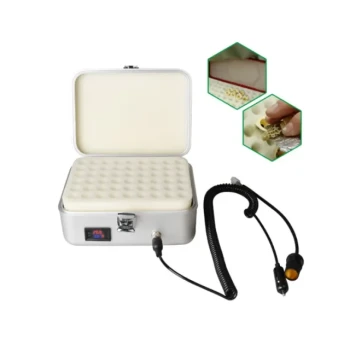
The primary technical advantage of using constant temperature biological incubators is the radical optimization of microbial metabolism. By strictly maintaining a thermal range of 33-35°C, these systems accelerate the fermentation process from a traditional 2.5 weeks to approximately 55-60 hours while ensuring superior consistency.
Core Insight: While natural hives are subject to environmental fluctuations, biological incubators standardize the "perfect day" for fermentation. This precise thermal control maximizes the enzymatic activity of lactic acid bacteria, allowing producers to achieve weeks of biochemical progress in less than three days.
Optimizing Microbial Kinetics
Simulating the Ideal Hive Environment
In nature, bees struggle to maintain hive temperatures, leading to variable fermentation rates.
Biological incubators eliminate this variable by locking in the optimal range of 33-35°C. This mimics the conditions of a healthy, active beehive without the interference of external weather patterns or seasonal changes.
Accelerating Lactic Acid Bacteria Activity
Temperature is the throttle for microbial growth.
By holding the substrate at this precise thermal setpoint, the incubator keeps lactic acid bacteria operating at peak metabolic efficiency. This prevents the bacteria from entering dormancy or slowing down, which occurs when temperatures drop in a natural setting.
Compressing Production Timelines
The most tangible impact of this optimization is speed.
Natural fermentation is a slow process, typically requiring up to 2.5 weeks to reach maturity. In contrast, the incubator completes this cycle in 55 to 60 hours, vastly increasing production throughput.
Enhancing Bioavailability and Stability
Breaking Down Pollen Defenses
Speed does not come at the cost of efficacy; it actually enhances enzymatic reactions.
The controlled environment facilitates the breakdown of the tough outer shell of bee pollen. This releases encapsulated proteins and antioxidants that would otherwise remain inaccessible, significantly increasing the bioavailability of the final product.
Natural Preservation Mechanisms
The rapid, controlled fermentation generates antimicrobial byproducts efficiently.
Specifically, the process stimulates the production of antimicrobial fatty acids. These compounds act as natural preservatives, extending the shelf life of the bee bread and protecting it against oxidative spoilage during storage.
Seasonal Independence
Traditional production relies on the biological rhythm of the bees and the seasons.
Incubators decouple production from nature's calendar. This allows for high-efficiency processing even during off-seasons, ensuring a steady supply regardless of external environmental constraints.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Dependence on Parameter Precision
While efficient, this method relies entirely on equipment stability.
A failure in the thermostat or power supply can ruin a batch much faster than in traditional methods. Because the metabolic rate is accelerated, there is a smaller margin for error; a temperature spike could kill the bacteria, while a drop could stall the process unexpectedly.
Infrastructure Overhead
Moving from hive-based to incubator-based fermentation introduces capital costs.
Unlike the passive environment of a hive, incubators require energy consumption and maintenance. The efficiency gains must be weighed against the operational costs of running continuous thermal regulation equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology aligns with your production needs, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Scalability: The reduction of cycle time from weeks to hours is critical for high-volume commercial production.
- If your primary focus is Standardization: The incubator eliminates batch-to-batch variance caused by weather, ensuring a uniform nutritional profile every time.
- If your primary focus is Nutrient Absorption: The enhanced enzymatic breakdown makes this method superior for creating high-potency supplements.
Precision thermal control transforms bee bread fermentation from a passive biological occurrence into an active, scalable manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Natural Hive Fermentation | Biological Incubator Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | Subject to weather fluctuations | Precise (Locked at 33-35°C) |
| Processing Time | Approx. 2.5 weeks | 55 - 60 hours |
| Microbial Efficiency | Variable/Weather-dependent | Peak enzymatic activity |
| Bioavailability | Standard | Enhanced protein & antioxidant release |
| Production Scale | Seasonal/Limited | Year-round/Industrial capacity |
Scale Your Apiary Production with HONESTBEE
Transform your honey processing from a seasonal gamble into a high-efficiency manufacturing powerhouse. HONESTBEE provides commercial apiaries and distributors with the professional-grade machinery needed to dominate the market. From specialized biological incubators and hive-making machines to honey-filling systems and premium industry consumables, we offer the complete toolkit for modern beekeeping.
Ready to reduce your production cycles and boost nutrient bioavailability? Contact our technical team today to explore our wholesale equipment solutions and cultural merchandise.
References
- G. Madzgarashvili, J. Natchkebia. Making Bee Bread from Pollen without honeycombs. DOI: 10.30574/gscbps.2022.20.2.0316
This article is also based on technical information from HonestBee Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Portable Queen Bee Incubator with 12V Car Adapter for Safe Transport
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Professional Queen Catcher and Introduction Queen Cage
- Versatile Ratchet Hive Strap with S-Hooks for Secure Fastening
- Stainless Steel Jack Type Honey Comb Press Machine Wax and Honey Separator
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-precision constant temperature incubator? Optimize Queen Bee Artificial Insemination
- How do high-precision temperature-controlled incubation units assist in the breeding of queen bees? Master Bee Genetics
- Why are high-precision constant temperature and humidity incubators necessary? Secure Your Queen Bee Emergence
- Why is an industrial constant temperature and humidity incubator required for queen bee development? Ensure Vitality.
- Why is a constant temperature incubator necessary for queen bee rearing? Achieve Superior Queen Quality