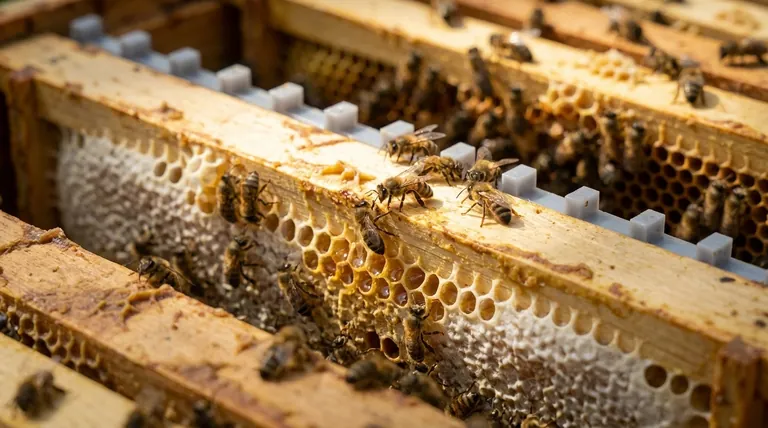
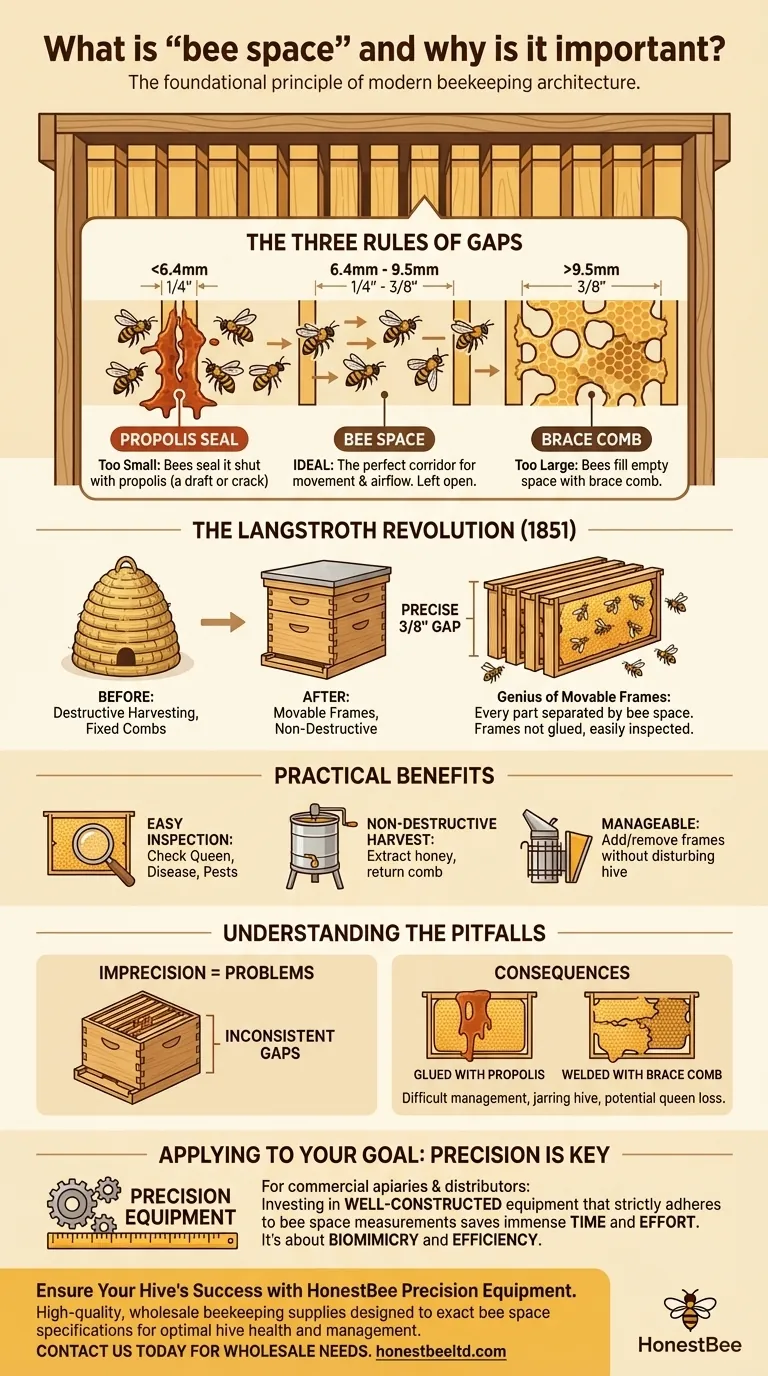
At its core, bee space is a precise measurement that dictates the architecture of a modern beehive. It is a gap, typically between 6.4mm and 9.5mm (1/4 and 3/8 of an inch), that honeybees will naturally leave open as a passageway. They will neither fill a space of this size with new wax comb nor seal it shut with their resinous glue, propolis.
Understanding "bee space" is not just about a measurement; it is about understanding the foundational principle that enabled modern beekeeping. This single insight into bee behavior allowed for the invention of the movable-frame hive, transforming a difficult and often destructive craft into a manageable and scalable practice.

The Fundamental Rule of Bee Architecture
Bee space is a concept rooted in the instinctual behavior of honeybees. It's less a choice and more a biological imperative that dictates how they build and organize their home.
The Three Rules of Gaps
Bees react to any gap within their hive in one of three predictable ways, all based on its size.
A gap smaller than 1/4 inch (6.4mm) is seen as a crack or draft. The bees will meticulously seal it shut with propolis, a sticky, antimicrobial substance they create from plant resins.
A gap larger than 3/8 inch (9.5mm) is considered empty, wasted space. The bees will fill it by building brace comb (or "burr comb"), connecting adjacent surfaces with new wax structures.
A gap between 1/4 and 3/8 inch is the "bee space." The bees recognize it as a perfect corridor, essential for movement and air circulation, and will leave it clear.
The "Why" Behind the Behavior
This behavior is a masterclass in efficiency. By keeping these specific pathways clear, a colony ensures it can move resources, patrol for intruders, and ventilate the hive effectively.
Sealing smaller cracks prevents drafts and keeps pathogens out. Building in larger empty spaces maximizes their storage capacity for honey and pollen. Bee space is the perfect equilibrium between these two actions.
The Langstroth Revolution: Putting Bee Space to Work
The discovery and application of bee space, credited to Rev. Lorenzo Langstroth in 1851, marks the single most important innovation in the history of beekeeping.
Beekeeping Before Bee Space
Prior to Langstroth, beekeepers used hives with fixed combs, such as straw skeps or wooden boxes. Inspecting the colony for disease or health was nearly impossible.
Honey harvesting was a destructive process. The beekeeper had to cut out the comb, often damaging the colony and killing a large number of bees in the process.
The Genius of the Movable Frame
Langstroth’s genius was not in inventing a box, but in designing a system of interior components. He created a hive where every part—each frame, the hive walls, and the cover—was separated from the next by a precise 3/8 inch gap.
Because this gap conformed to the bees' natural "bee space," they did not glue the frames to the hive walls or to each other. This allowed each frame to be removed, inspected, and replaced without disturbing the rest of the hive.
The Practical Benefits of Movable Frames
This simple design principle unlocked immense benefits. It allows a beekeeper to easily check the queen's health, look for signs of disease or pests, and manage space by adding or removing frames.
Most importantly, it enables non-destructive honey harvesting. A beekeeper can remove a frame full of honey, extract the honey without destroying the wax comb, and return the empty frame to the bees to be refilled.
Understanding the Pitfalls
While bee space is a simple principle, its application requires precision. Deviating from it, even by a few millimeters, leads to problems for the beekeeper.
The Importance of Precision
Hive components must be manufactured to exact dimensions. A poorly constructed hive with inconsistent gaps will not function as intended.
If the gaps are too large, the bees will build burr comb, effectively welding the frames together and making them impossible to remove without a fight.
When It Goes Wrong
If the gaps are too small, the bees will glue everything together with propolis. The beekeeper will have to pry frames apart, jarring the hive, angering the bees, and potentially crushing the queen.
In both cases, the core benefit of the movable-frame hive is lost, and hive management becomes a difficult and frustrating chore.
Applying This Principle to Your Goal
The concept of bee space is more than a piece of trivia; it's a practical guide for action, whether you are a beekeeper or an engineer.
- If your primary focus is beekeeping: Always invest in well-constructed equipment that strictly adheres to the bee space measurement, as this will save you immense time and effort.
- If your primary focus is design or engineering: View bee space as a prime example of biomimicry, where observing and respecting a natural principle leads to a revolutionary and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is historical understanding: Recognize the application of bee space as the clear dividing line between ancient, destructive beekeeping and modern, sustainable apiculture.
Respecting this simple dimension is the foundation for a productive and symbiotic relationship with one of the world's most vital insects.
Summary Table:
| Bee Space Size | Bee Behavior | Result for Beekeeper |
|---|---|---|
| < 6.4mm (1/4") | Seals gap with propolis | Frames become glued, difficult to inspect |
| 6.4mm - 9.5mm (1/4" - 3/8") | Leaves gap clear as a corridor | Ideal: Frames are movable and easy to manage |
| > 9.5mm (3/8") | Builds brace comb to fill space | Frames become welded together with wax |
Ensure Your Hive's Success with Precision Equipment
Properly manufactured equipment that respects the principle of bee space is the foundation of efficient, productive beekeeping. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and distributors with high-quality, precision-engineered beekeeping supplies and equipment through our wholesale-focused operations. Our products are designed to the exact specifications required for optimal hive health and management, saving you time and frustration.
Ready to equip your operation with reliable, bee-space-accurate gear? Contact our team today to discuss your wholesale needs and see how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Plastic Frame Spacer
- Ergonomic Plastic Frame Spacer Tool for Rapid Hive Management Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel 9 Frame Hive Spacer Durable Precise for Commercial Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Castellated Iron Frame Spacer for Multiple Hive Types
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to maintain accurate measurements in a Langstroth hive? Ensure Hive Health and Manageability
- Why use 9 frames in a 10 frame hive? Optimize Honey Harvesting with Strategic Spacing
- Why is it important to compress frames together in the center of the box after reassembly? Prevent Burr Comb and Hive Chaos
- How does the use of high-quality beehive and frame systems support the shook swarm technique in EFB management?
- What are the practical benefits of arranging hives in rows? Optimize Workflow and Bee Health with Proper Spacing



















