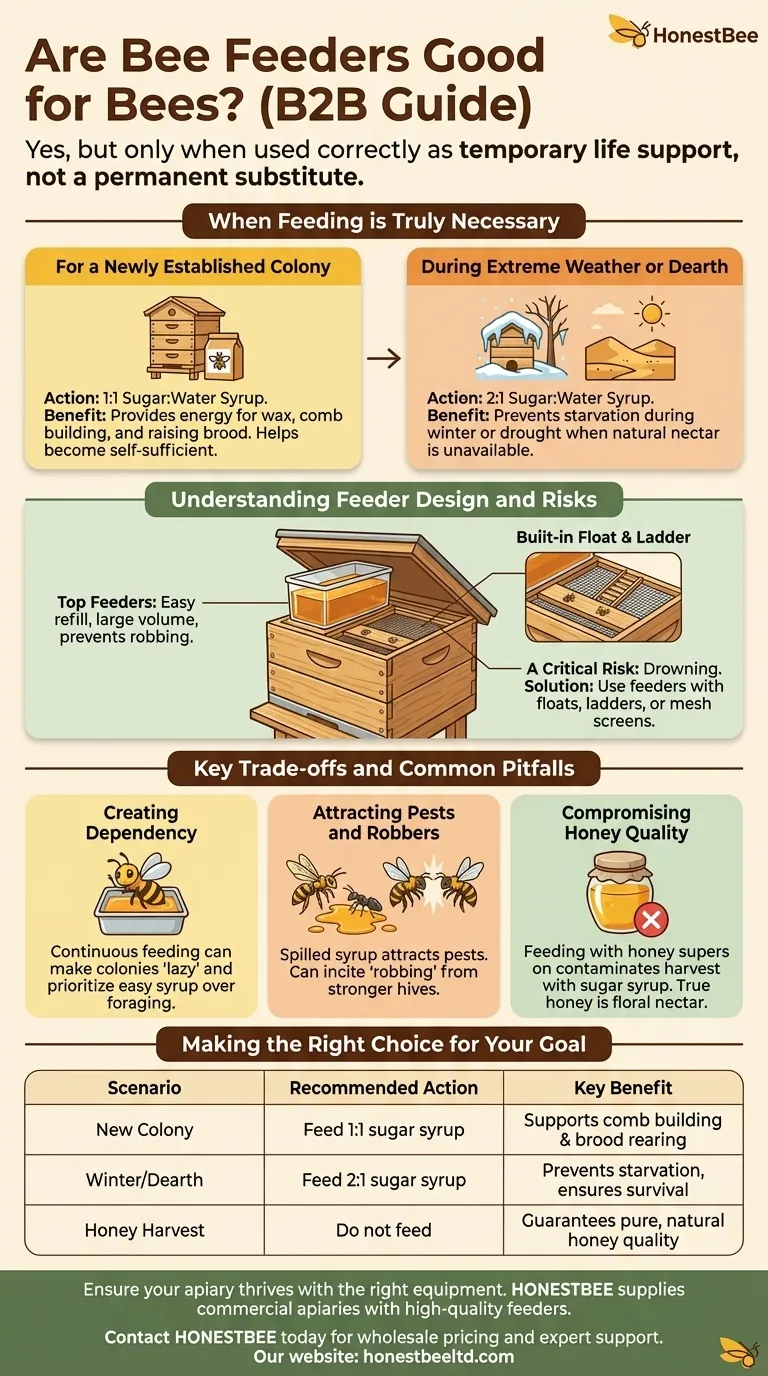
When Feeding is Truly Necessary
A responsible beekeeper uses a feeder as a targeted intervention, not a constant supplement. There are two primary scenarios where feeding is essential for a colony's survival.
For a Newly Established Colony
When you first install a package of bees or a nucleus hive ("nuc"), they have no stored food and no built-out comb to store it in.
Providing a 1:1 sugar-to-water syrup gives them the immediate carbohydrate energy they need to produce wax, build their comb, and begin raising brood, helping them become self-sufficient much faster.
During Extreme Weather or Dearth
A "dearth" is any period when there are no nectar-producing flowers available.
The most common dearth is winter, when cold temperatures prevent both plant growth and bee flight. A colony without sufficient honey stores will starve.
Extreme heat and drought can also cause a dearth, as plants stop producing nectar to conserve water. Supplemental feeding during these times can be the difference between survival and colony collapse.
Understanding Feeder Design and Risks
There are several types of feeders, but they all share common goals and potential risks. The main designs are entrance feeders, internal frame feeders, and top feeders.
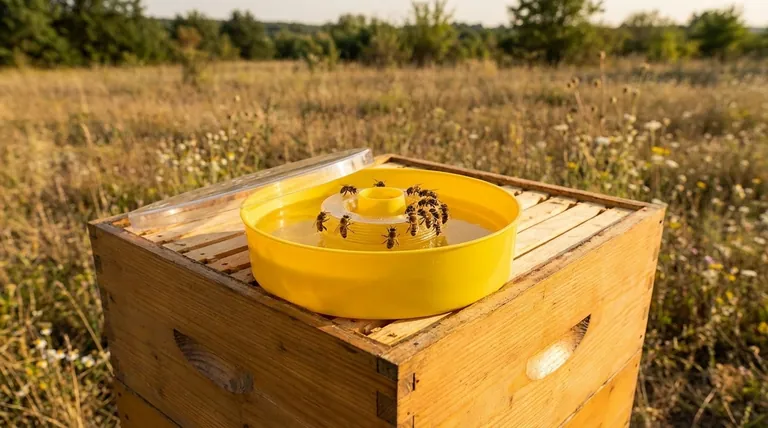
The Appeal of Top Feeders
Many beekeepers prefer top feeders because they sit directly on top of the hive boxes, under the main cover.
This design offers several advantages. They are easy to refill with minimal disturbance to the bees, hold large volumes of syrup, and their placement helps prevent robbing from other hives or pests.
A Critical Risk: Drowning
The most significant danger with any feeder is the risk of bees drowning in the syrup. This is especially true for top feeder models that have large, open reservoirs of liquid.
To prevent this, it is crucial to use feeders with built-in floats, ladders, or protective mesh screens that allow bees to access the syrup safely without falling in.
Key Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While feeders can be a lifeline, their misuse creates significant problems. Understanding these trade-offs is fundamental to responsible beekeeping.
Creating Dependency
Feeding bees continuously when natural nectar is abundant can make a colony "lazy." They may prioritize the easy-to-access syrup over foraging for more diverse natural resources.
Attracting Pests and Robbers
Spilled syrup or poorly designed feeders can be a magnet for ants, wasps, and other pests.
It can also incite "robbing," where stronger honey bee colonies attack a weaker, fed hive to steal its resources, often resulting in the death of the weaker colony.
Compromising Honey Quality
Never feed bees sugar syrup while you have honey supers on the hive that you intend to harvest for human consumption.
The bees will store the sugar syrup in the honeycomb right alongside the natural nectar, contaminating the final product. True honey must be made from floral nectar, not processed sugar.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to feed should be based entirely on the colony's immediate needs.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new hive: Feed them a 1:1 sugar syrup consistently until they have built out the comb in their first brood box.
- If your primary focus is ensuring winter survival: Check their food stores in the fall. If they seem light, feed them a thicker 2:1 sugar syrup to help them build up the necessary weight to survive the cold months.
- If your primary focus is harvesting honey: Do not feed the bees at all during the main nectar flow season to ensure your honey is pure and natural.
Ultimately, a bee feeder is a powerful tool that, when used with knowledge and purpose, helps you support your bees when they need it most.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Recommended Action | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| New Colony | Feed 1:1 sugar syrup | Supports comb building & brood rearing |
| Winter/Dearth | Feed 2:1 sugar syrup | Prevents starvation, ensures survival |
| Honey Harvest | Do not feed | Guarantees pure, natural honey quality |
Ensure your apiary thrives with the right equipment. Proper feeding is just one part of successful beekeeping. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, durable feeders and essential beekeeping supplies through our wholesale-focused operations. Let us help you build a stronger, more resilient operation.
Contact HONESTBEE today for wholesale pricing and expert support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Round Hive Top Bee Feeder for Syrup
- Rapid Bee Feeder White Plastic 2L Round Top Feeder for 8 or 10-Frame Bee Hives
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Professional Hive Nutrition Solution for Beekeeping
- Professional Hive Top Bee Feeder for Beekeeping
- Classic Boardman Entrance Bee Feeder Hive Front Feeding Solution
People Also Ask
- What can the round hive top feeder be used for? A Guide to Efficient, Safe Bee Feeding
- What are the features of top feeders for bees? Maximize Hive Health with Safe, High-Capacity Feeding
- How should the round hive top feeder be positioned? Master Internal Feeding for Stronger Colonies
- What is a top feeder for bees? Maximize Colony Health with Efficient Feeding
- What types of hive boxes is the round hive top feeder compatible with? Universal Fit for 8 & 10-Frame Langstroth Hives



















