At its simplest, a beehive is a man-made structure designed to house a honey bee colony. While early hives were little more than simple containers, the modern beehive is an engineered system that allows a beekeeper to manage the bees' health, encourage their population growth, and harvest excess honey without harming the colony.
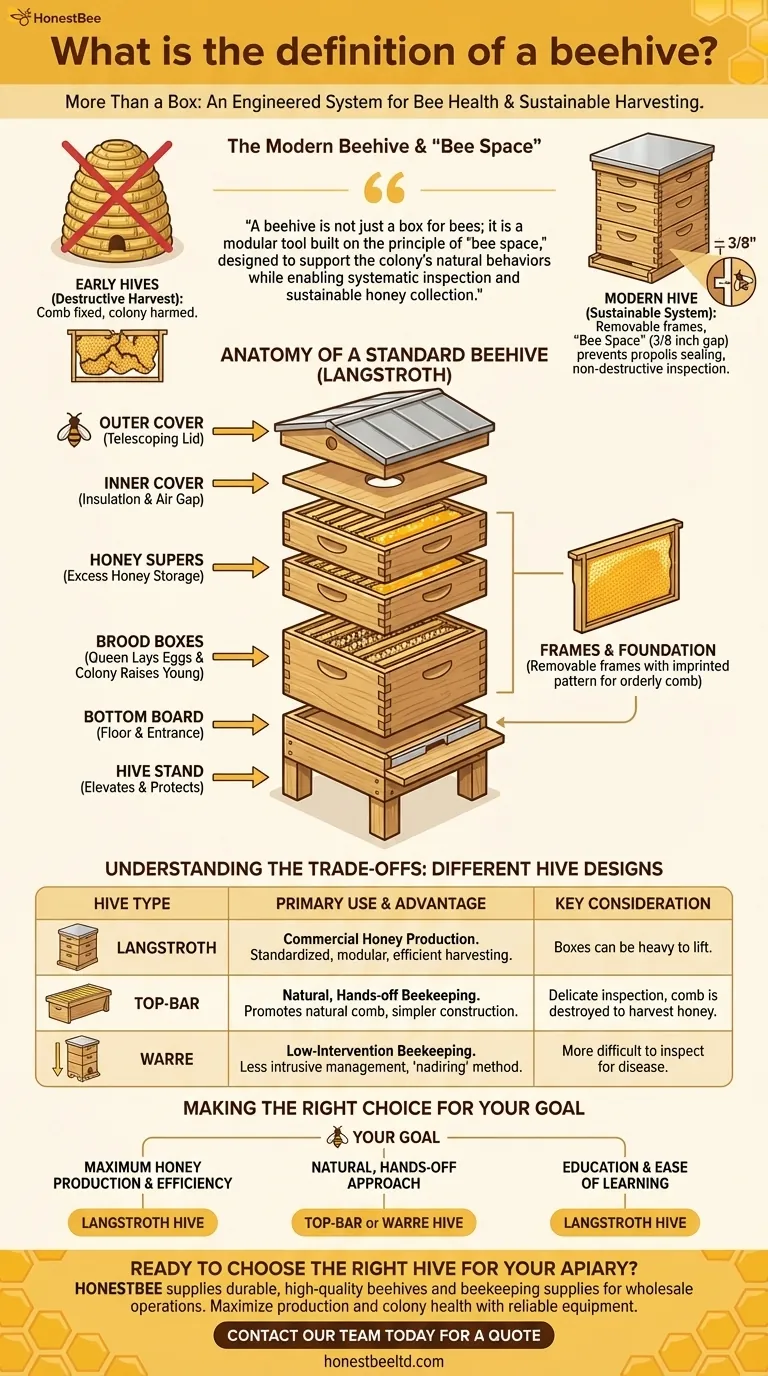
A beehive is not just a box for bees; it is a modular tool built on the principle of "bee space," designed to support the colony's natural behaviors while enabling systematic inspection and sustainable honey collection.

The Purpose of a Modern Hive
The primary goal of a beehive is to provide a safe, managed environment for a honey bee colony. This goes far beyond simply being a container for honey collection, which was the limit of older, more primitive designs.
The Problem with Early Hives
Early hives, such as straw skeps or hollowed logs, served as basic shelters. However, the comb was fixed to the hive walls, meaning the only way to harvest honey was to destroy the comb and often the colony itself.
The Langstroth Revolution: Bee Space
The modern beehive is based on the 1851 discovery of "bee space" by Reverend L.L. Langstroth. He observed that bees will leave a gap of about 3/8 of an inch (6-9 mm) between their combs and will not build comb or seal it with propolis.
By designing a hive with precisely spaced, removable frames, Langstroth created a system where a beekeeper could slide out any comb for inspection or harvesting without destroying the hive's structure. This was the single most important innovation in modern beekeeping.
Anatomy of a Standard Beehive
A modern Langstroth hive—the most common type in the world—is a stack of modular, interchangeable boxes. Each component serves a specific function for the bees and the beekeeper.
The Foundational Components
The bottom of the hive consists of a hive stand to elevate it off the ground, protecting it from moisture and pests, and a bottom board that serves as the floor and entrance.
The Brood Boxes
The largest boxes, known as hive bodies or brood boxes, form the core of the hive. This is where the queen lays her eggs and the colony raises its young bees (the brood).
The Honey Supers
Smaller, lighter boxes called honey supers are placed on top of the brood boxes. The colony uses these upper chambers to store their excess honey, which is what the beekeeper can then harvest.
The Frames and Foundation
Inside every box are removable frames. Each frame typically holds a sheet of foundation—a thin sheet of beeswax or plastic imprinted with a honeycomb pattern—that encourages bees to build straight, orderly comb.
The Covers
An inner cover sits on top of the uppermost box, providing insulation and an air gap. Finally, an outer cover, or telescoping lid, acts as the roof, protecting the entire hive from the elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Different Hive Designs
While the Langstroth is the most common, it is not the only type of hive. Different designs cater to different beekeeping philosophies and goals.
Langstroth Hive
This is the industry standard. Its key advantages are modularity, efficiency, and the vast availability of standardized equipment. The primary drawback is the weight of the boxes, which can be heavy to lift.
Top-Bar Hive
This hive is a single, long box with simple wooden bars across the top. Bees build their comb hanging down from these bars. It is simpler to build and promotes more natural comb, but inspection is more delicate and honey harvesting is done by crushing and straining the comb.
Warre Hive
The Warre hive is a vertical, top-bar style hive that is managed by adding new boxes to the bottom, a process called "nadiring." It is designed to be less intrusive but can be more difficult to inspect for disease.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" hive is the one that aligns with your specific objectives as a beekeeper, whether you are a hobbyist, a commercial operator, or simply curious.
- If your primary focus is maximum honey production and efficiency: The Langstroth hive is the clear choice due to its standardized components and streamlined harvesting methods.
- If your primary focus is a more natural, hands-off approach: A Top-Bar or Warre hive may align better with your philosophy, though they require different management techniques.
- If your primary focus is education and ease of learning: The Langstroth hive offers the most abundant educational resources, community support, and straightforward inspection processes.
Ultimately, a beehive is a carefully designed partnership between the beekeeper and the natural instincts of the honey bee colony.
Summary Table:
| Hive Type | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langstroth | Commercial Honey Production | Standardized, modular, efficient harvesting | Boxes can be heavy to lift |
| Top-Bar | Natural, Hands-off Beekeeping | Promotes natural comb, simpler construction | Delicate inspection, comb is destroyed to harvest honey |
| Warre | Low-Intervention Beekeeping | Less intrusive management, 'nadiring' method | More difficult to inspect for disease |
Ready to Choose the Right Hive for Your Apiary?
For commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, selecting the right equipment is the foundation of a successful operation. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality beehives and beekeeping supplies through our wholesale-focused operations.
We help you maximize honey production and colony health with reliable equipment built to last. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and get a quote on our full range of beekeeping solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Telescopic Beehive Outer Cover Lid Roof with Galvanised Sheeting for Langstroth Hive and Beehive Outer Cover
- Professional Hive Top Bee Feeder for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- 3.5L Plastic Beehive Frame Feeder Deep Frame Water Feeder for In Hive Use
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the inner and outer covers in a beehive? Essential for Hive Health & Management
- How can garden hive lids be secured to prevent them from being blown off? | Reliable Methods for Apiary Protection
- What is the purpose of the telescoping cover on a beehive? Superior Weather Protection for Your Colony
- What maintenance is recommended for the Langstroth hive roof? Protect Your Hive with Natural Tung Oil
- What are the two primary lid styles for Langstroth style beehives? Choose the Right Protection for Your Hives



















