The best substitute for feeding bees depends entirely on their nutritional needs. While bees' ideal food is the honey and pollen they gather themselves, beekeepers must sometimes intervene. The correct substitute is either a sugar syrup to replace carbohydrates for energy or a pollen substitute to replace protein for raising young.
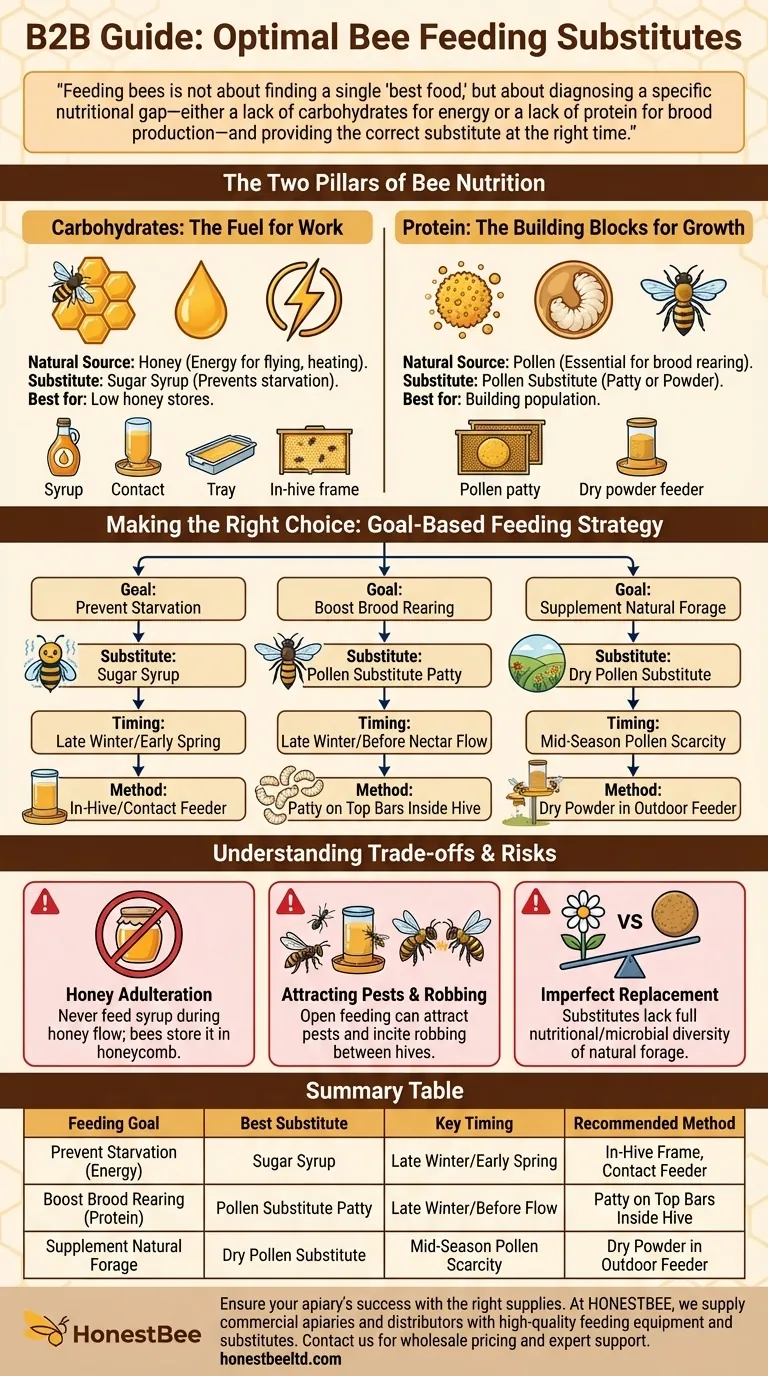
Feeding bees is not about finding a single "best food," but about diagnosing a specific nutritional gap—either a lack of carbohydrates for energy or a lack of protein for brood production—and providing the correct substitute at the right time.
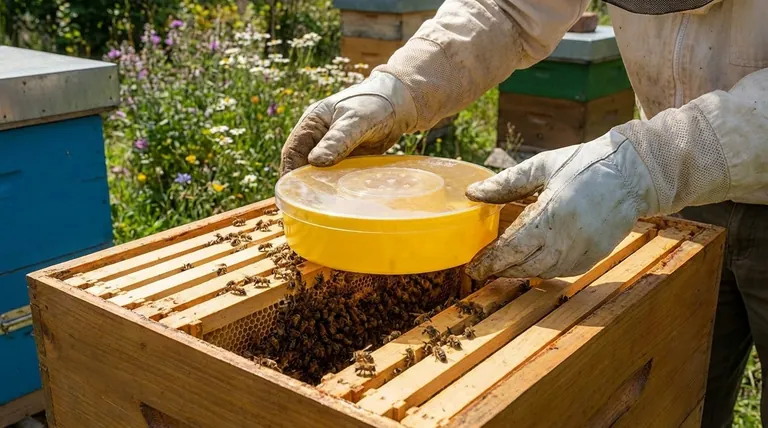

The Two Pillars of Bee Nutrition
To effectively manage a colony, you must understand the two distinct types of food they require and their substitutes.
Carbohydrates: The Fuel for Work
A bee's primary food source is honey, which is almost pure carbohydrate. This provides the energy for all hive activities, from flying and foraging to generating heat during winter.
The most common substitute for honey is sugar syrup. This is typically a mix of white table sugar and water, used to prevent starvation when a hive's honey stores are low.
Protein: The Building Blocks for Growth
Bees get protein, fats, and minerals from pollen. This is not primarily for the adult bees' energy but is absolutely essential for raising larvae (brood) and for the development of young bees.
When natural pollen is scarce, beekeepers use pollen substitutes. These are specially formulated powders that provide the protein and nutrients necessary to sustain and grow the colony's population.
Choosing the Right Substitute and Method
Knowing when and how to provide each type of feed is critical for the health of the colony.
When to Feed Sugar Syrup
The primary reason to feed sugar syrup is to prevent starvation. This is most common in late winter, early spring before flowers bloom, or during a long period of bad weather.
Slow feeding methods using contact feeders, tray feeders, or in-hive frame feeders are best. This minimizes drowning and prevents attracting pests or bees from other hives.
When to Feed Pollen Substitutes
Pollen substitutes are used to stimulate brood rearing. This is often done in late winter or early spring to build up the colony's population in time for the main nectar flow.
These substitutes can be offered in two forms: a moist pollen patty placed directly on the top bars inside the hive, or as a dry powder in a feeder outside the hive. Patties provide more targeted nutrition, while powder more closely mimics natural foraging.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Supplemental feeding is a powerful tool, but it is not without risks and should not be done without careful consideration.
Risk of Honey Adulteration
The most significant risk is contaminating your honey harvest. Never feed sugar syrup when bees are actively producing honey that you intend to harvest. The bees will store the syrup in the honeycomb, adulterating the final product.
Attracting Pests and Robbing
Openly feeding syrup or pollen substitutes can attract ants, wasps, and other pests. It can also incite "robbing," where stronger hives attack and steal the resources of a weaker, fed hive.
Substitutes Are Not a Perfect Replacement
While effective, commercial substitutes lack the full nutritional and microbial diversity of natural pollen and nectar. They are a crutch to be used when necessary, not a long-term replacement for a healthy environment with abundant natural forage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your feeding strategy on a clear objective for the colony's health.
- If your primary focus is preventing winter or early spring starvation: Use a slow feeder to provide sugar syrup inside the hive.
- If your primary focus is boosting population before the main nectar flow: Provide a pollen substitute patty inside the hive to encourage the queen to lay eggs.
- If your primary focus is supporting your bees during a mid-season pollen shortage: Offer a dry pollen substitute in an outdoor feeder to supplement their diet without being overly intrusive.
Ultimately, thoughtful feeding is a powerful tool to ensure your colony not only survives, but thrives.
Summary Table:
| Feeding Goal | Best Substitute | Key Timing | Recommended Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevent Starvation (Energy) | Sugar Syrup | Late Winter / Early Spring | In-Hive Frame Feeder, Contact Feeder |
| Boost Brood Rearing (Protein) | Pollen Substitute Patty | Late Winter / Before Nectar Flow | Patty on Top Bars Inside Hive |
| Supplement Natural Forage | Dry Pollen Substitute | Mid-Season Pollen Scarcity | Dry Powder in Outdoor Feeder |
Ensure your apiary's success with the right supplies.
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, reliable feeding equipment and substitutes mentioned in this guide. From durable in-hive feeders to effective pollen patties, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the tools your bees need to thrive.
Let's discuss your apiary's needs. Contact our team today for wholesale pricing and expert support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Round Hive Top Bee Feeder for Syrup
- Classic Boardman Entrance Bee Feeder Hive Front Feeding Solution
- Rapid Bee Feeder White Plastic 2L Round Top Feeder for 8 or 10-Frame Bee Hives
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Professional Hive Nutrition Solution for Beekeeping
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
People Also Ask
- What are the features of top feeders for bees? Maximize Hive Health with Safe, High-Capacity Feeding
- What types of hive boxes is the round hive top feeder compatible with? Universal Fit for 8 & 10-Frame Langstroth Hives
- How should syrup for bees be prepared? Master the Ratio for a Thriving Hive
- What can the round hive top feeder be used for? A Guide to Efficient, Safe Bee Feeding
- How do hive top feeders work? A Guide to Efficient, High-Capacity Bee Feeding



















