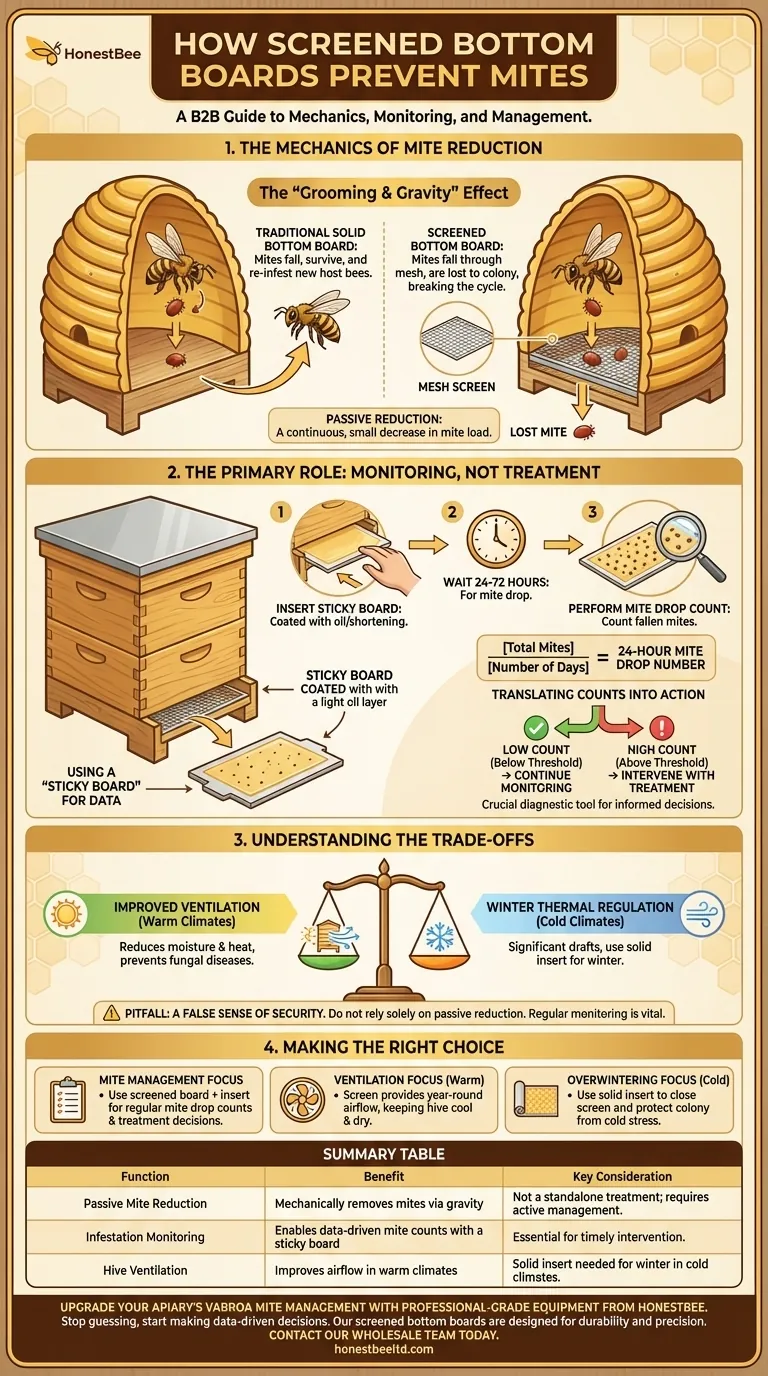
At its core, a screened bottom board aids in mite prevention through a simple mechanical process. Mites that naturally fall off bees—a process known as "mite drop"—pass through the screen and fall out of the hive entirely. This prevents them from climbing back onto another bee and re-infesting the colony.
While it offers a passive reduction in the mite population, its primary value is not as a treatment, but as a crucial diagnostic tool. It allows you to monitor the level of Varroa mite infestation within your hive, enabling you to make informed decisions about when more active treatments are necessary.

The Mechanics of Mite Reduction
Understanding how a screened bottom board works requires looking at the lifecycle and behavior of both bees and Varroa mites.
The "Grooming and Gravity" Effect
Bees are meticulous groomers. They groom themselves and each other, and in this process, they can dislodge Varroa mites that are attached to their bodies.
With a traditional solid bottom board, a dislodged mite falls to the floor of the hive. It can then simply wait for the next foraging or nurse bee to walk by and climb aboard a new host.
How the Screen Interrupts the Cycle
A screened bottom board changes this dynamic completely. When a mite is dislodged and falls, it passes through the mesh screen and onto the ground below the hive.
Once on the ground, the mite is effectively lost to the colony. It cannot climb back up into the hive, breaking its parasitic cycle and providing a small but continuous reduction in the hive's overall mite load.
The Primary Role: Monitoring, Not Treatment
The passive mite reduction is a secondary benefit. The true power of a screened bottom board lies in its ability to facilitate accurate mite monitoring.
Using a "Sticky Board" for Data
Most screened bottom boards come with a removable solid insert, often called a mite board or "sticky board". This board slides into a slot underneath the screen.
To perform a mite count, you coat this board with a light layer of oil or shortening (to trap the mites) and insert it for a set period, typically 24 to 72 hours.
Performing a Mite Drop Count
After the designated time, you carefully remove the board and count the number of Varroa mites that have fallen through the screen and become stuck.
By dividing the total number of mites by the number of days the board was in place, you get a "24-hour mite drop" number.
Translating Counts into Action
This number is a critical piece of data. Beekeeping associations and agricultural extensions provide thresholds for mite counts. If your 24-hour drop count exceeds the recommended threshold for that time of year, you know it is time to intervene with a dedicated mite treatment.
Without this data, you are essentially flying blind, only discovering a severe infestation when it is already causing significant harm to your colony.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any piece of equipment, screened bottom boards have both benefits and drawbacks that you must consider for your specific climate and management style.
Benefit: Improved Hive Ventilation
The screen provides excellent airflow through the hive. This increased ventilation is highly beneficial in hot and humid climates, as it helps the bees regulate temperature and reduces excess moisture that can lead to fungal diseases like chalkbrood.
Drawback: Winter Thermal Regulation
The biggest drawback is thermal performance in cold winters. The open screen creates a significant draft, making it much harder for the bee cluster to maintain its critical temperature.
For this reason, most beekeepers in colder climates use the solid insert to close off the bottom of the hive during the winter months.
Pitfall: A False Sense of Security
The most dangerous pitfall is assuming the screened bottom board is a complete mite solution. Relying solely on its passive mite-drop effect without performing regular counts and treating when necessary is a common and often fatal mistake for a colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
A screened bottom board is a tool, and its effectiveness depends entirely on how you use it.
- If your primary focus is effective mite management: Use the screened bottom board with its insert as a monitoring device to conduct regular mite drop counts and guide your treatment schedule.
- If your primary focus is hive ventilation in a warm climate: The screen provides a significant year-round benefit by helping to keep the hive cool and dry.
- If your primary focus is overwintering in a cold climate: Plan to use the solid insert to close the screen from the first frost until the last, protecting your colony from cold stress.
Ultimately, a screened bottom board transforms Varroa management from guesswork into a data-driven science, empowering you to protect the long-term health of your bees.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Passive Mite Reduction | Mechanically removes mites via gravity | Not a standalone treatment; requires active management |
| Infestation Monitoring | Enables data-driven mite counts with a sticky board | Essential for timely intervention to prevent colony collapse |
| Hive Ventilation | Improves airflow, reducing moisture and heat in warm climates | Can cause drafts; solid insert is needed for winter in cold climates |
Upgrade your apiary's Varroa mite management with professional-grade equipment from HONESTBEE.
Stop guessing and start making data-driven decisions to protect your colonies. Our screened bottom boards are designed for commercial apiaries and distributors who demand durability and precision.
We supply the reliable tools you need for effective monitoring and control. Let HONESTBEE be your trusted partner in beekeeping success.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your equipment needs and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
- HONESTBEE Wooden Bee Escape Board with Triangle Mesh Design for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Multi Exit Plastic Bee Escape Board for Efficient Honey Harvesting
- HONESTBEE 4-Way Metal Corner Wooden Bee Escape Board
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a screened bottom board on a beehive? Enhance Hive Ventilation & Pest Control
- How does a screened beehive bottom board assist with non-chemical pest control? Boost Hive Health Naturally
- What is the function of screened bottom boards in IPM for beekeeping? Boost Hive Health and Pest Control
- What is a screened bottom board and what are its uses? Enhance Hive Ventilation & Varroa Control
- What is the function of screening bottom boards in large-scale beekeeping management? Boost Colony Health with Data



















