Modern beekeeping demands precision in every tool—especially your smoker fuel. The right fuel choice impacts colony calmness, inspection efficiency, and long-term hive health. This guide unpacks the science behind smoke dynamics and provides actionable strategies for selecting, preparing, and troubleshooting fuels across diverse apiary conditions.
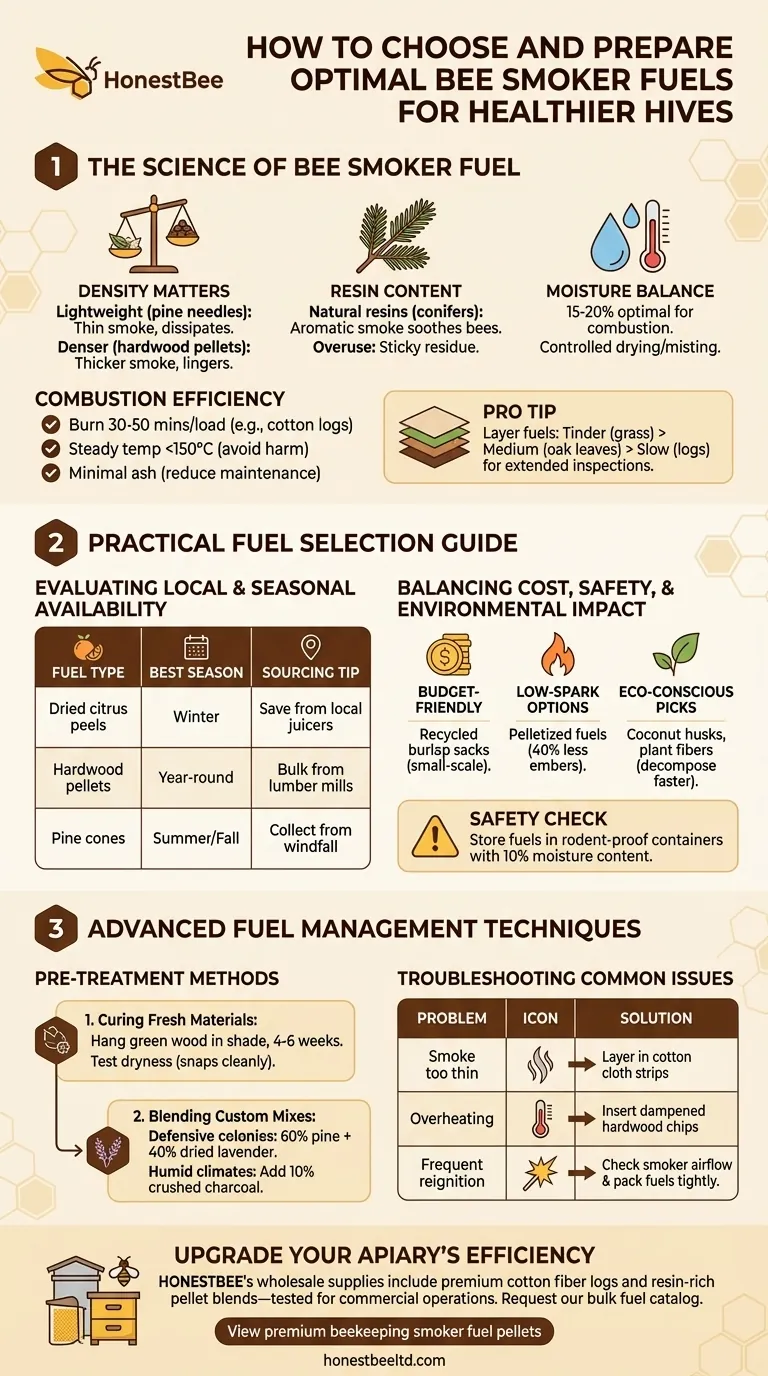
The Science of Bee Smoker Fuel
Bee smokes work by masking alarm pheromones, but not all fuels create equally effective smoke. Three factors determine performance:
How Fuel Properties Impact Smoke Quality
- Density Matters: Lightweight materials like pine needles ignite quickly but produce thin smoke that dissipates rapidly. Denser fuels (hardwood pellets, cotton fiber) generate thicker smoke that lingers longer during inspections.
- Resin Content: Natural resins in coniferous woods create aromatic smoke that soothes bees more effectively than non-resinous alternatives. However, overuse can leave sticky residues in smoker chambers.
- Moisture Balance: Research shows fuels with 15-20% moisture content (achieved through controlled drying or light misting) optimize combustion without excessive sparks.
Combustion Efficiency and Burn Duration
Commercial apiaries benefit from fuels that:
✔ Burn 30-50 minutes per load (e.g., compressed cotton logs)
✔ Maintain steady temperatures below 150°C to avoid harming bees
✔ Produce minimal ash to reduce smoker maintenance
Pro Tip: Layer fuels—start with fast-igniting tinder (dried grass), add medium-burning materials (oak leaves), then top with slow-burning logs for extended inspections.
Practical Fuel Selection Guide
Evaluating Local and Seasonal Fuel Availability
| Fuel Type | Best Season | Sourcing Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Dried citrus peels | Winter | Save peels from local juicers |
| Hardwood pellets | Year-round | Buy bulk from lumber mills |
| Pine cones | Summer/Fall | Collect from windfall areas |
Balancing Cost, Safety, and Environmental Impact
- Budget-Friendly: Recycled burlap sacks (chemical-free) provide excellent smoke at near-zero cost for small-scale keepers.
- Low-Spark Options: Commercial operations should prioritize pelletized fuels—they’re 40% less likely to eject embers than irregular wood chips.
- Eco-Conscious Picks: Coconut husks and compressed plant fibers decompose faster than synthetic alternatives while offering comparable burn times.
Safety Check: Always store fuels in rodent-proof containers with 10% moisture content to prevent spontaneous combustion.
Advanced Fuel Management Techniques
Pre-Treatment Methods for Consistent Combustion
-
Curing Fresh Materials:
- Hang green wood strips in shaded, breezy areas for 4-6 weeks
- Test dryness by snapping twigs—properly cured fuels break cleanly
-
Blending Custom Mixes:
- For defensive colonies: 60% pine needles + 40% dried lavender (enhanced calming effect)
- For humid climates: Add 10% crushed charcoal to improve ignition
Troubleshooting Common Fuel Issues
- Problem: Smoke too thin → Layer in cotton cloth strips
- Problem: Overheating → Insert dampened hardwood chips to regulate temperature
- Problem: Frequent reignition → Check smoker airflow and pack fuels more tightly
Upgrade Your Apiary’s Efficiency
HONESTBEE’s wholesale beekeeping supplies include premium cotton fiber logs and resin-rich pellet blends—meticulously tested for commercial operations needing reliable, long-lasting smoke. Request our bulk fuel catalog today to access beekeeper-approved materials at distributor pricing.
Final Thought: Like the bees themselves, your fuel choices thrive when adapted to local rhythms. Observe how your colonies respond to different smokes—their calmness (or lack thereof) will guide your perfect blend.
Products You Might Be Looking For:
View premium beekeeping smoker fuel pellets
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 54-Piece Smoker Fuel Pellets for Beekeeping Beehive Smoker Fuel
- European Stainless Steel Bee Smoker for Honey Bee Hive
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
- Economy Galvanized Beekeeping Honey Bee Smoker for Wholesale
- Premium Traditional Copper Bee Smoker with Bellows
Related Articles
- The Art of Persuasion: Why Your Bee Smoker Fuel is a Dialogue with the Hive
- How to Maintain Your Bee Smoker for Optimal Performance and Safety
- How to Optimize Your Bee Smoker: Fuel, Safety, and Maintenance Guide
- How to Use a Bee Smoker Effectively Without Harming Your Hive
- How to Master Bee Smoker Techniques: Science-Backed Hive Management




















