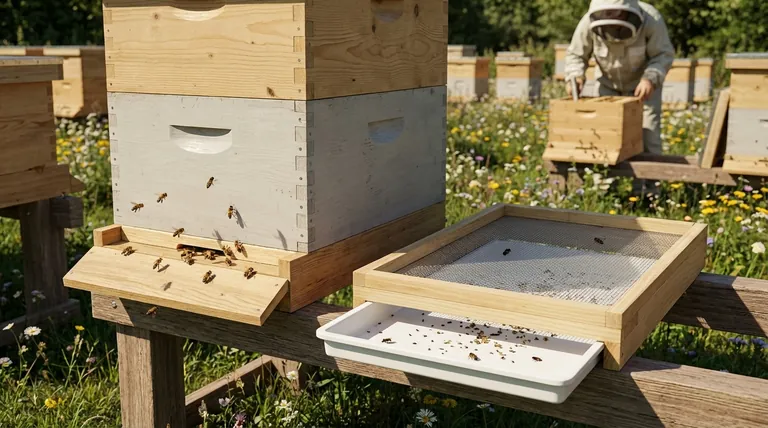
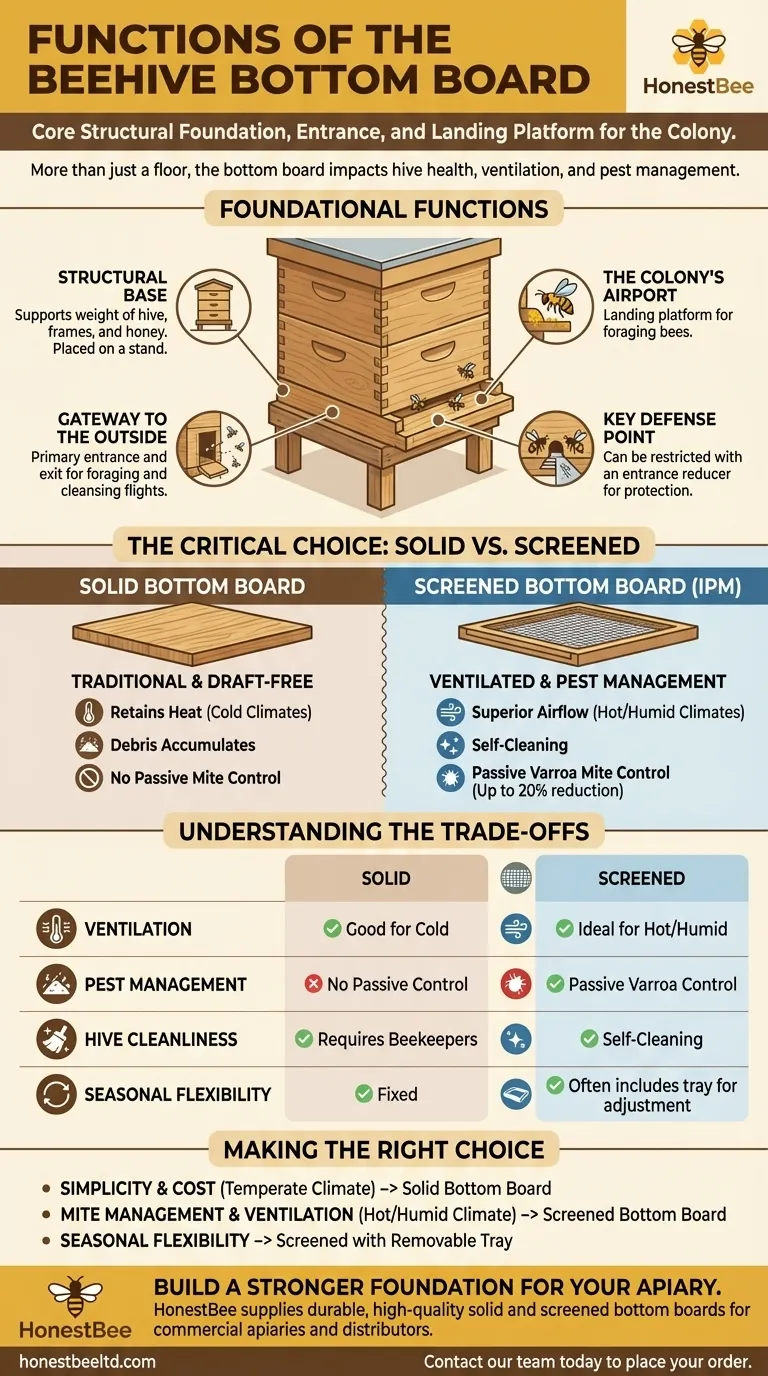
At its core, the bottom board is far more than just the floor of a beehive. It serves as the structural foundation for the entire colony, creates the primary entrance and exit, and acts as the crucial takeoff and landing platform for all foraging bees. The design of this single component has significant implications for hive health, ventilation, and pest management.
While every bottom board provides a foundation and entrance, the critical choice between a solid and a screened design directly impacts your hive's ventilation, moisture levels, and your strategy for managing pests like the Varroa mite.

Foundational Functions of Any Bottom Board
Every beehive, regardless of its specific design, relies on the bottom board to perform several essential duties for the colony.
The Hive's Structural Base
The bottom board is the floor of the hive. It provides a stable base that supports the weight of all the hive bodies, frames, honey, and the bees themselves. It is typically placed on a stand to raise it off the damp ground, prolonging the life of the wood.
The Gateway to the Outside World
When the first hive body is placed on top of it, the bottom board creates the main entrance and exit for the colony. This opening is the bees' only connection to the outside world for foraging and cleansing flights.
The Colony's Airport
The portion of the bottom board that extends out from the front of the hive acts as a landing platform. Foraging bees, often heavily laden with pollen and nectar, use this area to land before entering the hive.
A Key Point of Defense
For smaller or younger colonies, the entrance created by the bottom board can be too large to defend effectively. Beekeepers can install an entrance reducer to restrict the opening, making it easier for guard bees to protect the hive from intruders like wasps or mice.
The Critical Choice: Solid vs. Screened Bottom Boards
The most significant decision regarding a bottom board is choosing between a solid or a screened design. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages that affect how you manage your hive.
The Solid Bottom Board
A solid bottom board is a simple, solid piece of wood. It completely encloses the bottom of the hive, creating a draft-free floor. This is the traditional design that has been used for centuries.
The Screened Bottom Board
A screened bottom board, also known as an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) board, replaces much of the solid wood floor with a durable wire screen or mesh. This creates an open, ventilated floor for the hive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between solid and screened is not about which is "better," but which is better for your specific climate, goals, and management style.
Ventilation and Climate Control
A screened board offers superior ventilation. In hot summers, it allows excess heat to escape, keeping the colony cooler. In cold, damp winters, it allows moisture-laden air to exit, preventing condensation from dripping down on the cluster.
A solid board retains more heat. This can be an advantage in colder climates, as it may help the colony build up its population more quickly in the early spring.
Pest Management: The Varroa Mite
This is the primary reason for the screened board's popularity. As Varroa mites fall off bees, many will drop through the screen and out of the hive, unable to return. This can reduce mite populations by up to 20%.
However, a screened board is not a complete mite treatment. It is a passive control method that must be combined with a comprehensive mite management plan.
Hive Cleanliness
A screened bottom board allows debris like wax cappings and dead bees to fall out of the hive, resulting in a cleaner interior. With a solid board, this debris accumulates and must be periodically cleaned out by the beekeeper or the bees.
Making the Right Choice for Your Colony
Your choice of bottom board should be a deliberate decision based on the needs of your bees and your local environment.
- If your primary focus is on simplicity and cost-effectiveness in a temperate climate: A solid bottom board is a reliable and traditional choice that helps retain heat for spring buildup.
- If your primary focus is on managing Varroa mites and providing maximum ventilation in a hot or humid climate: A screened bottom board offers significant passive benefits for hive health and moisture control.
- If you want the flexibility to adapt to changing seasons: Many beekeepers use a screened bottom board with a removable tray, allowing them to close it off in winter and open it up in summer.
Ultimately, understanding these functions and trade-offs empowers you to provide the ideal foundation for a thriving colony.
Summary Table:
| Function | Solid Bottom Board | Screened Bottom Board |
|---|---|---|
| Ventilation | Retains heat, good for cold climates | Superior airflow, ideal for hot/humid climates |
| Pest Management | Debris accumulates; no passive mite control | Passive Varroa mite control; debris falls through |
| Hive Cleanliness | Requires periodic cleaning by beekeeper/bees | Self-cleaning; reduces interior debris |
| Seasonal Flexibility | Fixed design | Often includes removable tray for seasonal adjustment |
Build a stronger foundation for your apiary. The right bottom board is critical for hive health and productivity. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality solid and screened bottom boards to commercial apiaries and distributors. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable equipment your business needs. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and place your order.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
- HONESTBEE Wooden Bee Escape Board with Triangle Mesh Design for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Frame Wiring Board and Jig
- HONESTBEE Durable Frame Wiring Board with Integrated Tensioner
People Also Ask
- What are the overall benefits of using wire mesh for a beehive floor? Improve Hive Health & Reduce Maintenance
- What are the advantages of a screened bottom board? Boost Hive Health with Superior Ventilation & Pest Control
- What is a screened bottom board for bee hives? A Key Tool for Ventilation & Mite Control
- What are the potential disadvantages of using a screened bottom board? Hidden Risks for Your Apiary Management
- How should the screened bottom board be used throughout the year? A Guide for Healthy Hives



















