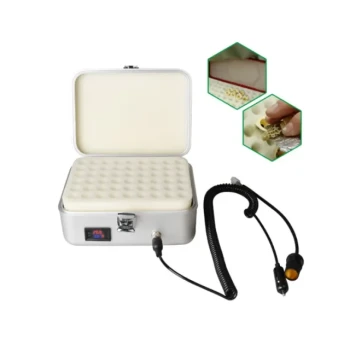
High-precision incubators for laboratory-controlled queen rearing are specifically calibrated to maintain a constant temperature of 35°C and a relative humidity of 70%. These exact parameters are selected to accurately simulate the stable microclimate of a natural honey bee brood nest, ensuring that capped queen pupae develop normally and emerge successfully without the variables introduced by a field environment.
Core Insight: The value of these incubators extends beyond simple temperature control; they serve as an isolation chamber. By replacing the hive environment with a sterile, stable climate, researchers eliminate worker bee interference and outdoor weather fluctuations, guaranteeing that data collected on newly emerged queens—such as viral load analysis—is statistically pure and reproducible.
Replicating the Natural Brood Nest
Precise Thermal Regulation
To ensure successful emergence, the incubator must hold a steady temperature of 35°C. This specific thermal set-point is critical because it mimics the metabolic heat generated by a cluster of worker bees in a healthy colony.
Deviations from this temperature can lead to developmental abnormalities or failure to emerge. The high-precision nature of the equipment ensures that the temperature does not fluctuate, regardless of external room conditions.
Humidity Control for Physiology
Along with temperature, maintaining a relative humidity of 70% is essential for proper physiological development. This humidity level prevents the sensitive pupae from desiccating (drying out) during their final metamorphic stages.
By locking in this moisture level, the incubator replicates the humid atmosphere created by the respiration and nectar evaporation of a living colony.
The Strategic Advantage of Isolation
Eliminating Worker Bee Interference
In a natural hive, worker bees actively clean and manage the brood. While beneficial for the colony, this introduces an uncontrolled variable for researchers.
High-precision incubation protects the pupae from cleaning behaviors, such as the removal of sick or infested brood. This allows researchers to study queens that might otherwise have been culled by the colony, providing a complete picture of viral loads or genetic defects.
Shielding from Environmental Stress
Outdoor environments are unpredictable, subjecting hives to heat waves or cold snaps. High-precision incubators provide a buffer against these fluctuations.
By removing the stress of thermal regulation, the developing queens can allocate all their energy toward metamorphosis. This results in higher emergence rates and greater uniformity among the test subjects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Artificiality
While incubators offer stability, they lack the adaptive intelligence of a superorganism. If a mechanical failure occurs, there are no worker bees to compensate for the drop in heat or humidity.
Loss of Social Signals
Laboratory incubation isolates the queen from the pheromonal landscape of the hive. While this is necessary for certain isolation studies, researchers must account for the fact that the queens emerge in a social vacuum, which may influence immediate post-emergence behaviors compared to those born in a colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your experimental protocol, align your environmental controls with your specific research outcomes.
- If your primary focus is Viral Load Analysis: Prioritize the isolation aspect of the incubator to prevent worker bees from removing infected pupae, ensuring your sample represents the true infection rate.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Emergence Rates: Focus on the stability of the 35°C/70% RH parameters to reduce physiological stress and prevent developmental abnormalities.
By rigorously controlling these environmental variables, you transform a biological process into a quantifiable, reproducible data set.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | Target Parameter | Biological Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 35°C (Constant) | Mimics metabolic heat of worker bee cluster |
| Relative Humidity | 70% | Prevents pupae desiccation during metamorphosis |
| Biotic Control | Sterile Isolation | Eliminates worker bee cleaning and interference |
| Atmosphere | Stable Microclimate | Buffers against outdoor weather/thermal stress |
Elevate Your Queen Rearing and Laboratory Operations with HONESTBEE
At HONESTBEE, we understand that precision is the foundation of a successful commercial apiary and research program. Whether you are a large-scale distributor or a commercial honey producer, our comprehensive range of professional beekeeping machinery—from advanced incubation solutions and hive-making equipment to high-efficiency honey-filling machines—is designed to optimize your productivity.
Why partner with HONESTBEE?
- Wholesale Excellence: Access a full spectrum of durable beekeeping tools and essential consumables at scale.
- Technical Innovation: From laboratory-grade precision to heavy-duty field machinery, we supply the hardware that powers the industry.
- Expert Support: We provide more than just equipment; we offer the reliability needed to ensure consistent, high-quality results for your customers and colonies.
Ready to scale your operation or upgrade your wholesale portfolio? Contact us today to discuss our wholesale offerings and discover how HONESTBEE can streamline your beekeeping business.
References
- Sagar Bhandari, Esmaeil Amiri. Honey bee queen susceptibility to viral infection varies across developmental stages in queen rearing operations. DOI: 10.1101/2025.10.13.682001
This article is also based on technical information from HonestBee Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Portable Queen Bee Incubator with 12V Car Adapter for Safe Transport
- Frame Punching Hole Puncher Machine for Bee Frame Producing Line
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- JZBZ Style Push-In Cell Protector for Professional Queen Rearing Kits
People Also Ask
- Why are high-precision constant temperature and humidity incubators necessary? Secure Your Queen Bee Emergence
- What is the primary function of a constant temperature and humidity incubator in queen bee rearing? Optimize Emergence
- How do high-precision temperature-controlled incubation units assist in the breeding of queen bees? Master Bee Genetics
- Why is an industrial constant temperature and humidity incubator required for queen bee development? Ensure Vitality.
- What biosecurity risks are associated with honeybee breeding tools? Protect Your Apiary from Transboundary Disease