At its core, a beehive frame is a removable rectangular structure that fits inside a hive body. Frames are designed to hold a sheet of foundation, which gives bees a guide for building their honeycomb. This simple innovation is the key that unlocks modern beekeeping, allowing for hive inspection, management, and honey harvesting without destroying the colony’s home.
The single most important function of a beehive frame is to make the colony's comb removable and manageable. This transforms beekeeping from a destructive harvest into a sustainable practice of hive stewardship.

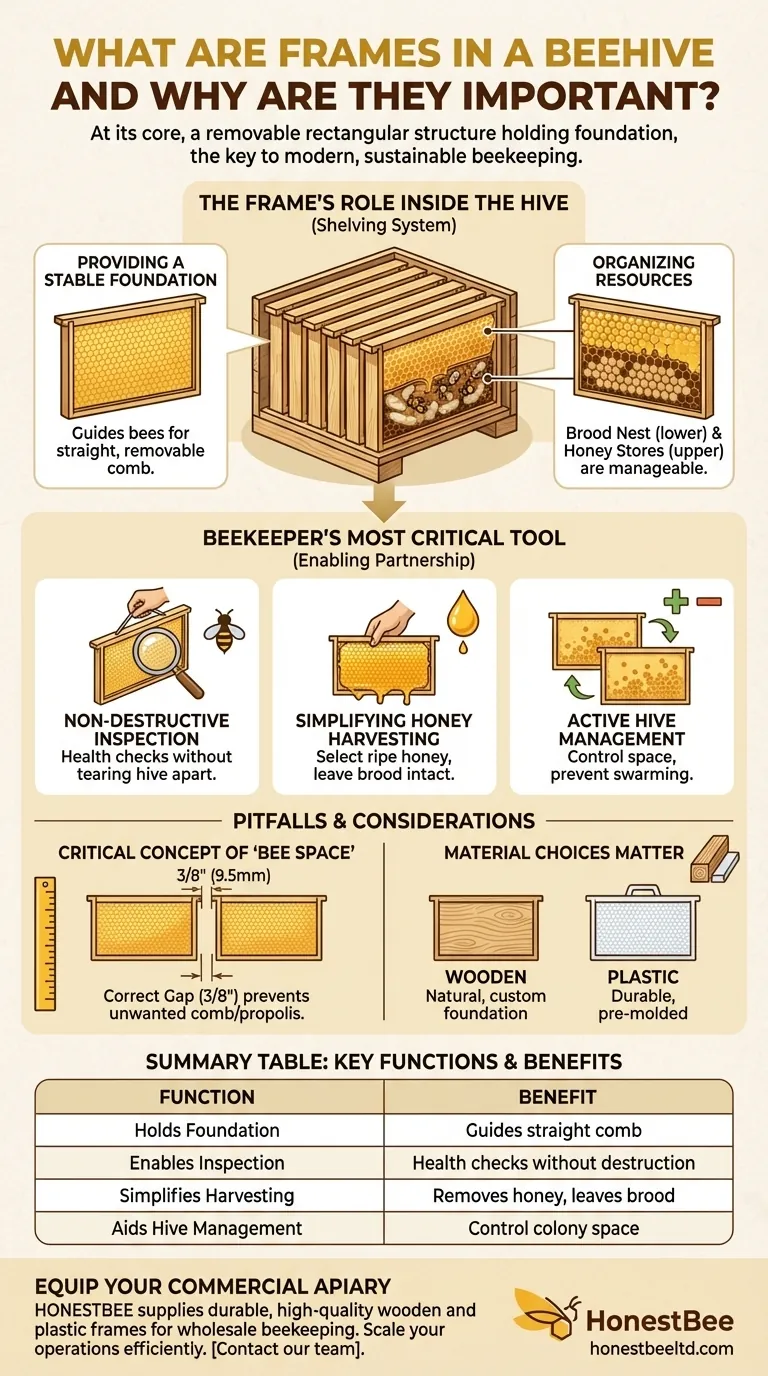
The Frame's Role Inside the Hive
Think of frames as the shelving and filing system for the honeybee colony. They provide the essential internal structure that brings order to the complex life of the hive.
Providing a Stable Foundation
Each frame typically holds a sheet of foundation, which is a thin sheet of beeswax or plastic imprinted with the hexagonal shape of honeycomb cells. This gives the bees a stable and straight guide to start their work.
Without this guide, bees would build comb in natural, curving patterns that would attach to the hive walls, making it impossible to remove without cutting it apart.
Organizing the Colony's Resources
Frames dictate where bees build their comb, creating an organized system. This comb is used for two primary purposes: raising the next generation of bees (brood) and storing food (honey and pollen).
Bees naturally organize these resources, often with the brood nest in the lower boxes and honey stores in the upper boxes. Frames make this organization predictable and easy for a beekeeper to read.
Why Frames Are a Beekeeper's Most Critical Tool
The invention of the movable-frame hive was a revolutionary moment in beekeeping. It shifted the practice from a one-time, destructive harvest to a sustainable, long-term relationship with the colony.
Enabling Non-Destructive Inspection
The most significant advantage of frames is that they allow a beekeeper to lift out and inspect individual sections of the hive.
This allows for crucial health checks, such as looking for signs of disease, assessing the queen's egg-laying pattern, and checking the colony's food stores without tearing the hive apart.
Simplifying Honey Harvesting
When it's time to harvest honey, frames make the process efficient and far less disruptive. Beekeepers can select and remove only the frames that are full of cured honey.
This leaves the rest of the colony's brood and food stores completely intact, minimizing stress on the bees.
Allowing for Active Hive Management
Frames give the beekeeper incredible control over the hive's space. You can add empty frames to give a growing colony more room to expand, which can help prevent swarming.
Conversely, you can remove frames to improve airflow or consolidate a smaller colony for the winter.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While frames are essential, they are part of a system that requires understanding. Their effectiveness depends entirely on correct implementation.
The Critical Concept of "Bee Space"
Frames work because they maintain a specific gap—known as "bee space"—between each frame and between the frames and the hive walls. This space is roughly 3/8 of an inch (9.5mm).
If the space is too large, bees will build unwanted comb to fill it. If it is too small, they will seal the gap with propolis, gluing the frames together. Proper spacing is non-negotiable for movable frames to work.
Material Choices Matter
Frames come in two primary materials: wood and plastic. Each has its own set of advantages.
Wooden frames are traditional and allow for more customization with different foundation types. Plastic frames are often more durable, less prone to warping, and come with a pre-molded foundation, making them simpler for beginners.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right frame setup depends on your beekeeping philosophy and objectives.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and durability: All-in-one plastic frames are often the easiest and fastest way to get started.
- If your primary focus is maximum honey production: Many commercial beekeepers prefer plastic frames for their durability and efficiency in extraction equipment.
- If your primary focus is a more natural approach: Wooden frames with pure beeswax foundation allow the bees to build their comb with minimal artificial material.
Ultimately, frames are the fundamental interface between the beekeeper and the bees, enabling a partnership that benefits both.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Holds Foundation | Guides bees to build straight, removable comb |
| Enables Inspection | Allows for health checks without destroying hive |
| Simplifies Harvesting | Permits removal of honey frames, leaving brood intact |
| Aids Hive Management | Provides control over colony space to prevent swarming |
Equip your commercial apiary or distribution business with the right frames for maximum efficiency and honey production. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality wooden and plastic beehive frames designed for the demands of wholesale beekeeping. Our equipment helps you manage colonies effectively and scale your operations. Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your frame and equipment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Plastic Bee Frame Beekeeping Hive Frames for Wholesale
- Assembled Wooden Bee Frames with Beeswax Foundation Ready to Use by HONESTBEE
- HONESTBEE Wired and Assembled Wooden Bee Frames Foundation for a Thriving Hive
- Heart-Shaped Comb Honey Frame and Honeycomb Cassette
- Assembled Wooden Bee Frames with Plastic Foundation for Durability and Convenience by HONESTBEE
People Also Ask
- How long do bee frames last? A Guide to Lifespan and Replacement for Healthy Hives
- What are assembled beehive frames? Save Time and Effort with Pre-Built Beekeeping Essentials
- What are the advantages of movable-frame beekeeping equipment for disease control? Enhance Your Apiary Health Today
- Why is storing beehive frames in high-ventilation and well-lit areas critical? Stop Wax Moth Damage Effectively
- What are the advantages of using swarms on combs? Accelerate Apiary Growth with Immediate Production Units
- Why is it necessary to use complete hive frames and sealed honey when collecting samples? Ensure Analytical Precision
- How does standardizing beehive sizes to 5-frame or 9-frame configurations benefit queen bee introduction experiments?
- How are Langstroth frames typically oriented in a hive? Mastering 'The Cold Way' for Optimal Ventilation



















