For beekeepers, feeding inside the hive offers unmatched control and protection. This method provides a direct, weather-proof food source that is exclusively available to your colony. It prevents pests from accessing the feed, eliminates waste, and safeguards your bees from the dangers of open feeding.
Internal feeding is fundamentally about risk management. By moving the food source inside the hive, you eliminate external threats like pests and poor weather, but you must carefully manage the internal risks, primarily spills and leaks.

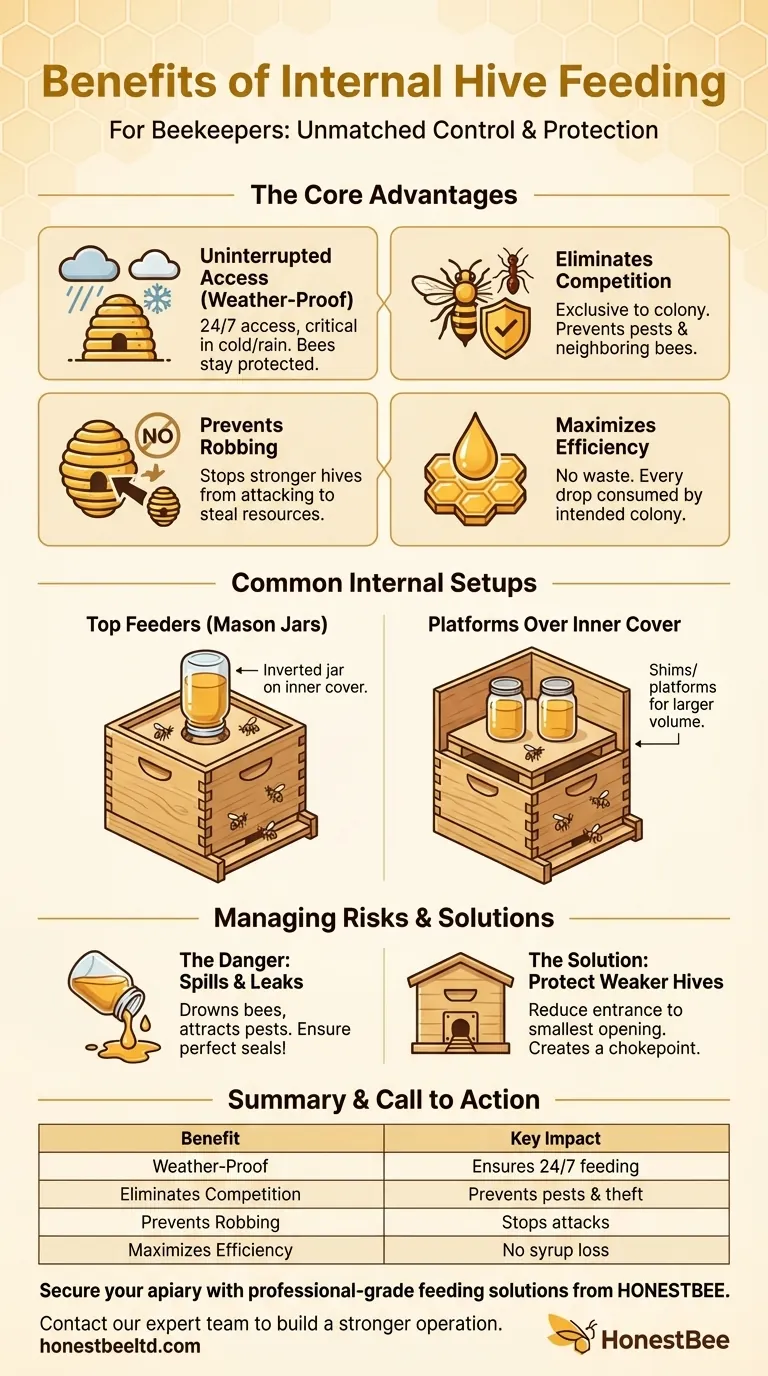
The Core Advantages of Internal Feeding
Placing a feeder inside the hive is a strategic decision that directly impacts colony health, security, and efficiency. The benefits go far beyond simple convenience.
Uninterrupted Access, Regardless of Weather
Bees cannot fly in cold, windy, or rainy conditions. Internal feeders allow the colony to access food 24/7, which is especially critical during early spring, late fall, or unexpected cold snaps when natural forage is scarce and bees are confined to the hive.
Eliminating Competition
An internal feeder ensures the food is only accessible to your bees. This prevents other insects like wasps and ants, as well as bees from neighboring hives, from consuming the resources you provide for your colony.
Preventing Robbing Behavior
Open, external feeding can trigger a dangerous behavior known as robbing. Stronger hives can detect the food source, trace it back to your hive, and launch an attack to steal its resources. This can quickly decimate a weaker colony. Internal feeding completely removes this threat.
Maximizing Efficiency
With an internal feeder, every drop of sugar syrup is consumed by the intended colony. There is no loss to other insects or evaporation, making it a highly economical and effective method for delivering nutrition.
Common Internal Feeding Setups
While many feeder types exist, the principle remains the same: place the food source within the enclosure of the hive body.
Top Feeders (e.g., Mason Jars)
One of the simplest methods involves inverting a mason jar with small holes in the lid. This can be placed directly on the top bars of the frames or, more commonly, over the hole in the hive's inner cover. You can place an empty hive box around the jar to protect it.
Using Platforms Over the Inner Cover
A slight variation involves using a platform or a purpose-built shim on top of the inner cover. This allows you to place one or more feed jars inside, increasing the volume of syrup and reducing the frequency of refills.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While highly effective, internal feeding requires attention to detail to prevent creating new problems for your colony.
The Danger of Spills and Leaks
This is the single greatest risk of internal feeding. A leaky feeder can drip syrup all over the bees, combs, and hive floor. Drenched bees will quickly die, and a significant leak could even harm the queen.
Furthermore, if syrup leaks out of the hive entrance, it can attract pests and trigger the very robbing behavior you sought to avoid. Always ensure your feeder has a perfect seal.
Protecting Weaker Hives from Intruders
Even with an internal feeder, a weak hive with a large entrance is vulnerable. If robbers investigate the hive, they can easily overpower the few guard bees.
For this reason, whenever you are feeding a weak or new colony, you must reduce the hive entrance to its smallest opening. This creates a defensible chokepoint that the colony's guard bees can protect.
How to Apply This to Your Colony
Your choice of feeding method should be guided by your colony's specific needs and your beekeeping goals.
- If your primary focus is colony security: Internal feeding is the superior choice, as it virtually eliminates the risk of robbing and competition from pests.
- If you are nursing a weak or new colony: Use an internal feeder and reduce the hive entrance to its smallest opening to give the colony the best chance of survival.
- If your priority is stimulating brood production: An internal feeder provides the consistent resource flow necessary for the queen to confidently expand her laying.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently use internal feeding to build a stronger, healthier, and more resilient colony.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Weather-Proof Access | Ensures 24/7 feeding, critical in cold/rainy weather. |
| Eliminates Competition | Prevents pests & other bees from stealing resources. |
| Prevents Robbing | Stops stronger hives from attacking to steal food. |
| Maximizes Efficiency | Every drop of syrup is consumed by your colony. |
Ready to secure your apiary with professional-grade feeding solutions?
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, reliable internal feeders and hive equipment needed to protect your investment and maximize colony health. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the best value.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and build a stronger, more resilient operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- In-Hive Dual Compartment Frame Bee Feeder for Targeted Colony Nutrition
- Professional Hive Top Bee Feeder for Beekeeping
- Boardman Entrance Bee Feeder Durable Galvanized Steel and Wood Construction for Beekeeping
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
- HONESTBEE Professional Entrance Bee Feeder Hive Nutrition Solution
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when feeding bees inside the hive? Safeguard Your Colony from Robbing and Leaks
- How does the internal feeder method work? Protect Your Hive from Robbing and Cold
- How is a frame feeder utilized in different scales of beekeeping? Optimize Your Hive Feeding Strategy
- What is a frame feeder? A High-Capacity, Secure In-Hive Feeding Solution
- What is a frame feeder and what are its pros and cons? Secure Your Colony with Effective In-Hive Feeding



















