Spreading an insect is a foundational technique in entomology that goes far beyond simple pinning. The core benefits are twofold: it restores a dead specimen to a more natural, lifelike posture for display and, more critically, it arranges the wings, legs, and other appendages to reveal key features essential for accurate scientific identification.
The decision to spread an insect is a decision about its purpose. It's the step that transforms a dead specimen from a simple keepsake into a valuable, analyzable record for either scientific study or high-quality educational display.
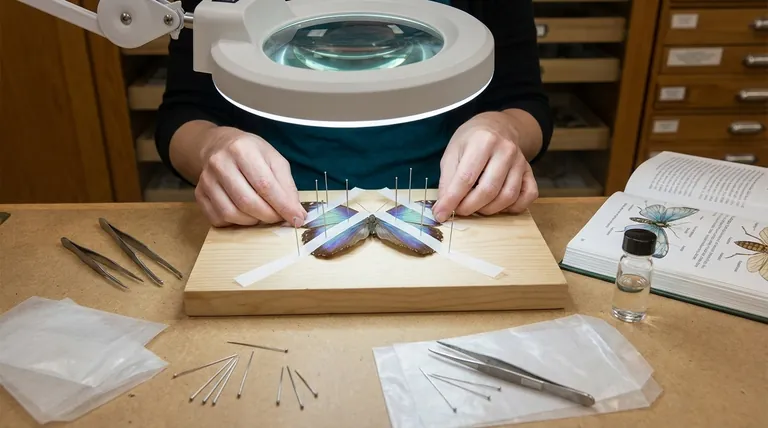

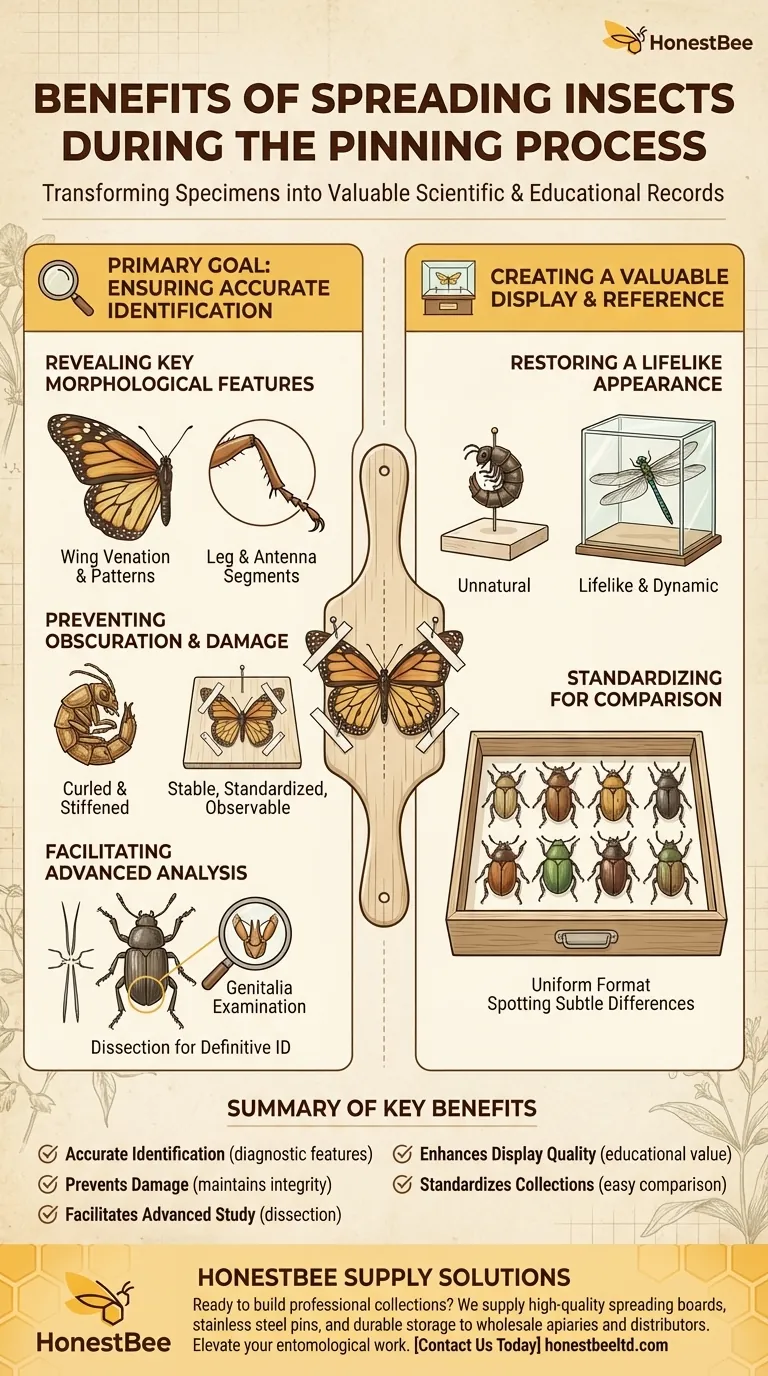
The Primary Goal: Ensuring Accurate Identification
Properly preparing a specimen is fundamental to its scientific value. An unspread insect often has its most important diagnostic features obscured.
Revealing Key Morphological Features
Many insect species are identified by subtle characteristics. Spreading the wings flat reveals their complete shape, color patterns, and the unique map of veins (venation) that can distinguish one species from another.
Similarly, positioning the legs and antennae allows for clear examination of their segments, spines, and claws, which are often crucial for identification.
Preventing Obscuration and Damage
As an insect dries after death, its appendages tend to curl and stiffen in a contracted position. Spreading the insect while it is still relaxed and positioning it on a spreading board ensures it dries in a stable, standardized, and observable state.
Facilitating Advanced Analysis
For many groups of insects, particularly moths, beetles, and flies, external features are not enough to separate closely related species. In these cases, dissection and examination of the genitalia is the only method for a definitive identification.
The process of spreading and preparing the specimen is the first step in making this kind of detailed analysis possible.
Creating a Valuable Display and Reference
Beyond pure science, the goal of a collection is often education and aesthetic appreciation. Spreading is essential for creating a professional and useful physical reference.
Restoring a Lifelike Appearance
An insect pinned with its wings closed and legs curled under appears unnatural and conveys little information about how it looked in life. A properly spread specimen, with its wings displayed as if in flight, is far more effective for museum displays and educational purposes.
Standardizing for Comparison
When all specimens in a collection are spread in a consistent manner, it becomes much easier to compare them side-by-side. This uniformity is critical for spotting subtle differences between individuals or species.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While the benefits are clear, the process requires care and is not always necessary for every situation.
The Investment of Time and Skill
Spreading is a delicate and time-consuming craft that requires practice. A rushed or inexperienced attempt can easily result in broken antennae, torn wings, or snapped legs, permanently damaging the specimen.
Not All Insects Require Spreading
For very small or soft-bodied insects, or for collections intended for rapid biodiversity surveys, a simple pin through the thorax or preservation in alcohol may be sufficient. The decision to invest the time in spreading depends entirely on the intended use of the specimen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you should spread a specimen depends on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is scientific research or species-level identification: Spreading is non-negotiable to expose the necessary anatomical details for accurate analysis.
- If your primary focus is creating an educational or aesthetic display: Spreading is essential for achieving a professional, lifelike presentation that maximizes the specimen's visual impact.
- If your primary focus is a rapid field survey with basic classification: You may choose to skip spreading for less critical specimens to save time, but this will limit their future scientific value.
Ultimately, spreading an insect elevates it from a simple object to a lasting piece of biological data.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Accurate Identification | Reveals wing venation, leg segments, and other diagnostic features for species-level analysis. |
| Prevents Damage | Stabilizes appendages during drying to avoid obscuration and maintain specimen integrity. |
| Facilitates Advanced Study | Enables dissection (e.g., genitalia examination) for definitive identification. |
| Enhances Display Quality | Restores a lifelike posture for educational or aesthetic purposes. |
| Standardizes Collections | Allows for easy comparison between specimens in a uniform format. |
Ready to build a professional insect collection with precision? HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality spreading boards, stainless steel pins, and durable storage solutions. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get reliable tools for creating scientifically valuable specimens. Contact us today to discuss your equipment needs and elevate your entomological work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Nicot Queen Rearing Kit for Beekeeping and Grafting in Nicot System
- HONESTBEE Multi Exit Plastic Bee Escape Board for Efficient Honey Harvesting
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Can anyone use Queen Rearing with JZBZ? A Beginner-Friendly System for All Beekeepers
- What do queen rearers do with queens that fail to lay on time? The Critical Quality Control Decision
- What should be done once eggs are present in the comb box? A Guide to Maximizing Queen Rearing Success
- What are the methods of queen rearing? Master Grafting, Direct Lay & More
- In what ways do modern queen rearing equipment and grafting tools improve competitiveness? Boost Breeding Success Rate



















