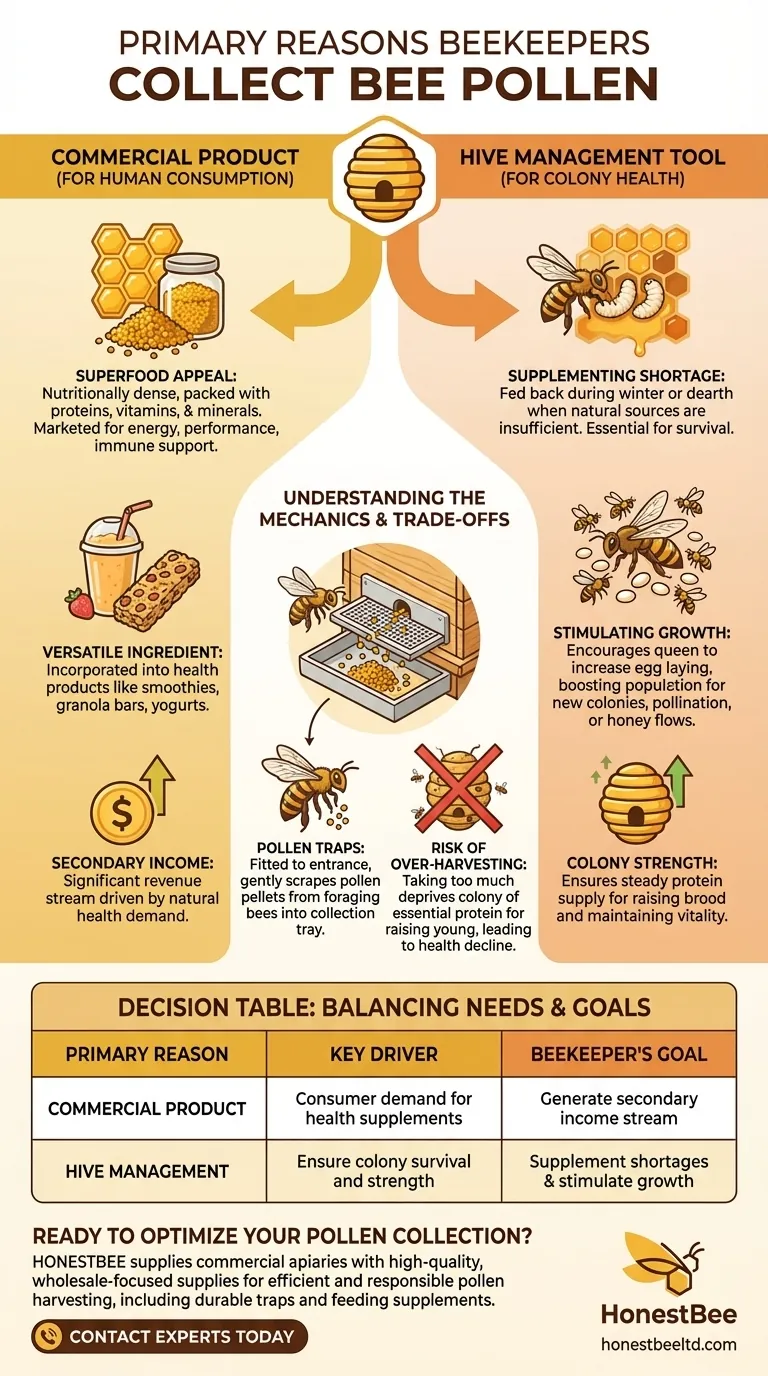
The primary reasons beekeepers collect bee pollen are twofold. It is harvested both as a valuable commercial product for human consumption, driven by its reputation as a health food, and as a critical nutritional supplement to feed back to the bees themselves to ensure colony survival and strength.
Bee pollen collection is a practice of balance, viewing pollen as both a source of income for the beekeeper and a vital food source for the hive. The decision to collect it hinges entirely on managing the needs of the colony against the goals of the apiarist.

The Value of Pollen as a Commercial Product
For many beekeepers, pollen represents a significant secondary income stream alongside honey. This market is driven almost entirely by consumer interest in natural health and wellness products.
The "Superfood" Appeal
Bee pollen is widely marketed to humans as a "superfood." It is a nutritionally dense substance, packed with proteins, vitamins, and minerals, leading to its popularity as a dietary supplement.
Consumers purchase it for perceived benefits ranging from increased energy and athletic performance to general immune support.
Versatile Food Ingredient
Beyond being sold in its raw, granular form, bee pollen is also incorporated into a variety of health-focused food products. You might find it in smoothies, granola bars, yogurts, and other items where its nutritional profile is a key selling point.
Pollen as a Hive Management Tool
Experienced beekeepers understand that a healthy hive depends on a steady supply of protein-rich pollen. Collecting pollen is often done specifically to create a reserve for the bees themselves.
Supplementing a Natural Shortage
There are specific times when a colony's natural pollen sources are insufficient. Beekeepers feed stored pollen back to their hives during the cold months of winter or during a "dearth" when few flowers are blooming.
This supplemental feeding can be the difference between a colony starving or surviving until the next nectar flow.
Stimulating Colony Growth
Feeding pollen can also be used to intentionally mimic an abundance of natural resources. This encourages the queen to increase her rate of laying eggs, rapidly boosting the colony's population.
This is a common strategy when establishing a new colony or preparing a hive for pollination services or a major honey flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Mechanics
Collecting pollen is not a passive activity; it is an active intervention in the life of the hive that requires specific equipment and careful consideration.
How Pollen Traps Work
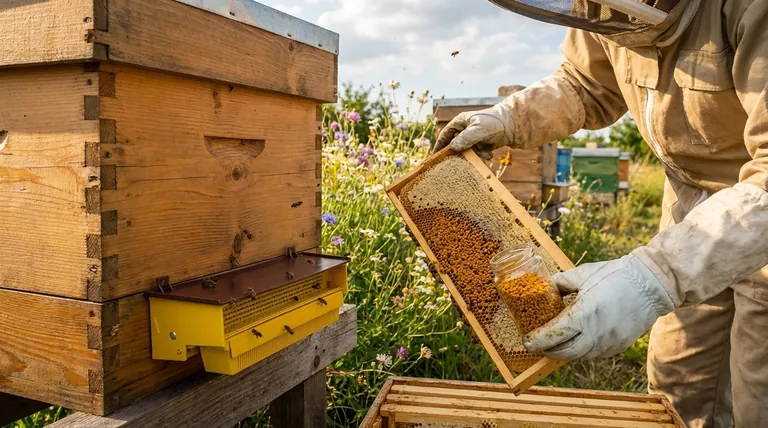
Beekeepers use a device called a pollen trap, which is fitted to the hive entrance. This trap has a screen or set of small holes that are just large enough for a bee to squeeze through.
As the foraging bees enter, the screen gently scrapes some of the pollen pellets from their hind legs (pollen baskets). This dislodged pollen falls into a collection tray below, ready for the beekeeper to harvest.
The Risk of Over-Harvesting
The most significant risk is taking too much pollen. Pollen is the bees' primary source of protein, essential for raising young bees (brood).
A well-designed pollen trap is built to knock off only a portion of the pollen a bee carries, ensuring enough still gets into the hive. However, irresponsible or prolonged use of a trap can deprive the colony of this critical resource, leading to a decline in health and population.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for collecting bee pollen will determine your entire approach, from the equipment you use to the timing of your harvest.
- If your primary focus is hive health and sustainability: You will likely only collect pollen during periods of extreme abundance to create a reserve for feeding back to your bees during winter or a nectar dearth.
- If your primary focus is generating income: You must invest in efficient pollen traps and a system for drying and storing the pollen, while constantly monitoring your colonies to ensure you are not harvesting so much that it damages their health and productivity.
Ultimately, responsible pollen collection is about understanding its dual role as both a product and a pillar of colony nutrition.
Summary Table:
| Primary Reason | Key Driver | Beekeeper's Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Product | Consumer demand for natural health supplements. | Generate a secondary income stream. |
| Hive Management | Ensure colony survival and strength. | Supplement natural shortages and stimulate population growth. |
Ready to optimize your pollen collection and hive management?
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies needed for efficient and responsible pollen harvesting. From durable pollen traps to essential feeding supplements, we provide the tools for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can support your hive health and profitability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Removable Plastic Pollen Trap With Ventilated Tray for Bees Pollen Collector
- 30 cm Plastic Entrance Hole Bee Pollen Trap and Collector
- Plastic Bee Pollen Trap Strips Comb Catcher Collector
- Removable Washable Hive Beetle Trap Attractants for Small Hive Beetles
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
People Also Ask
- What is the function of outdoor pre-mounted pollen traps? Optimize Collection and Research for Your Apiary
- How does a bee pollen trap work? Master the Mechanics of Efficient Pollen Collection for Your Apiary
- What is the function of front entrance pollen traps? Optimize Castanea Pollen Harvesting for Better Results
- How does the design of a Low-bottom pollen trap influence pollen quality? Manage Moisture and Fungal Risk Effectively
- Why is a Pollen Trap installed at the beehive entrance? Optimize Your Floral Resource Surveys & Data



















