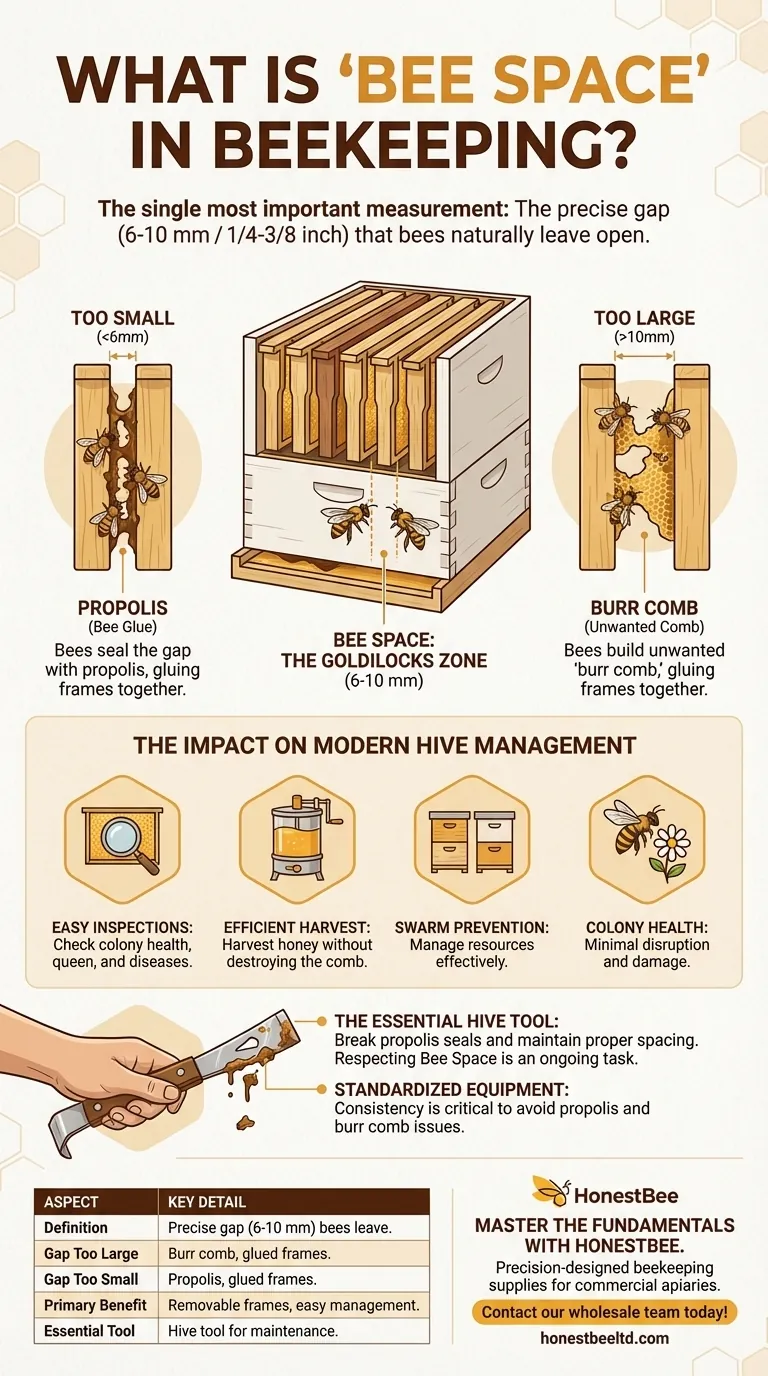
In beekeeping, Bee Space is the single most important measurement. It is the precise gap—typically between 6 and 10 millimeters (1/4 to 3/8 inch)—that honeybees naturally leave open between their combs. This specific distance allows them to move freely but discourages them from building unwanted comb or sealing the gap with propolis, a resinous glue. Understanding and respecting this space is the foundational principle of all modern, removable-frame hives.
The concept of Bee Space is what separates a simple box of bees from a manageable, inspectable beehive. By designing all hive components around this precise measurement, beekeepers can remove frames for inspection and harvest honey without destroying the colony's structure, a revolutionary advance in apiculture.

The Genius of Bee Space: How a Simple Measurement Works
The discovery of Bee Space in the 19th century by Rev. L.L. Langstroth transformed beekeeping from a primitive hunt into a form of animal husbandry. His insight was that bees operate on a simple, predictable spatial logic.
Defining the "Goldilocks Zone"
Bee Space is not a single number but a "just right" range. While the exact measurement varies slightly by honeybee species—for example, 7-9 mm for Apis cerana indica (Indian bees) versus around 9-10 mm for Apis mellifera (European bees)—the principle is universal.
This dimension is perfect for two bees to pass back-to-back, allowing for efficient movement and communication throughout the hive.
The Bee's Natural Instinct: Build or Seal
A colony's response to any given space is highly predictable. This is the core of why Bee Space is so powerful.
If a gap is larger than 10 mm, bees will treat it as wasted space and fill it with "burr comb" or "brace comb." This connects frames to each other and to the hive walls, making them impossible to remove without tearing the hive apart.
If a gap is smaller than 6 mm, bees cannot pass through it and will seal it shut with propolis, a sticky plant resin. This effectively glues frames and other hive components together.
The Impact on Modern Hive Management
When a hive is constructed so that every space between frames, and between the frames and the hive box, adheres to Bee Space, the frames hang freely.
This allows the beekeeper to easily slide each frame out individually. This simple act is the key to all modern beekeeping practices, including:
- Inspecting colony health for signs of disease or pests.
- Verifying the queen is present and laying eggs properly.
- Managing swarm prevention by adding or removing resources.
- Harvesting honey without destroying the comb or harming the colony.
Without Bee Space, none of this would be possible without significant disruption and damage to the hive.
Understanding the Practical Challenges
While the principle is simple, reality in the hive can be more complex. Respecting Bee Space is an ongoing task, not a one-time setup.
The Myth of Perfect Spacing
Wood can warp, plastic components can have manufacturing tolerances, and bees do not always follow the rules perfectly. Beekeepers must be prepared for minor deviations.
Even in a perfectly built hive, bees may occasionally build small amounts of burr comb, especially if a frame is slightly out of place.
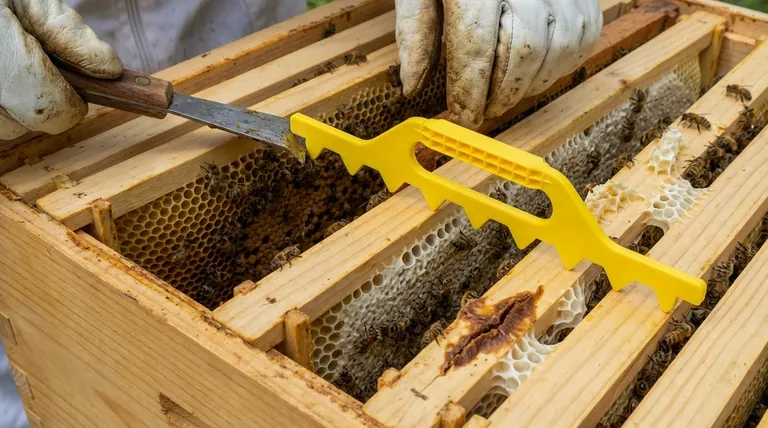
The Essential Role of the Hive Tool
Because bees will inevitably use some propolis to seal small cracks, every beekeeper's most essential tool is the hive tool.
This is a small, strong pry bar used to gently break the propolis seal and separate frames before lifting them. It is also used to scrape away any unwanted burr comb to maintain correct spacing for the future.
The Importance of Standardized Equipment
Modern hives, like the Langstroth hive, are meticulously designed around Bee Space. All internal dimensions are calculated to create this precise gap.
Mixing components from different hive types or manufacturers can inadvertently violate Bee Space, leading to a hive that is glued together with propolis and burr comb. Consistency is critical.
Applying the Principle of Bee Space
As a beekeeper, your actions in and around the hive should always be guided by this fundamental principle.
- If your primary focus is assembling new equipment: Ensure you are using the correct number of frames for the box (e.g., 8 or 10) and that they are pushed together evenly to create the proper spacing on the sides.
- If your primary focus is inspecting a hive: Always use your hive tool to clean off any excess burr comb or propolis from the frame tops and ends to maintain proper spacing for your next inspection.
- If your primary focus is building your own hive: Meticulously follow established plans for a standard hive type, as even a few millimeters of deviation can render your hive unmanageable.
Mastering this single concept is the first and most critical step toward becoming a successful and responsible beekeeper.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Definition | A precise gap (6-10 mm / 1/4-3/8 inch) bees naturally leave between combs. |
| If Gap is Too Large (>10mm) | Bees build unwanted "burr comb," gluing frames together. |
| If Gap is Too Small (<6mm) | Bees seal the gap with propolis, gluing frames together. |
| Primary Benefit | Enables removable frames for inspection and honey harvesting without destroying the hive. |
| Essential Tool | A hive tool is needed to break propolis seals and maintain proper spacing. |
Master the fundamentals of beekeeping with HONESTBEE.
Proper hive management starts with equipment designed to the exact specifications of Bee Space. For commercial apiaries and distributors, this precision is non-negotiable for efficiency and colony health. HONESTBEE supplies high-quality, standardized beekeeping supplies and equipment through wholesale-focused operations, ensuring your hives are productive and manageable.
Let's discuss your supply needs. Contact our wholesale team today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ergonomic Plastic Frame Spacer Tool for Rapid Hive Management Beekeeping
- Durable Plastic Frame Spacer
- Stainless Steel 9 Frame Hive Spacer Durable Precise for Commercial Beekeeping
- Professional Castellated Iron Frame Spacer for Multiple Hive Types
- Manual Spur Wheel Wire Embedder for Foundation
People Also Ask
- How is bee space managed in a top bar hive? Master Natural Comb Spacing & Volume Control
- What to do if bees are building combs between frames? A Guide to Fixing Burr Comb
- What is the technical logic behind using nails as spacers in the frame assembly? Mastering Bee Space and Hive Efficiency
- What is the recommended spacing for placing beehives in an apiary? Optimize Hive Layout for Better Colony Health
- What are the spacing requirements for beehive accessibility and maintenance? Optimize Your Apiary Layout for Success



















