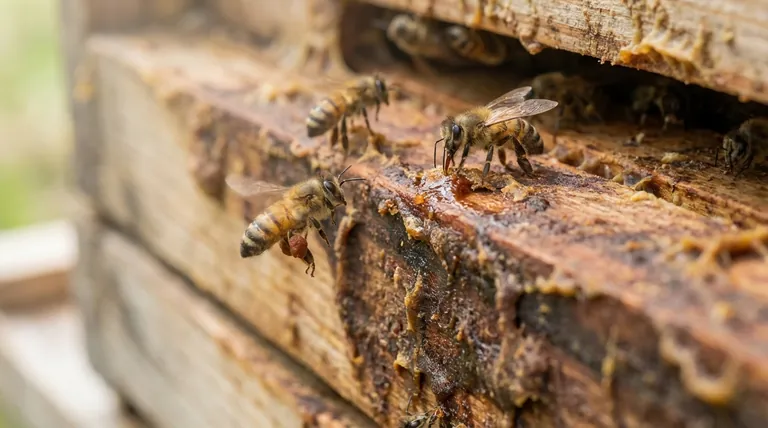
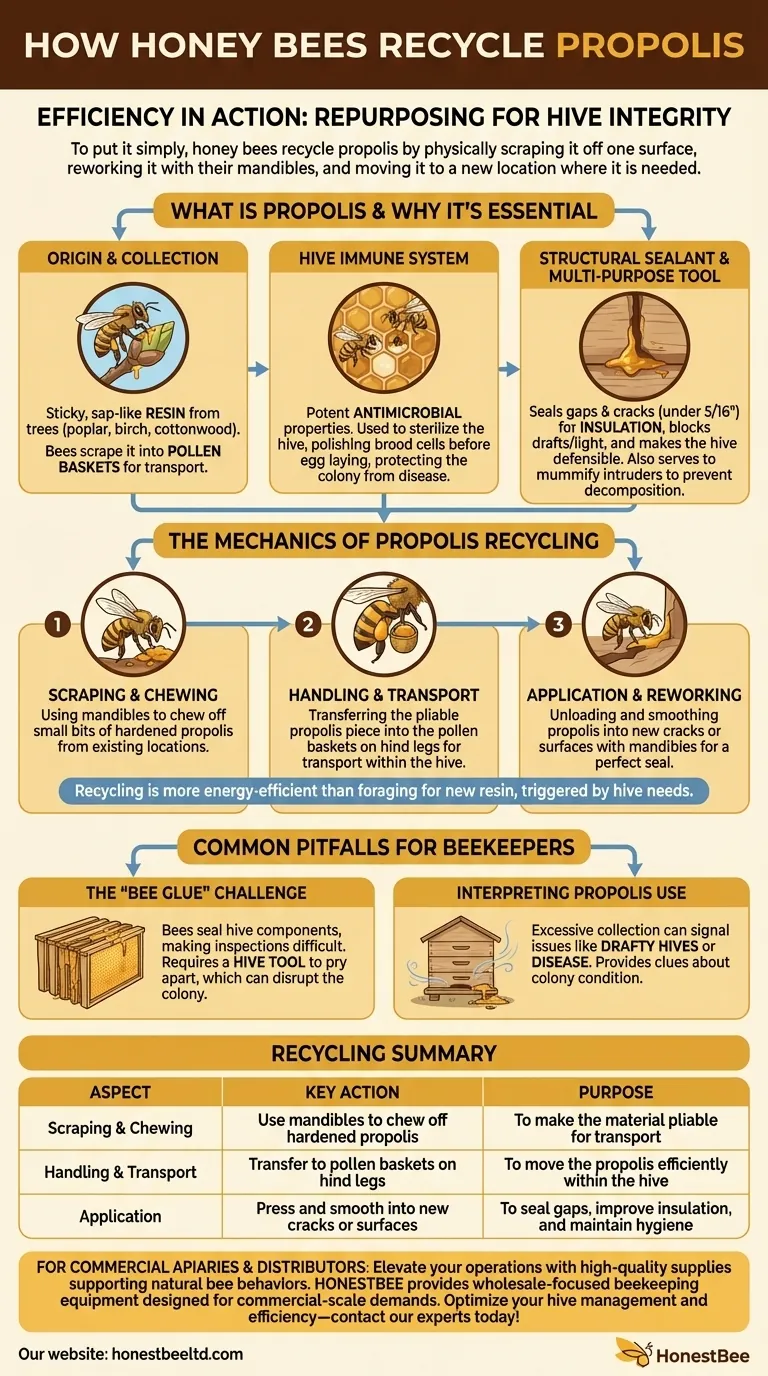
To put it simply, honey bees recycle propolis by physically scraping it off one surface, reworking it with their mandibles, and moving it to a new location where it is needed. They chew off small pieces of the existing propolis, transfer it to their front feet, and then pack it into the pollen baskets on their hind legs for transport within the hive.
Propolis recycling is an act of profound efficiency. Instead of expending energy foraging for new plant resins, bees repurpose this valuable material to continuously maintain their hive's structural integrity and hygiene.

What is Propolis and Why is it Essential?
Before understanding the recycling process, it's critical to grasp why propolis is indispensable to a honey bee colony. It isn't just a simple glue; it's a multifunctional compound vital for survival.
The Origin of Propolis
Propolis begins as a sticky, sap-like resin produced by trees and plants like poplar, birch, and cottonwood. The plants use these resins to protect their buds and heal wounds.
Worker bees scrape these resins from the plants, pack them into their pollen baskets, and carry them back to the colony.
The "Hive Immune System"
Propolis possesses potent antimicrobial properties. Bees use it to sterilize the hive, polishing the inside of brood cells before the queen lays her eggs.
This hygienic barrier helps protect the colony from diseases and contamination, acting as a form of external, collective immunity.
The Ultimate Structural Sealant
Functionally, bees use propolis to seal small cracks and gaps within the hive, typically those smaller than 5/16th of an inch.
This sealant improves insulation against cold, blocks unwanted drafts and light, and reduces the size of the hive entrance to make it more defensible.
A Multi-Purpose Tool
Beyond sealing and sterilizing, bees use propolis to wrap and entomb the bodies of intruders like mice that are too large to remove. This mummification process prevents the carcass from decomposing and spreading disease throughout the hive.
The Mechanics of Propolis Recycling
Recycling existing propolis is often more energy-efficient than foraging for new resins. The process is methodical and triggered by the hive's immediate needs.
Step 1: Scraping and Chewing
A worker bee identifies a location where propolis is no longer needed or can be better used elsewhere. Using its strong mandibles (jaws), it carefully chews off small bits of the hardened propolis.
Step 2: Handling and Transport
The bee manipulates the now-pliable piece of propolis with its mandibles and front feet. It then skillfully transfers the propolis chunk into the pollen baskets on its hind legs—the same structures used to transport pollen and fresh resins.
Step 3: Application and Reworking
After transporting the recycled propolis to the new site, the bee unloads it and begins applying it to the new crack or surface. It uses its mandibles to press and smooth the material into place, ensuring a perfect seal.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While propolis is a sign of a healthy, functioning colony, a beekeeper's perspective reveals a key trade-off.
The Challenge of "Bee Glue"
Bees do not discriminate between a natural crack in a tree and the man-made gaps between hive boxes or frames. They will diligently seal these components together.
This makes hive inspections difficult, as frames and boxes become glued tight. Beekeepers must use a hive tool to pry these components apart, which can disrupt and agitate the colony.
Interpreting Propolis Use
Excessive propolis collection can be an indicator of underlying issues. It may signal a drafty hive with poorly fitting components or even the presence of a disease that the bees are trying to combat through sterilization.
Observing where and how much propolis is being used can provide valuable clues about the colony's condition and the structural integrity of its home.
Applying This to Your Understanding
Understanding why and how bees use propolis provides a deeper insight into their remarkable adaptability and resourcefulness.
- If your primary focus is bee behavior: Recycling propolis is a perfect example of energy conservation, showing how bees prioritize tasks and reuse materials to maximize colony efficiency.
- If your primary focus is beekeeping: Recognizing that bees will move and reuse propolis explains why you find it in inconvenient places and highlights the importance of using well-constructed hive equipment.
- If your primary focus is natural materials: Propolis is a masterclass in multifunctionality, serving as a structural sealant, an insulator, and a powerful antimicrobial agent all in one.
This constant maintenance and recycling ensure the honey bee colony remains a secure, insulated, and sanitary fortress.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Recycling | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Scraping & Chewing | Use mandibles to chew off hardened propolis | To make the material pliable for transport |
| Handling & Transport | Transfer to pollen baskets on hind legs | To move the propolis efficiently within the hive |
| Application | Press and smooth into new cracks or surfaces | To seal gaps, improve insulation, and maintain hygiene |
For Commercial Apiaries & Distributors: Elevate your beekeeping operations with high-quality, durable supplies that support natural bee behaviors like propolis recycling. HONESTBEE provides wholesale-focused beekeeping equipment and supplies designed for the demands of commercial-scale beekeeping and distribution. Optimize your hive management and efficiency—contact our experts today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Long-Handled Silicone Honey Scraper for Beekeeping
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
People Also Ask
- What function does Multi-Stage Precision Filter Paper serve in the purification of propolis ethanol extracts?
- Why is a low-temperature freezer necessary for the pre-treatment of raw propolis samples? Optimize Your Extraction
- What technical problem does the use of specialized filter paper solve during propolis extraction? Achieve Purity
- How does a laboratory grinder contribute to optimizing the efficiency of propolis water extraction?
- What are the technical advantages of using specialized Propolis Traps? Boost Purity and Efficiency in Your Apiary
- How do specialized propolis collection curtains work? Optimize Harvesting Purity and Efficiency for Your Apiary
- How does the application of micro-porous mesh coatings on sensor surfaces prevent propolization in beehives?
- What is the importance of professional propolis collection and extraction tools? Boost Your Commercial Apiary Value



















