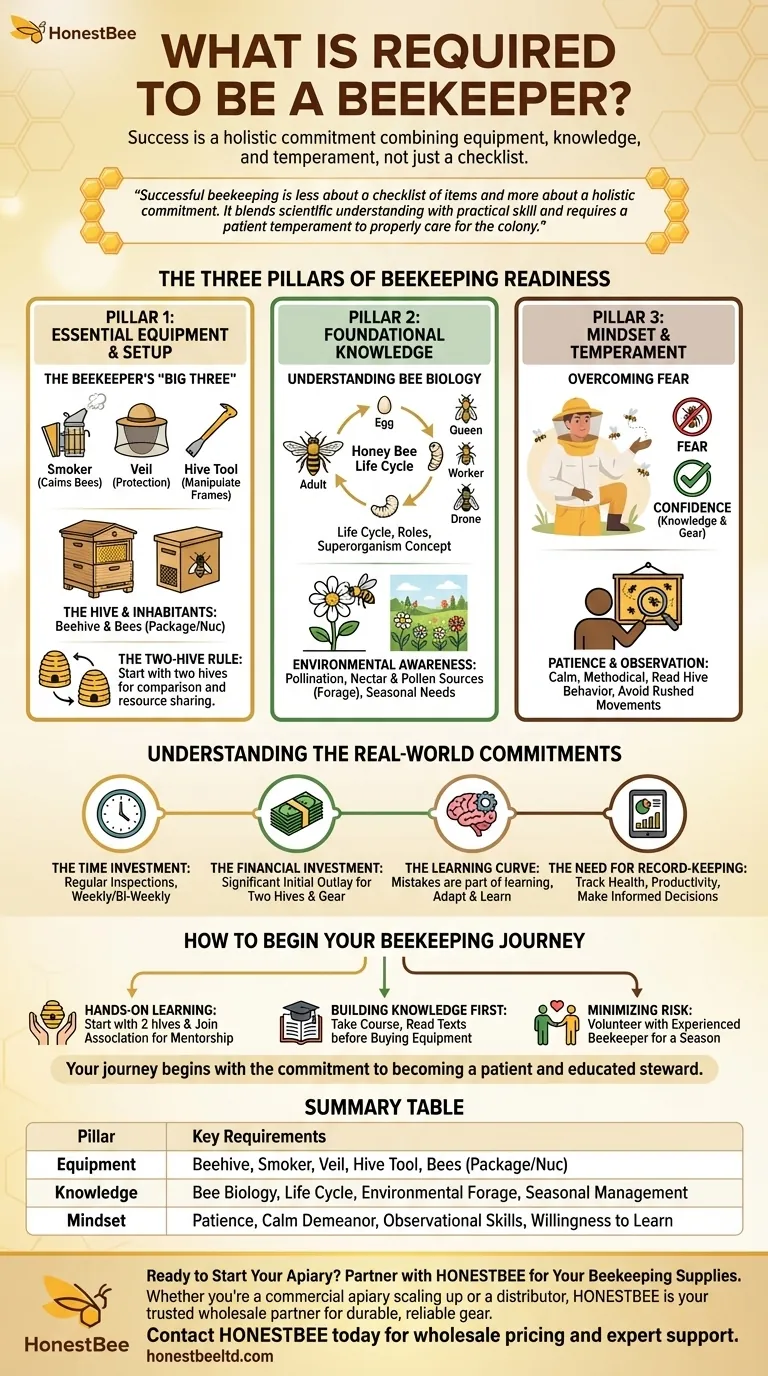
To become a beekeeper, you need a combination of tangible equipment, foundational knowledge, and the right personal temperament. The essentials include protective gear like a veil, a hive tool for inspections, and a smoker to calm the bees, but success hinges just as much on understanding bee biology and maintaining a calm, observant demeanor when managing the hives.
Successful beekeeping is less about a checklist of items and more about a holistic commitment. It blends scientific understanding with practical skill and requires a patient temperament to properly care for the colony.
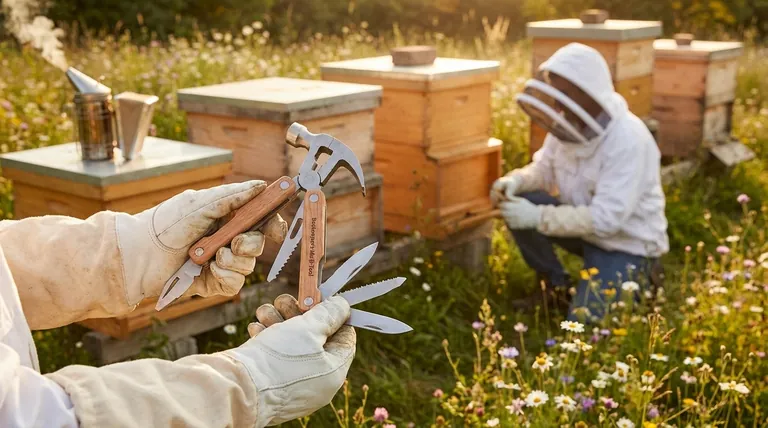

The Three Pillars of Beekeeping Readiness
To truly prepare, you must focus on three distinct areas: your equipment, your knowledge base, and your personal mindset. Each is critical for the long-term health of your bees and your success as their steward.
Pillar 1: Essential Equipment and Setup
The physical tools are the most straightforward requirement. This is your interface for interacting with the hive safely and effectively.
The Beekeeper's "Big Three" The absolute non-negotiables are the bee smoker, veil, and hive tool. The smoker helps calm the bees during inspections, the veil protects your face and neck, and the hive tool is a specialized pry bar used to open the hive and manipulate frames.
The Hive and Its Inhabitants You will need at least one beehive, which is the physical structure that houses the colony. You will also need the bees themselves, typically acquired as a "package" or a "nuc" (a small nucleus colony).
The Two-Hive Rule It is strongly recommended that new beekeepers start with two hives instead of one. This allows you to compare colony health and progress. If one hive becomes weak or loses its queen, you can often use resources from the stronger hive to save it.
Pillar 2: Foundational Knowledge
Beekeeping is applied biology. Operating without a basic understanding of the bees' life cycle and needs is a recipe for failure.
Understanding Bee Biology You must learn the fundamentals of the honey bee life cycle, the roles of the queen, worker, and drone, and how the colony functions as a single "superorganism." This knowledge informs every decision you make.
Environmental Awareness Bees are intrinsically linked to their environment. Understanding pollination and identifying the primary nectar and pollen sources (forage) in your area will help you anticipate the colony's needs throughout the seasons.
Pillar 3: Mindset and Temperament
Your personal approach is just as important as your equipment. Bees are sensitive creatures, and your state of mind directly impacts your interactions with them.
Overcoming Fear A persistent fear of bees is a significant barrier. Feeling unsafe prevents you from performing necessary inspections and care. Confidence comes from knowledge and proper use of protective gear.
Patience and Observation Successful beekeepers are calm, patient, and methodical. You must learn to "read" the hive by observing the bees' behavior, sounds, and patterns. Rushed, jerky movements will only agitate the colony.
Understanding the Real-World Commitments
Beyond the initial requirements, beekeeping demands ongoing investment and carries inherent risks. Acknowledging these realities is crucial for long-term success.
The Time Investment
Beekeeping is not a "set-it-and-forget-it" hobby. It requires regular inspections—weekly or bi-weekly during peak season—to monitor for disease, check the queen's status, and manage space.
The Financial Investment
The startup costs for two hives, bees, protective gear, and basic tools can be significant. Be prepared for this initial financial outlay before you expect any return in honey.
The Learning Curve
You will make mistakes. Colonies can be lost to pests, disease, or simple errors. This is a natural part of the learning process. The key is to learn from each setback and not become discouraged.
The Need for Record-Keeping
As your apiary grows, so does the need for diligent records. Tracking the health, productivity, and temperament of each hive is essential for making informed management decisions, a practice that requires discipline and attention to detail.
How to Begin Your Beekeeping Journey
Your starting point depends on your preferred learning style and comfort level with risk.
- If your primary focus is hands-on learning: Start with two hives and immediately join a local beekeeping association to gain practical experience and mentorship.
- If your primary focus is building knowledge first: Take a local or online beekeeping course and read foundational texts before investing in any equipment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing risk: Volunteer to help an experienced beekeeper for a full season before committing to your own hives.
Your journey begins not with the first hive, but with the commitment to becoming a patient and educated steward of these vital creatures.
Summary Table:
| Pillar | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Equipment | Beehive, Smoker, Veil, Hive Tool, Bees (Package/Nuc) |
| Knowledge | Bee Biology, Life Cycle, Environmental Forage, Seasonal Management |
| Mindset | Patience, Calm Demeanor, Observational Skills, Willingness to Learn |
Ready to Start Your Apiary? Partner with HONESTBEE for Your Beekeeping Supplies.
Whether you're a commercial apiary scaling up operations or a distributor stocking quality equipment, HONESTBEE is your trusted wholesale partner. We supply the durable, reliable gear that beekeepers depend on—from smokers and veils to hive tools and complete hive setups. Let us help you build a stronger, more productive operation.
Contact HONESTBEE today for wholesale pricing and expert support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE 15-in-1 Beekeeper Multi-Tool with Hammer and Pliers for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- Wooden Bee Brush with Triple Row Artificial Fiber for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does specialized transport equipment support migratory beekeeping? Scale Your Apiary Revenue Effectively
- How do refrigeration and freezing equipment contribute to the processing of bee specimens? Preserve DNA and Structure
- Why is a bubbling time of 120 seconds recommended for beekeeping ozone? Ensure Maximum Pathogen Kill Power
- What role does professional beekeeping equipment play in urban agriculture? Scaling Impact and Economic Success
- What are the considerations when making your own beekeeping equipment? Master DIY Hive Precision
- What are the primary functions of high-strength nylon ropes in forest honey harvesting? Safety and Harvest Integrity
- What equipment do you need to make honey? A Complete Guide to Starting Your Apiary
- What are the technical advantages of using Basswood or Cork Oak for beehives? Create a Natural Colony Habitat



















