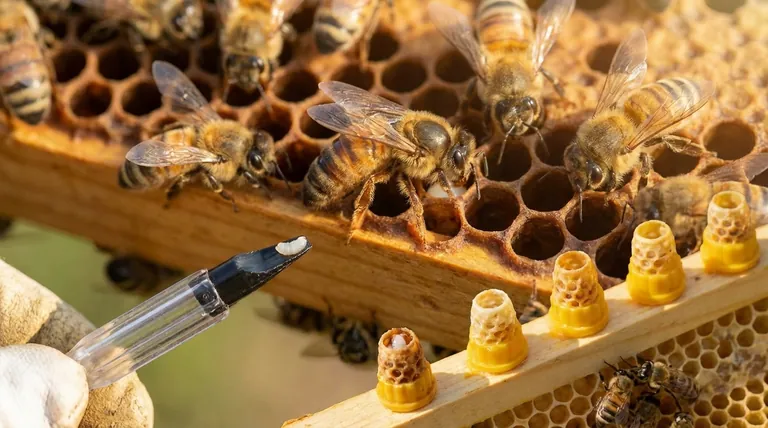
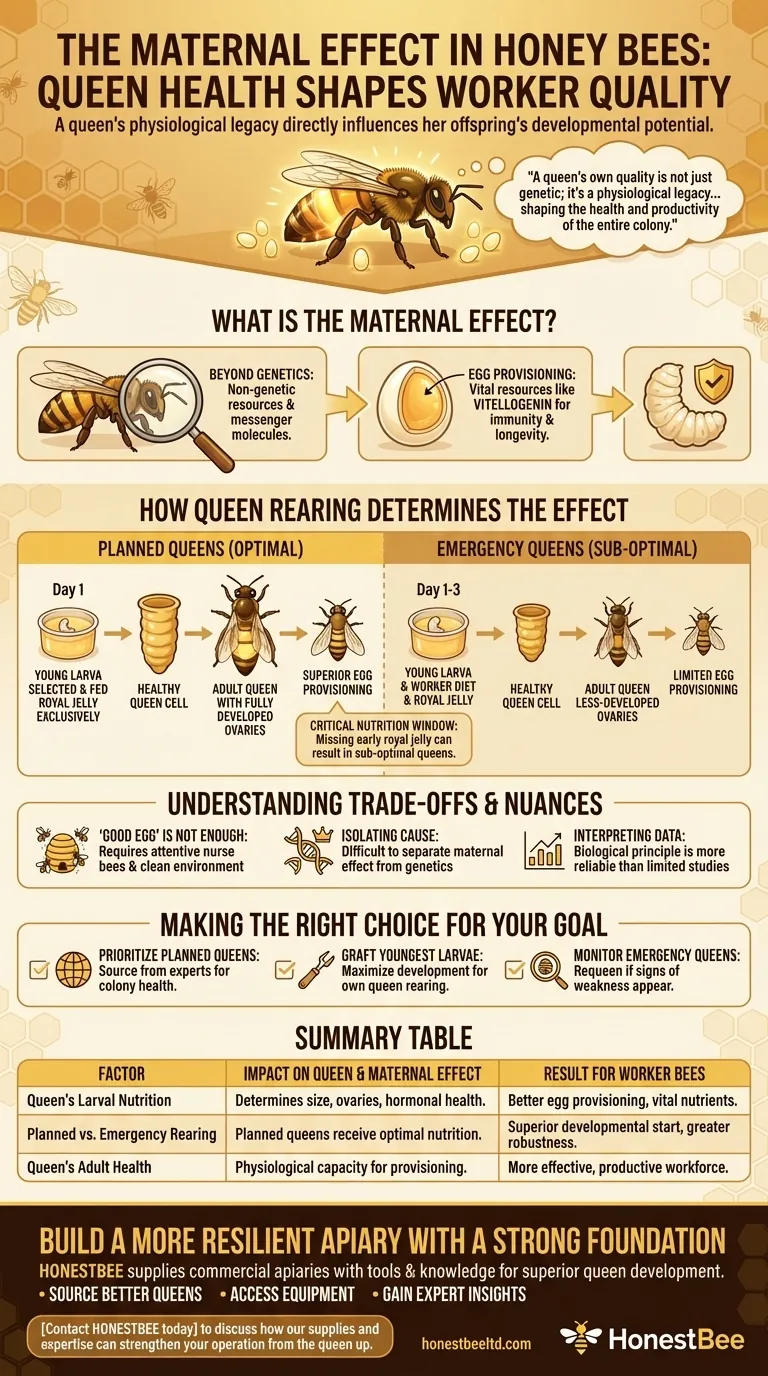
The maternal effect in honey bees is the direct influence of a queen's own health and developmental history on the quality of the eggs she lays. A well-reared queen provisions her eggs with superior resources, which gives the resulting worker bees a better developmental start, leading to a more robust and effective workforce.
The core principle is that a queen's own quality is not just genetic; it's a physiological legacy passed to her offspring. A queen that was optimally raised has the biological capacity to produce higher-potential workers, directly shaping the health and productivity of the entire colony.

What is the Maternal Effect in Honey Bees?
The maternal effect describes how a mother influences her offspring's traits in ways that are independent of the genes she passes on. For honey bee queens, this is a critical factor in colony success.
Beyond Simple Genetics
Every worker receives half its DNA from the queen. However, the maternal effect involves the non-genetic package the queen provides with that DNA. This includes the nutrients, hormones, and messenger molecules she deposits into the egg.
The Role of Egg Provisioning
A healthy, well-fed queen with fully developed ovaries packs her eggs with vital resources. This includes vitellogenin, a key protein that acts as a nutrient source and plays a role in immunity and longevity for the developing larva. A better-provisioned egg gives the larva a significant head start.
A Queen's Health is the Foundation
A queen's capacity for this provisioning is determined by her own larval development. A queen that received abundant, high-quality royal jelly throughout her development will be larger, have more egg-producing tubules (ovarioles), and have better hormonal regulation, all of which contribute to laying higher-quality eggs.
How Queen Rearing Determines the Maternal Effect
The method by which a queen is raised has a profound impact on her adult physiology and, therefore, on the maternal effect she can exert.
Planned vs. Emergency Queens
Colonies raise queens under two main conditions. Planned queens (supersedure or swarm cells) are created intentionally by the bees in a strong, queenright colony. Larvae are selected at the youngest possible age and fed royal jelly exclusively from day one.
Emergency queens are raised in response to the sudden loss of a queen. The workers must choose a young worker larva and switch its diet to royal jelly. This larva may be up to three days old and has already spent part of its life on a less-rich "worker diet."
The Critical Nutrition Window
That initial period is critical. Missing out on a pure royal jelly diet, even for a day, can result in a sub-optimal queen. She may be smaller, mate less successfully, and have less-developed ovaries, limiting her ability to provision her eggs effectively throughout her life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While the principle is clear, its real-world application has complexities. The quality of a worker bee is the result of many influences, not just one.
The "Good Egg" is Not Enough
A high-quality egg is a starting point, not a guarantee. That egg must still be laid in a clean cell and cared for by attentive and well-fed nurse bees. A strong maternal effect provides potential, but the colony environment must realize that potential.
Isolating the Cause
It can be difficult to separate the maternal effect from the queen's genetics. A queen from a strong genetic line who was also raised under ideal conditions will likely produce excellent workers, but both factors are contributing to that success.
Interpreting Limited Data
Some studies may produce counterintuitive results. The reference to "QE-derived queens" producing better workers is a good example. This is not the general consensus in apiculture and is noted as coming from "limited analysis." It's more reliable to trust the broader biological principle: a better-developed mother provides a better start for her offspring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this principle allows you to make more strategic decisions for your colonies.
- If your primary focus is colony health and productivity: Prioritize sourcing queens that were reared by experts under planned, non-emergency conditions.
- If your primary focus is raising your own queens: Always graft from the youngest possible larvae (less than 24 hours old) and place them in a strong, well-fed cell builder colony to maximize their development.
- If you discover a colony has raised an emergency queen: Monitor its performance carefully. While it may succeed, be prepared to requeen if the colony shows signs of weakness or poor productivity.
By recognizing that a queen's quality is the foundational blueprint for her colony's potential, you can make deliberate choices that foster more resilient and successful hives.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Queen & Maternal Effect | Result for Worker Bees |
|---|---|---|
| Queen's Larval Nutrition | Determines queen size, ovary development, and hormonal health. | Better egg provisioning with vital nutrients like vitellogenin. |
| Planned vs. Emergency Rearing | Planned queens receive optimal nutrition from day one. | Workers have a superior developmental start, leading to greater robustness. |
| Queen's Adult Health | A healthy queen has the physiological capacity for effective egg provisioning. | A more effective and productive workforce for the entire colony. |
Build a more resilient and productive apiary with queens built on a strong foundation.
At HONESTBEE, we understand that a high-quality queen is the cornerstone of a successful colony. Our wholesale-focused operations supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the tools and knowledge to foster superior queen development.
Let us help you achieve your goals:
- Source better queens for improved colony health and honey production.
- Access equipment for optimal queen rearing and hive management.
- Gain expert insights into best practices for maximizing the maternal effect in your hives.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss how our supplies and expertise can strengthen your operation from the queen up.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
- Nicot Queen Rearing Kit for Beekeeping and Grafting in Nicot System
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
- Brown Nicot Queen Cell Cups for Breeding Queen Bees Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the Doolittle method of queen rearing? Master Controlled Queen Production for Your Apiary
- What are the five methods of queen rearing? From Simple Splits to Commercial Grafting
- Are queen rearing systems suitable for all beekeepers? Modern Tools for Every Experience Level
- What is the purpose of using multi-story large hive boxes? Ensure Data Integrity in Experimental Honeybee Colonies
- How long can a hive survive queenless? The Critical Countdown to Save Your Colony



















