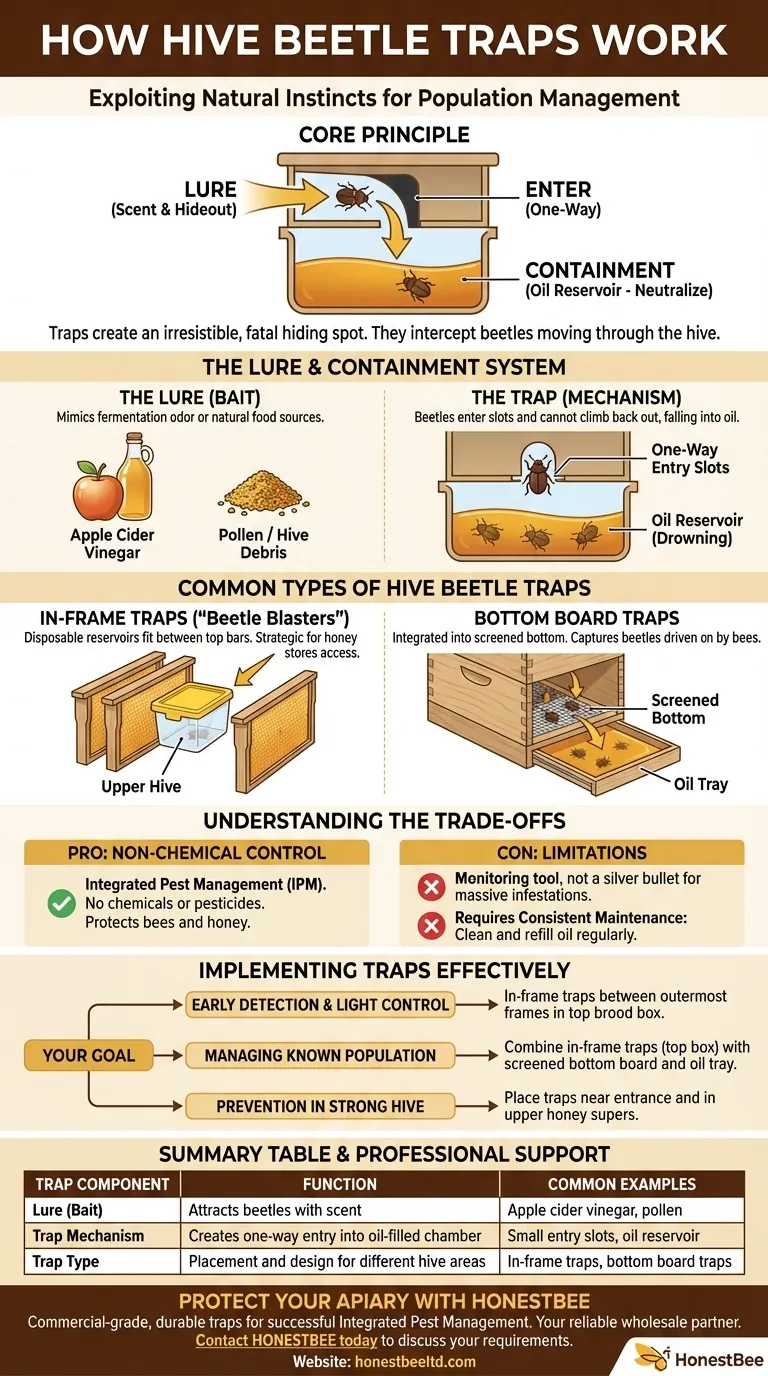
At their core, hive beetle traps work by exploiting the beetle's natural instincts. They use a combination of a lure and a containment mechanism. The traps create an attractive, dark hiding spot baited with an attractant, tricking the Small Hive Beetle (SHB) into entering a chamber from which it cannot escape, where it is ultimately neutralized.
The central principle behind any hive beetle trap is not to actively hunt the beetles, but to create an irresistible and fatal hiding place that intercepts them as they move through the hive. They are a tool for population management, not eradication.
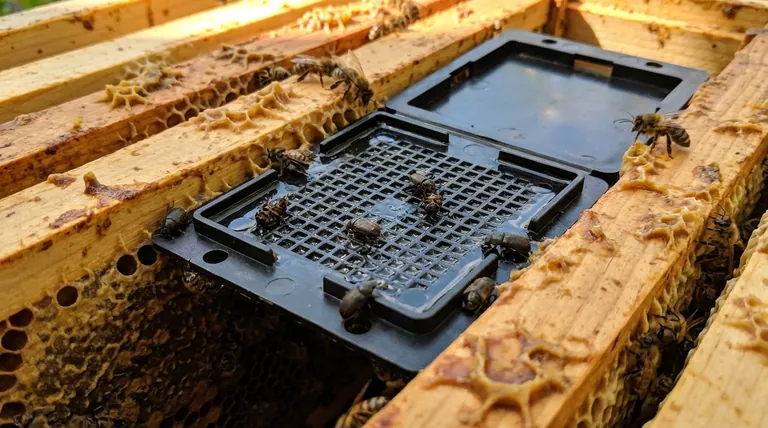

The Core Principle: Lure and Containment
Effective beetle traps are designed around the beetle's predictable behavior. Understanding this principle is key to using them successfully.
Exploiting Beetle Behavior
Small Hive Beetles instinctively flee from bees and seek refuge in the darkest, tightest crevices they can find inside a hive. Traps are engineered to mimic these ideal hiding spots, making them more appealing to beetles than natural cracks in the woodwork.
The Lure (The Bait)
To enhance their appeal, traps are baited. The goal is to attract beetles that are moving throughout the hive.
Common attractants include:
- A small amount of apple cider vinegar: The scent of fermentation mimics the odor that can occur during a beetle infestation, which draws them in.
- Pollen or hive debris: Using a small pinch of pollen or debris from the bottom board can also serve as a natural food-based lure.
The Trap (The Mechanism)
The second part of the system is the capture mechanism, which is almost always a reservoir of oil.
Beetles crawl through small slots into the trap's main compartment. These slots are designed to be a one-way street. Once inside, the beetles are unable to climb back out and subsequently fall into the oil, where they drown. This is a simple, non-chemical method of neutralization.
Common Types of Hive Beetle Traps
While the principle is the same, several designs exist, each with a specific placement and use case.
In-Frame Traps ("Beetle Blasters")
These are the most common type. They are small, disposable plastic reservoirs designed to fit snugly between the top bars of two frames inside the hive body. Their placement in the upper parts of the hive is strategic, as beetles often try to access honey stores there.
Bottom Board Traps
These are integrated into a screened bottom board. Bees will harass and chase beetles, causing many to fall. With a screened bottom, the beetles fall through the mesh and land in a tray of oil placed underneath the hive. This method captures beetles from all over the hive as they are driven downward by the bees.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Hive beetle traps are a valuable tool, but they are not a perfect solution. It's critical to understand their limitations.
Pro: A Non-Chemical Control Method
Traps are a form of Integrated Pest Management (IPM). They allow you to control beetle populations without introducing any chemicals or pesticides into your hive, protecting your bees and your honey.
Con: A Monitoring Tool, Not a Silver Bullet
Traps are excellent for controlling low-to-moderate beetle numbers and for monitoring the scale of your problem. However, they will not save a colony that is already collapsing from a massive infestation. In that scenario, more drastic measures are required.
Con: Requires Consistent Maintenance
For traps to be effective, they must be checked and maintained. The oil reservoirs need to be cleaned out and refilled regularly. A trap that is full of dead beetles or has had its oil evaporate is completely useless.
Implementing Traps Effectively in Your Hive
Your specific goal will determine the best strategy for trap placement and management.
- If your primary focus is early detection and light control: Use disposable in-frame traps placed between the two outermost frames in the top brood box.
- If your primary focus is managing a known population: Combine in-frame traps in the top box with a screened bottom board and an oil tray below for a more aggressive, two-pronged approach.
- If your primary focus is prevention in a strong hive: Place traps near the entrance and in the upper honey supers where beetles often congregate first.
By understanding that these traps are a passive system of interception, you can use them effectively to help your bees defend their colony.
Summary Table:
| Trap Component | Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Lure (Bait) | Attracts beetles with scent (e.g., apple cider vinegar, pollen). | Apple cider vinegar, hive debris. |
| Trap Mechanism | Creates a one-way entry into an oil-filled chamber where beetles drown. | Small entry slots, oil reservoir. |
| Trap Type | Placement and design for different hive areas and infestation levels. | In-frame traps (e.g., Beetle Blasters), bottom board traps. |
Protect Your Apiary with Professional-Grade Equipment from HONESTBEE
Effectively managing Small Hive Beetles is crucial for the health of your colonies and the productivity of your operation. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, high-quality traps and supplies needed for successful Integrated Pest Management.
We understand the challenges you face. Let us be your reliable wholesale partner for all your beekeeping equipment needs.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your requirements and discover how our products can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Reusable Clear Small Hive Beetle Traps for Beehives Beetle Trapping Tools
- Reusable Aluminium Beetle Trap for Small Hive Beetles Silver Bullet
- Removable Washable Hive Beetle Trap Attractants for Small Hive Beetles
- Plastic Beetle Blaster Trap Beekeeping Tools and Supplies
People Also Ask
- Why are hive beetle traps important for beekeepers? Protect Your Hive from a Devastating Infestation
- How should filled beetle traps be handled? Safely Remove and Dispose to Protect Your Hive
- What is the best time to use beetle traps? Master the Spring Strategy for Effective Hive Protection
- What should be done if a hive shows signs of a small hive beetle infestation? Protect Your Hive Now
- How do specialized physical traps and isolation devices assist in the management of Small Hive Beetle (Aethina tumida)?



















