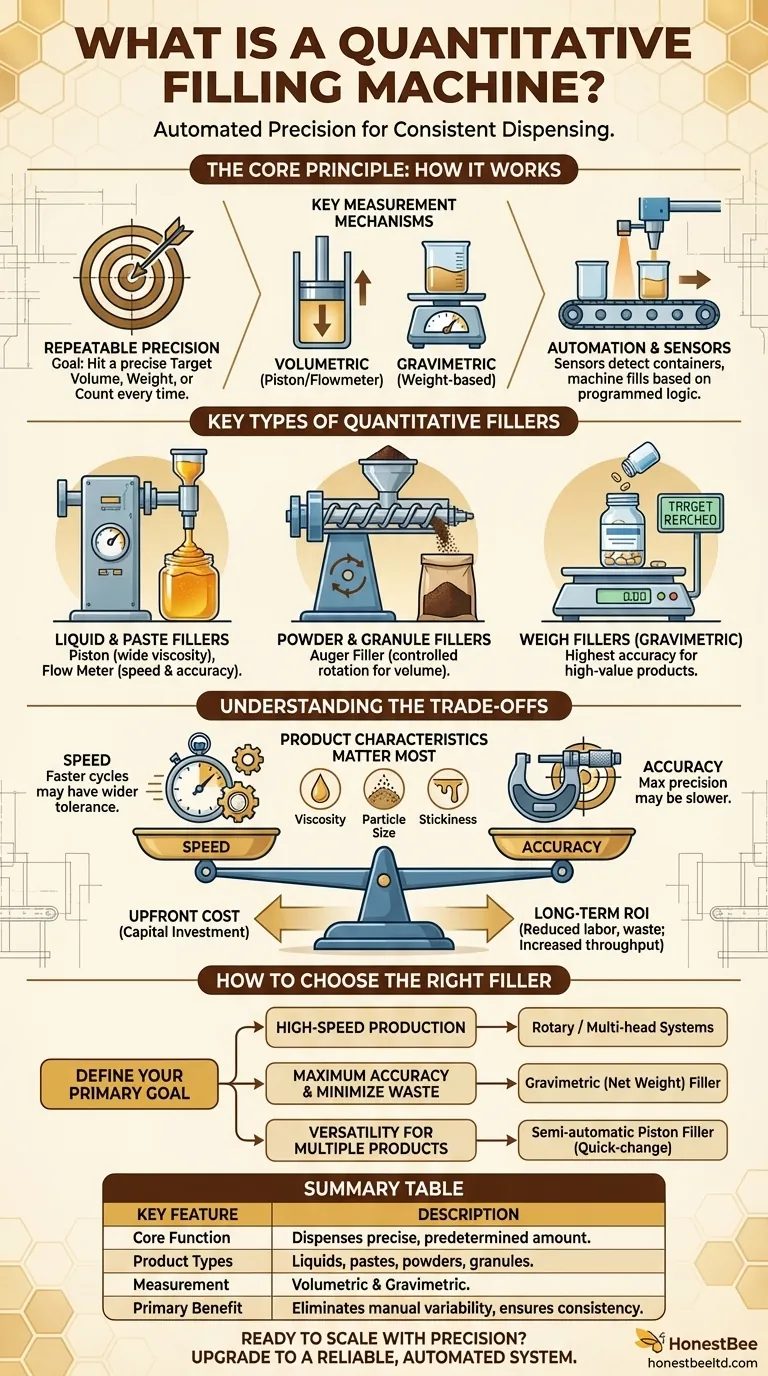
At its core, a quantitative filling machine is an automated or semi-automated system designed to dispense a precise, predetermined amount of a product into a container. Whether the product is a liquid, paste, powder, or granule, the machine's primary function is to ensure each container is filled with a consistent and accurate quantity, eliminating the variability and inefficiency of manual filling.
The true value of a quantitative filler isn't just dispensing product; it's about transforming a manual, inconsistent process into a reliable, scalable, and highly efficient manufacturing operation.

The Core Principle: How Quantitative Filling Works
To appreciate the role of these machines, it's essential to understand the principles that drive them. The goal is always the same: to hit a target fill amount repeatably with minimal error.
The Goal: Repeatable Precision
The fundamental purpose is to control the filling process to achieve a specific target volume, weight, or count for every single container. This consistency is critical for product quality, cost control, and regulatory compliance.
Key Measurement Mechanisms
These machines use different methods to achieve their precision. The two most common approaches are:
- Volumetric Filling: The machine dispenses a specific volume of product. This is often done with a piston that draws in and then expels a set amount, or a flowmeter that measures the liquid passing through it.
- Gravimetric Filling: The machine dispenses product until the container reaches a specific target weight. A load cell or scale under the container provides real-time feedback to the filler, telling it precisely when to stop.
The Role of Automation
Modern quantitative fillers are programmed to manage the entire process. Sensors detect when a container is in place, the machine fills it based on its programmed logic (volume or weight), and then the cycle repeats for the next container with minimal to no human intervention.
Key Types of Quantitative Fillers
The right machine is determined entirely by the characteristics of your product. Fillers are not one-size-fits-all; they are specialized tools for specific materials.
Liquid and Paste Fillers
These are the most common types. Piston fillers are excellent for a wide range of viscosities, from thin liquids like water to thick pastes like honey or cream. Flow meter fillers are ideal for low to medium-viscosity liquids and offer high speed and good accuracy.
Powder and Granule Fillers
For dry products like flour, spices, or coffee grounds, an auger filler is the standard. This machine uses a rotating screw (the auger) to dispense a controlled amount of powder into the container. The volume dispensed is controlled by the number of rotations the auger makes.
Weigh Fillers (Gravimetric)
Also known as net weight fillers, these systems provide the highest level of accuracy. They are perfect for high-value products (like pharmaceuticals or specialty foods) where minimizing product giveaway is critical. They are also ideal for products with inconsistent density, where filling by volume would lead to inaccurate weights.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filling machine involves balancing several key factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making a sound investment.
Speed vs. Accuracy
Generally, the fastest filling machines may have a slightly wider accuracy tolerance. Conversely, systems designed for maximum precision, like some gravimetric fillers, might operate at a slower cycle speed. Your required production rate (containers per minute) must be weighed against your tolerance for fill-weight variation.
Product Characteristics Matter Most
A machine that works perfectly for a free-flowing liquid will fail completely with a thick paste. Viscosity, particle size, and whether the product is sticky or dusty are the primary factors that dictate the appropriate filling technology.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term ROI
Automated filling machines are a significant capital investment. However, the return on investment (ROI) is realized through reduced labor costs, minimized product waste from overfilling, and dramatically increased production throughput. A manual process simply cannot scale in the same way.
How to Choose the Right Filler for Your Operation
Base your decision on your single most important operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production: Look for rotary fillers or multi-head linear systems that can fill numerous containers simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and minimizing waste: A gravimetric (net weight) filler is almost always the superior choice, especially for valuable products.
- If your primary focus is versatility for multiple products: A semi-automatic piston filler with quick-change, easy-to-clean parts can provide an excellent balance of flexibility and performance.
Selecting the right quantitative filling machine is a foundational step toward building a professional and scalable production line.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Dispenses a precise, predetermined amount of product into containers. |
| Product Types | Liquids, pastes, powders, and granules. |
| Measurement Methods | Volumetric (piston, flowmeter) and Gravimetric (weight-based). |
| Primary Benefit | Eliminates manual variability, ensuring consistency and efficiency. |
Ready to Scale Your Production with Precision?
Upgrade from inconsistent manual filling to a reliable, automated system. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the robust, high-accuracy filling machines needed for professional operations. Whether you're filling honey, creams, or other viscous products, we provide the equipment to boost your throughput and minimize waste.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss the best quantitative filling solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- Fully Automatic Honey Filling Packaging Machine for Processing Line
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Manual Honey Filling Machine Bottling Machine for Honey
People Also Ask
- How does a packaging machine work? A Guide to Form-Fill-Seal vs. Premade Pouch Systems
- How do automated honey filling and packaging machines contribute to rural employment? Boost Value & Jobs
- Why is professional honey filling machinery critical for honey production? Scale Your Apiary's Profit & Efficiency
- What types of honey filling machines are available? Find the Perfect System for Your Apiary
- How do automated honey packaging and filling systems support diversified product lines? Enhance Your Brand Identity
- What role does commercial honey filtration and filling machinery play in export-oriented production? | HONESTBEE Guide
- Why is the use of professional honey extraction and honey-filling machines emphasized? Boost Quality & Efficiency
- How does high-precision filling equipment ensure quality and efficiency? Optimize Your Honey Packaging Performance



















