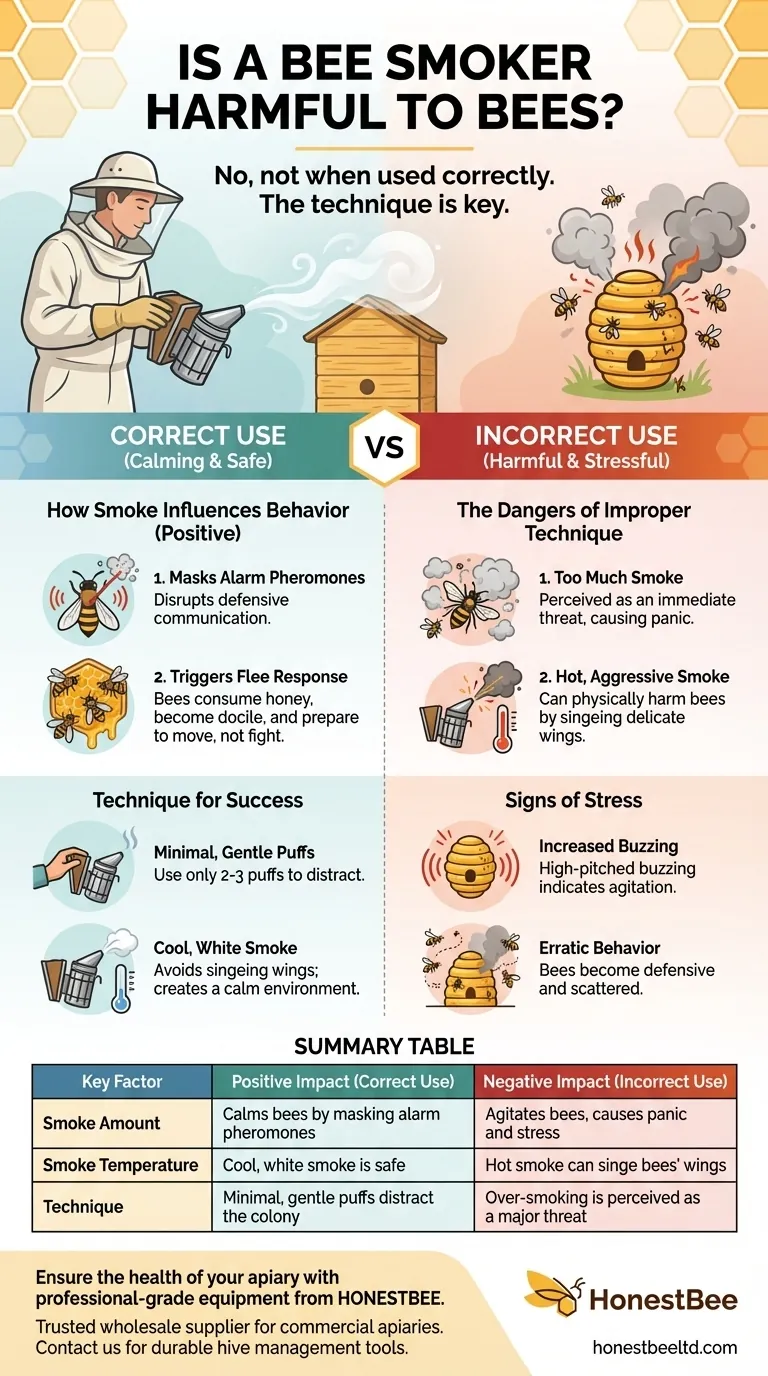
In short, a bee smoker is not inherently harmful to bees when used correctly. Its primary function is to calm the colony by masking the alarm pheromones that trigger a defensive response. However, improper use—specifically applying too much or overly hot smoke—can be stressful and agitate the hive, turning a tool of peace into a source of harm.
The question isn't whether the tool is harmful, but whether the technique is. A smoker's impact on bees is entirely dependent on the beekeeper's skill. The goal is to use minimal, cool smoke to gently distract the colony, not to overwhelm them with a perceived threat.

How Smoke Influences Bee Behavior
To use a smoker effectively and safely, it's crucial to understand what the smoke is actually doing to the colony's communication system.
Masking the Alarm Pheromones
When a hive is disturbed, guard bees release an alarm pheromone. This chemical signal instantly alerts the rest of the colony to a potential intruder, putting them on high alert and preparing them to sting.
Smoke effectively neutralizes this communication channel. The particles in the smoke bind with the bees' antennae, temporarily disrupting their ability to smell the alarm pheromone and preventing a coordinated defensive response.
Triggering a Flee Response
Smoke also triggers a more primal instinct in bees. The presence of smoke mimics a forest fire, a natural and severe threat to any colony.
Their instinctual reaction is not to fight, but to prepare to flee. They begin consuming honey from their stores to have enough energy for a potential journey to a new home. This act of engorging on honey makes them more docile and less inclined to sting.
The Critical Point: When Smoke Becomes Harmful
The line between a calming tool and a harmful stressor is defined by moderation and proper technique.
The Problem of "Too Much" Smoke
The most common mistake is over-smoking the hive. While a few puffs are a distraction, a large volume of smoke is perceived as a genuine, immediate threat.
Instead of calming the bees, this agitates them. It creates panic and stress, leading to more erratic behavior and undermining the very purpose of using the smoker.
The Importance of Cool Smoke
The smoke should always be cool and white. Hot smoke, often produced when a smoker is puffed too aggressively or packed incorrectly, can physically harm the bees by singeing their delicate wings.
A properly managed smoker produces a gentle, cool stream of smoke that calms without causing injury.
How to Use a Smoker Responsibly
Your technique determines whether the smoker is a tool of care or a source of stress. The principle is simple: use as little as necessary.
- If your primary focus is a calm inspection: Start with just two or three gentle puffs at the hive entrance before you open it. After waiting a minute, lift the lid slightly and apply a few more puffs across the top of the frames.
- If your primary focus is minimizing stress: Pay close attention to the sound of the hive. A low, steady hum is good. If the buzzing increases in pitch and volume after you've smoked, it's a clear sign you have used too much.
- If your primary focus is bee safety: Always ensure your smoker is producing cool, white smoke. If it's shooting out sparks or hot air, let it cool down and manage your fuel source better.
Ultimately, the responsible use of a smoker is a core skill that protects both the beekeeper and the bees.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Positive Impact (Correct Use) | Negative Impact (Incorrect Use) |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke Amount | Calms bees by masking alarm pheromones | Agitates bees, causes panic and stress |
| Smoke Temperature | Cool, white smoke is safe | Hot smoke can singe bees' wings |
| Technique | Minimal, gentle puffs distract the colony | Over-smoking is perceived as a major threat |
Ensure the health of your apiary with professional-grade equipment from HONESTBEE.
As a trusted wholesale supplier for commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, we provide the durable, reliable tools you need for safe and effective hive management. A well-made smoker is the first step toward responsible beekeeping.
Let's discuss your supply needs. Contact our team today to learn how our products support the success and sustainability of your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- European Stainless Steel Bee Smoker for Honey Bee Hive
- Economy Galvanized Beekeeping Honey Bee Smoker for Wholesale
- Professional Bee Smoker with Elongated Spout and Durable Bellows for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
- Premium Traditional Copper Bee Smoker with Bellows
People Also Ask
- Can I use smoke to get rid of bees? Why Smoke is a Tool, Not a Solution
- Do bee smokers work? Unlock the Secret to Calm, Safe Hive Inspections
- How should smoke be applied to a beehive during inspection? Master the Gentle Art of Calming Bees
- How do bee smokers work? A Guide to Calming Your Hive for Safer Inspections
- How can beekeepers reduce the likelihood of getting stung? Master Gentle Handling & Protective Gear



















