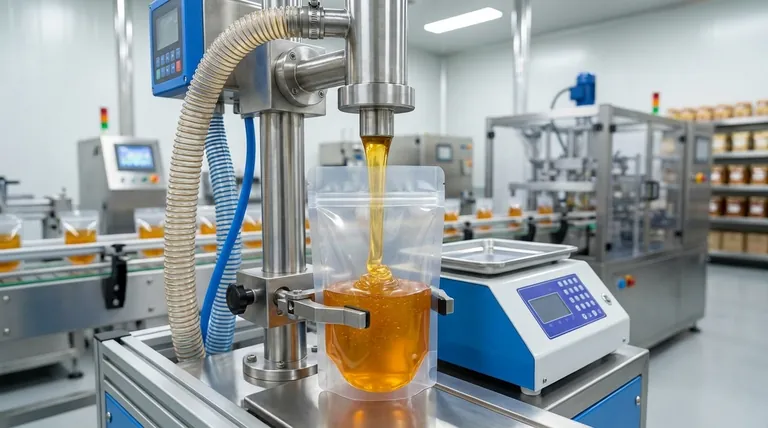
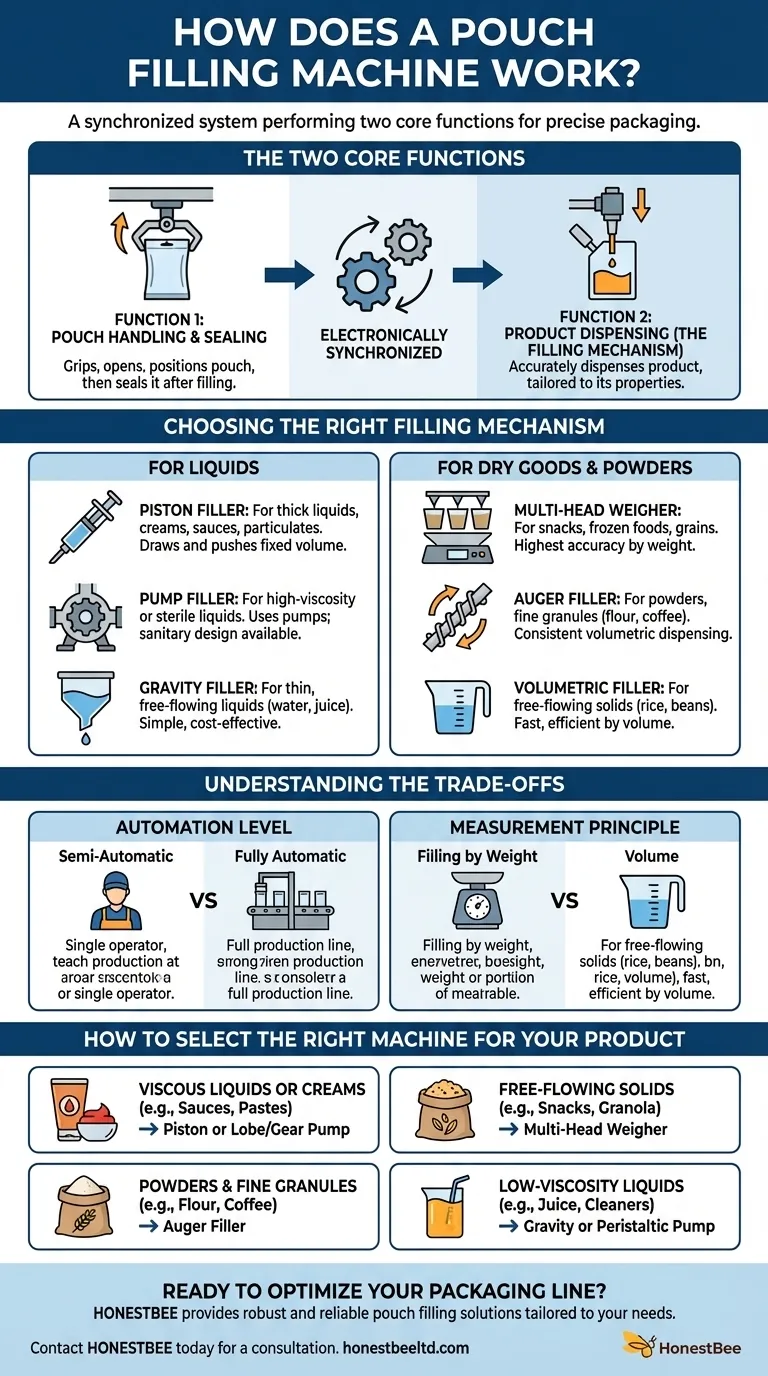
At its core, a pouch filling machine is a synchronized system that performs two primary jobs. First, it handles the empty pouch by opening it and positioning it for filling. Second, it uses a specialized mechanism—like a pump, auger, or scale—to accurately dispense a specific amount of product into the pouch before sealing it shut.
The critical insight is that there is no single type of "pouch filling machine." Instead, it is a combination of a pouch handling system and a distinct filling apparatus, where the filling technology is chosen specifically to match the product's unique properties—whether it's a liquid, powder, or solid.

The Two Core Functions of Any Pouch Filling System
To understand how these machines work, you must see them as two integrated but separate functions working in perfect harmony.
Function 1: Pouch Handling and Sealing
This is the part of the machine that manages the physical pouch. The process typically involves gripping the pre-made pouch, pulling it open with vacuum or mechanical grippers, and holding it steady under the filling nozzle.
Once the product has been dispensed, the machine moves the filled pouch to a sealing station. Here, heat and pressure are applied to create a secure, airtight seal.
Function 2: Product Dispensing (The Filling Mechanism)
This is the heart of the machine and the function that varies most. The dispensing mechanism is engineered to handle the specific characteristics of your product, such as its viscosity, consistency, and particle size.
The pouch handling and dispensing components are electronically synchronized. The filling process begins only when the machine confirms a pouch is open and correctly positioned, ensuring no product is wasted.
Choosing the Right Filling Mechanism for Your Product
The choice of filling mechanism is the most important decision you will make. It directly impacts accuracy, speed, and product integrity. The primary methods are categorized by the type of product they handle.
For Liquids: Piston, Pump, and Gravity Fillers
Liquid fillers are designed to manage flow and viscosity.
A piston filler uses a cylinder that draws in a set volume of product from a hopper and then pushes it out through a nozzle. This method is exceptionally versatile and is ideal for thick liquids, creams, sauces, and even products with large particulates.
Pump fillers use different types of pumps for various liquids. Lobe or gear pumps are excellent for high-viscosity products, while peristaltic pumps, which use flexible tubing, are perfect for sterile or corrosive liquids because the product never touches the mechanical parts.
A gravity filler is the simplest design. Product is held in a hopper above the filling station and flows downward into the pouch by gravity. It is best suited for thin, free-flowing liquids like water or juice.
For Dry Goods & Powders: Weighers, Augers, and Volumetric Fillers
Handling dry products requires precise control over weight or volume.
A multi-head weigher uses a series of weighing buckets to measure out an exact weight of a product before dropping it into the pouch. This is the most accurate method for solids like snacks, grains, or frozen foods.
An auger filler uses a large, screw-like device (an auger) that rotates to dispense a consistent volume of fine powders or granules, such as flour, spices, or coffee grounds.
A volumetric filler dispenses product by volume rather than weight. It uses cups of a specific size that are filled and then emptied into the pouch. This method is fast and works well for free-flowing, consistent-density products like rice or beans.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right machine involves balancing automation, precision, and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making a sound investment.
Automation Level: Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic
A semi-automatic machine requires an operator to manually place the pouch for filling. The machine then handles the dispensing and sealing automatically. This offers high precision at a lower initial cost and is suitable for smaller production runs.
A fully automatic system integrates the entire process from pouch forming to filling, sealing, and final packaging without operator intervention, maximizing speed and efficiency for large-scale operations.
Measurement Principle: Filling by Weight vs. Volume
Filling by weight (gravimetric) offers the highest level of accuracy because it is not affected by changes in product density. This is crucial for high-value products where precise measurement is essential.
Filling by volume (volumetric) is generally faster and less expensive. However, its accuracy depends on the product having a consistent density. It is an efficient choice for many free-flowing solids and liquids where minor weight variations are acceptable.
How to Select the Right Machine
Your product dictates the technology. Focus on matching the filling mechanism to the product's characteristics to ensure optimal performance.
- If your primary focus is viscous liquids or creams (e.g., sauces, pastes): A piston filler or a lobe/gear pump filler provides the power and precision needed for thick products.
- If your primary focus is free-flowing solids (e.g., snacks, granola): A multi-head weigher delivers the highest accuracy by measuring the exact target weight for each pouch.
- If your primary focus is powders or fine granules (e.g., flour, coffee): An auger filler is the industry standard for dispensing these challenging products consistently.
- If your primary focus is low-viscosity liquids (e.g., juice, cleaning solutions): A simple gravity filler or a sanitary peristaltic pump filler offers a cost-effective and efficient solution.
Understanding these core mechanisms empowers you to choose a system that ensures both product integrity and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Filling Mechanism | Best For Product Types | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | Thick liquids, creams, sauces | Versatile; handles products with particulates |
| Pump Filler | High-viscosity or sterile liquids | Sanitary; product doesn't touch pump parts |
| Gravity Filler | Thin, free-flowing liquids (e.g., water, juice) | Simple, cost-effective design |
| Multi-Head Weigher | Solids, snacks, frozen foods | Highest weight accuracy |
| Auger Filler | Powders, fine granules (e.g., flour, coffee) | Consistent volumetric dispensing |
| Volumetric Filler | Free-flowing solids (e.g., rice, beans) | Fast, efficient for consistent-density products |
Ready to optimize your packaging line?
As a trusted wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and equipment distributors, HONESTBEE provides robust and reliable pouch filling solutions tailored to your specific products—from honey and supplements to powders and more. Our expertise ensures you get the right machine for maximum accuracy, speed, and efficiency.
Contact HONESTBEE today for a consultation and discover how our packaging equipment can drive your operation's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- Professional Durable Customizable Blister Packing Machine
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
- Honey Stick Filler Vertical Paste Sachet Packing Machine for Honey Sachets
People Also Ask
- How do automatic capsule filling machines ensure royal jelly quality? Precision Systems for Large-Scale Packaging
- How does an automatic honey-filling machine ensure quality? From Raw Forest Honey to Commercial Success
- How long to let honey sit before bottling? A Guide to Perfectly Clear Honey
- What value do automatic honey-filling machines offer? Scaling Commercial Honey Production with Precision
- Why are automatic honey filling machines critical? Scale Your Brand with Industrial Precision and Efficiency
- Why is the motor an important factor when selecting a filling machine? Boost Efficiency and Simplify Production
- Why is specialized Honey Extraction and Filling Machinery critical? Unlock Scalability for Your Apiary
- What factors should be considered when choosing a semi-automatic filling machine? A Guide for Apiaries & Distributors



















