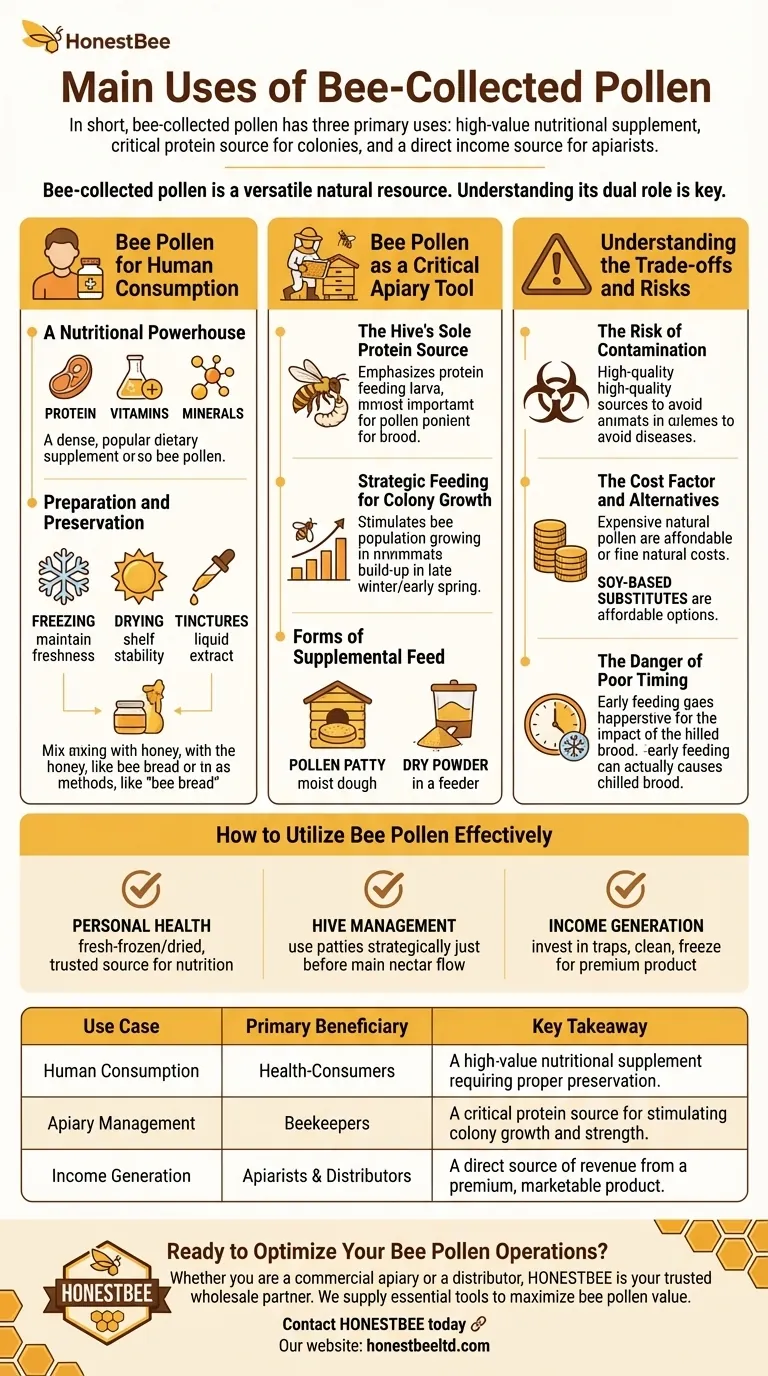
In short, bee-collected pollen has three primary uses. It is harvested as a high-value nutritional supplement for human consumption, used by beekeepers as a critical protein source to feed and strengthen their own bee colonies, and serves as a direct source of income for apiarists who sell the final product.
Bee-collected pollen is far more than just bee food; it's a versatile natural resource. Understanding its dual role as both a human health product and a critical tool for hive management is key to appreciating its value.
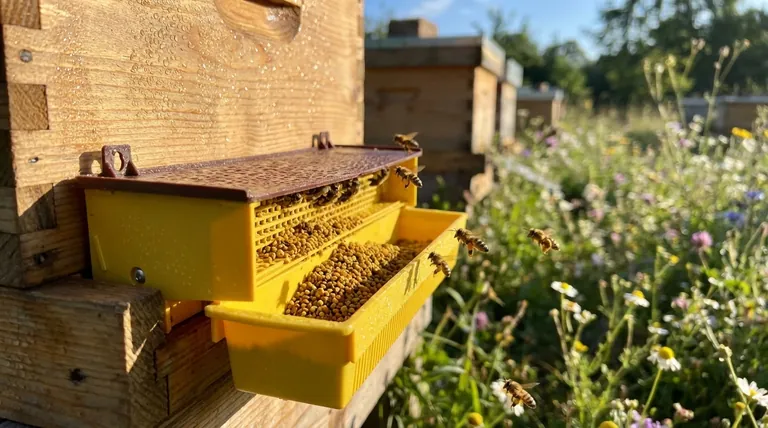

Bee Pollen for Human Consumption
Bee pollen is increasingly sought after in the nutritional and pharmaceutical industries for its perceived health benefits. It is often marketed as a natural health food and performance booster.
A Nutritional Powerhouse
Pollen is the honey bee's sole source of protein, and this dense nutritional profile is what makes it attractive for human use. Its composition of proteins, vitamins, and minerals has positioned it as a popular dietary supplement.
Preparation and Preservation
For human consumption, pollen must be properly preserved. Common methods include freezing to maintain freshness, drying for shelf stability, or creating tinctures. Some also mix it with honey to create a product similar to "bee bread," the fermented pollen bees store in the hive.
Bee Pollen as a Critical Apiary Tool
For beekeepers, managing pollen is fundamental to maintaining a healthy and productive colony. It is the foundation of the hive's diet.
The Hive's Sole Protein Source
Bees rely on pollen for the protein, lipids, and vitamins necessary to raise their young (brood). A lack of pollen can severely limit a colony's ability to grow and survive.
Strategic Feeding for Colony Growth
Beekeepers often feed pollen or pollen substitutes back to their hives. This is typically done to stimulate the build-up of the colony's population in late winter or early spring, ensuring a strong workforce is ready for the main nectar flow.
Forms of Supplemental Feed
Supplemental pollen is provided in two main forms. A moist, doughy pollen patty, often mixed with sugar syrup, is placed directly inside the hive. Alternatively, dry powder can be provided in a feeder outside the hive for bees to collect naturally.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While beneficial, the use of bee pollen in beekeeping is not without its challenges and required considerations.
The Risk of Contamination
When feeding pollen back to bees, it is critical to use a high-quality, reputable source. Low-quality pollen can introduce harmful substances or diseases into a hive, causing more harm than good.
The Cost Factor and Alternatives
Natural bee pollen can be expensive. Because of this, many beekeepers use more affordable pollen substitutes, which are often soy-based powders formulated to mimic the nutritional profile of real pollen.
The Danger of Poor Timing
Feeding pollen patties too early in the season can be a mistake. It can cause the queen to lay eggs and expand the brood nest before there are enough adult bees to keep the new brood warm, potentially leading to chilled and dead brood.
How to Utilize Bee Pollen Effectively
- If your primary focus is personal health: Seek out fresh-frozen or properly dried pollen from a trusted beekeeper to ensure maximum nutritional value.
- If your primary focus is hive management: Use pollen patties as a strategic tool to build colony strength just before, but not too far in advance of, the main spring nectar flow.
- If your primary focus is generating income: Invest in efficient pollen traps and a reliable process for cleaning and freezing the harvest to create a premium, marketable product.
Ultimately, mastering the collection and application of bee pollen allows you to harness one of nature's most concentrated nutritional substances for both human and honey bee vitality.
Summary Table:
| Use Case | Primary Beneficiary | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Human Consumption | Health-Consumers | A high-value nutritional supplement requiring proper preservation. |
| Apiary Management | Beekeepers | A critical protein source for stimulating colony growth and strength. |
| Income Generation | Apiarists & Distributors | A direct source of revenue from a premium, marketable product. |
Ready to Optimize Your Bee Pollen Operations?
Whether you are a commercial apiary looking to strengthen your colonies or a beekeeping equipment distributor seeking high-quality supplies, HONESTBEE is your trusted wholesale partner. We supply the essential tools—from pollen traps to feeding equipment—to help you maximize the value of bee pollen for health, hive management, and sales.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our supplies can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Removable Plastic Pollen Trap With Ventilated Tray for Bees Pollen Collector
- 30 cm Plastic Entrance Hole Bee Pollen Trap and Collector
- Plastic Bee Pollen Trap Strips Comb Catcher Collector
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why is a Pollen Trap installed at the beehive entrance? Optimize Your Floral Resource Surveys & Data
- What is the function of industrial-grade pollen traps in the production of diverse bee products? Drive Apiary Growth
- How effective are pollen traps at collecting pollen? Optimize Your Harvest Efficiency and Hive Health
- What is the function of outdoor pre-mounted pollen traps? Optimize Collection and Research for Your Apiary
- How does a bee pollen trap work? Master the Mechanics of Efficient Pollen Collection for Your Apiary



















