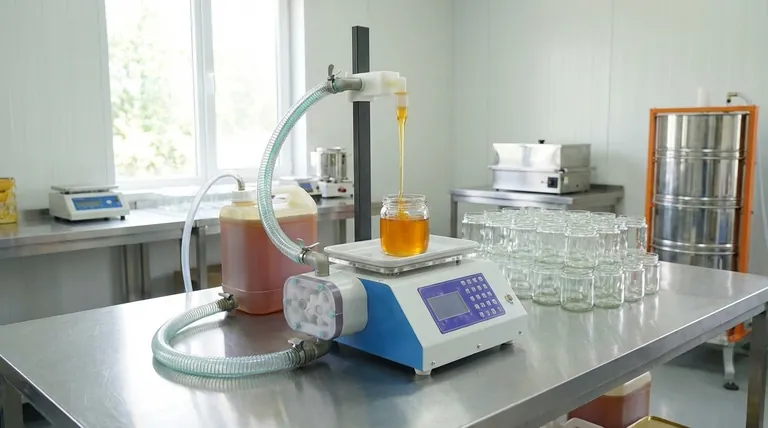
At its core, the piston filling principle uses a simple, highly effective mechanical action to dispense honey. The machine draws a precise volume of honey from a hopper into a cylinder during a backward stroke and then pushes that exact amount into a container during a forward stroke, ensuring exceptional accuracy.
The fundamental reason piston fillers dominate honey packaging is their ability to handle high-viscosity liquids with unmatched volumetric precision. Unlike methods that rely on gravity or timed flow, a piston filler dispenses an exact, repeatable amount of product every single time, regardless of changes in honey's thickness or temperature.

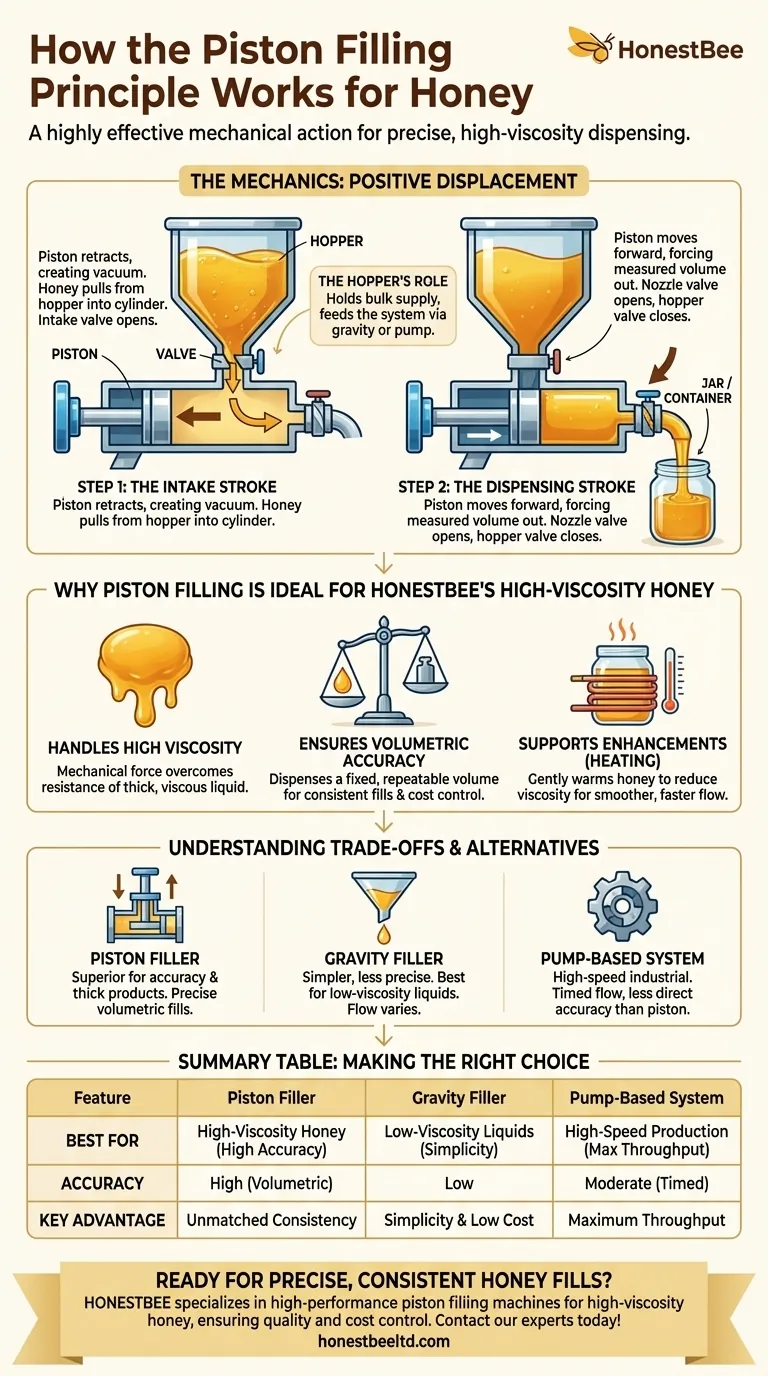
The Mechanics of a Piston Filler
A piston filler operates on a principle known as positive displacement. It physically moves a measured volume of product from a source to a destination. This process can be broken down into two primary phases.
Step 1: The Intake Stroke
During the intake stroke, the piston retracts within a cylinder. This retraction creates a vacuum, which pulls honey from a connected storage container, known as a hopper.
A valve system ensures the honey flows from the hopper into the cylinder and not back out through the dispensing nozzle.
Step 2: The Dispensing Stroke
Once the cylinder is filled with the predetermined volume of honey, the valves switch. The piston then moves forward, forcing the honey out of the cylinder.
This measured volume of honey is pushed through a nozzle and directly into the jar or container waiting below. The volume of the cylinder dictates the fill amount, making the process highly precise.
The Role of the Hopper
The hopper is a large tank that holds the bulk honey supply. It feeds the piston filling system, typically using gravity or a pump to maintain a continuous and efficient flow of honey into the cylinder for each cycle.
Why Piston Filling is Ideal for Honey
Honey's unique physical properties make certain filling technologies more suitable than others. Piston fillers excel for several key reasons.
Handling High Viscosity
Honey is a thick, viscous liquid. Methods that rely on gravity struggle to move it efficiently or consistently. A piston filler uses mechanical force to move the honey, overcoming its natural resistance to flow.
Ensuring Volumetric Accuracy
This is the piston filler's greatest strength. Because it dispenses a fixed volume (the displacement of the cylinder), it provides highly accurate and consistent fills from one container to the next. This is critical for product quality, regulatory compliance, and cost control.
Supporting Process Enhancements
Some honey filling machines incorporate heating mechanisms. Gently warming the honey reduces its viscosity, allowing it to flow more smoothly. This helps prevent air bubbles and ensures a cleaner, faster fill, complementing the piston's mechanical action.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While piston fillers are a standard for honey, it is useful to understand them in the context of other available technologies.
The Piston Filler Advantage
For any operation where fill accuracy and the ability to handle thick products are paramount, the piston filler is the superior choice. It is versatile enough for liquids of varying viscosities and even products with large particulates.
Gravity Fillers
Gravity fillers are simpler and often less expensive. They rely on the weight of the honey to fill containers. This method is better suited for lower-viscosity liquids and is generally less precise for thick honey, as flow rates can vary with temperature and tank level.
Pump-Based Systems
Pump fillers are typically used for high-speed, industrial-scale operations. They regulate the flow of honey into jars, often on a timed basis. While fast, their accuracy can be less direct than the fixed-volume measurement of a piston system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right filling technology depends entirely on your operational priorities, from small-scale beekeeping to large-scale industrial packaging.
- If your primary focus is accuracy and product consistency with viscous honey: The piston filler is the definitive industry standard, providing precise, repeatable volumetric fills.
- If your primary focus is simplicity for thinner, lower-viscosity liquids: A gravity filler can be a cost-effective, albeit less precise, alternative.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput in a high-speed production line: A pump-based system is engineered for speed and integration into fully automated processes.
Ultimately, understanding these principles empowers you to select the machine that best aligns with your product and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Piston Filler | Gravity Filler | Pump-Based System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-Viscosity Honey | Low-Viscosity Liquids | High-Speed Production |
| Accuracy | High (Volumetric) | Low | Moderate (Timed) |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched Consistency | Simplicity & Low Cost | Maximum Throughput |
Ready to achieve precise, consistent honey fills for your commercial apiary or distribution business? HONESTBEE specializes in supplying high-performance, wholesale-focused beekeeping equipment. Our piston filling machines are engineered to handle high-viscosity honey with unmatched volumetric accuracy, ensuring product quality and cost control for your operation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect filling solution for your production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Fully Automatic Honey Filling Packaging Machine for Processing Line
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
- Automatic Honey Filling and Filtering Machine for Beekeeping Bottle Filling
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does commercial honey filtration and filling machinery play in export-oriented production? | HONESTBEE Guide
- How does industrial honey filling and processing machinery aid colony management? Optimize Yield & Data Intelligence
- What is a syrup filling machine? Achieve Precision & Speed in Your Packaging Line
- What is the purpose of a heating mechanism in honey filling machines? Achieve Efficient, High-Quality Bottling
- What is the economic significance of using honey-filling machines? Boost Profits and Secure Pollination Services
- What role does temperature play in the viscosity of honey during filling? Achieve Optimal Flow and Quality
- What is the purpose of a Weighing Filling Machine? Ensure Precision and Profitability
- What is the primary role of specialized honey-filling machines in commercial beekeeping operations? Scaling Efficiency.



















