At its core, a bottle seal is created when a capping machine applies a cap lined with a special material onto a container. This process then uses heat, electricity, or pressure to bond that liner to the rim of the bottle, creating a protective barrier that is either airtight, tamper-evident, or both.
The primary function of a modern bottle seal is not just to prevent leaks. It is a critical engineering system designed to guarantee product integrity by providing a hermetic seal for freshness and a visual guarantee of tamper-evidence for consumer safety.
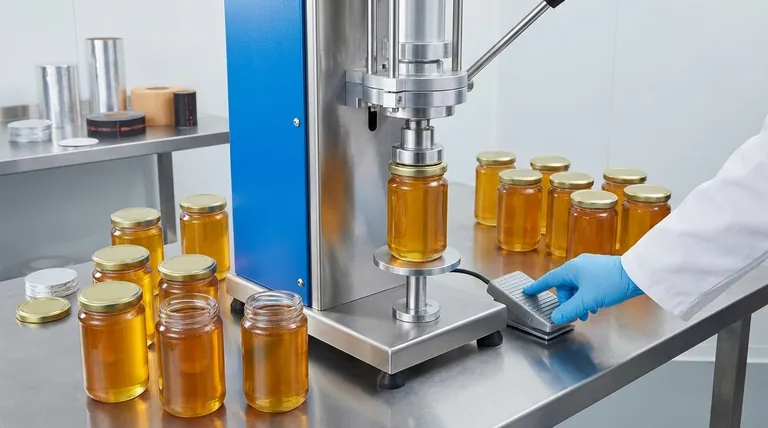

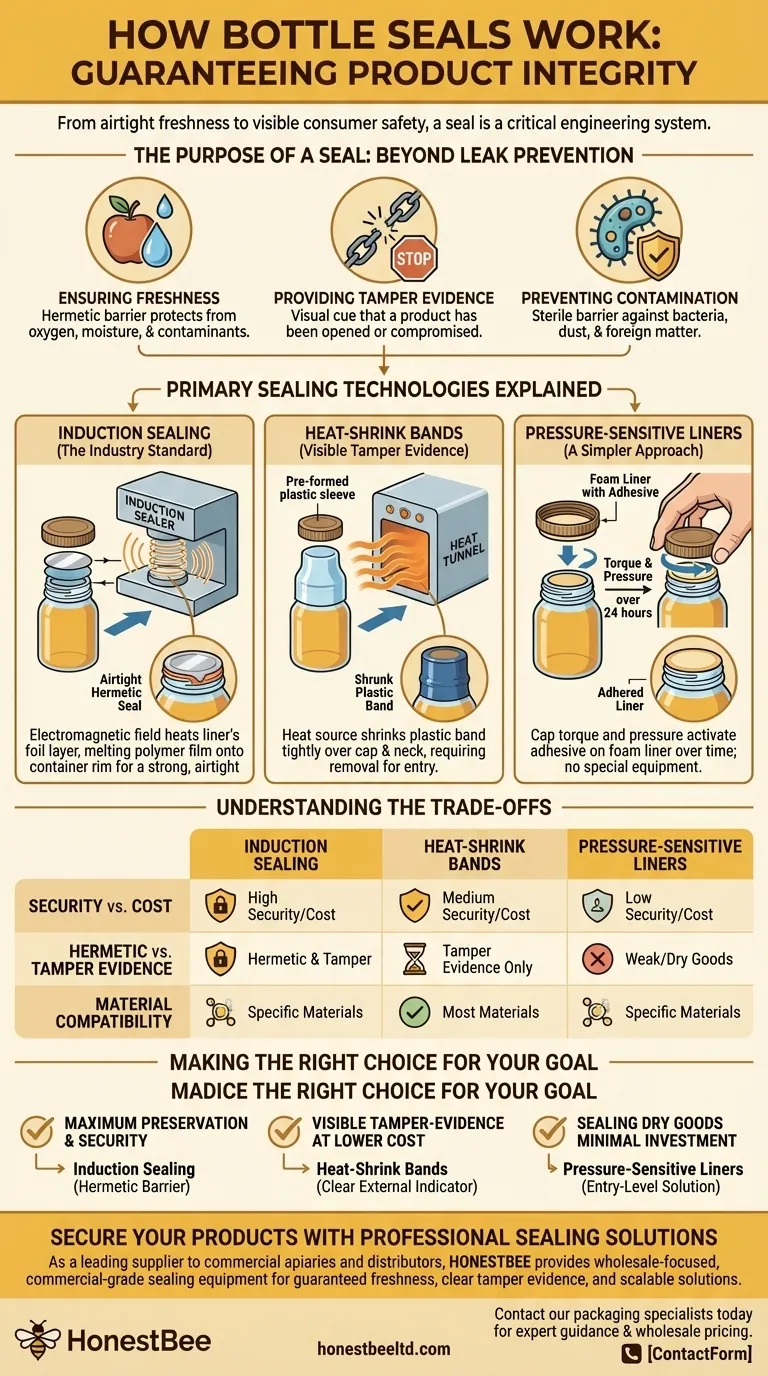
The Purpose of a Seal: Beyond Leak Prevention
A simple cap can stop a bottle from leaking, but a true seal serves several deeper, more critical functions in modern packaging.
Ensuring Product Freshness
Many seals are hermetic, meaning they are completely airtight. This barrier is crucial for protecting the contents from oxygen, moisture, and other environmental contaminants that degrade quality, alter taste, or spoil the product.
Providing Tamper Evidence
A broken seal is an unambiguous visual cue that a product has been opened or potentially compromised. This gives consumers confidence that the item they are purchasing is in the exact state it was in when it left the factory.
Preventing Contamination
For pharmaceuticals, foods, and beverages, the seal acts as a final sterile barrier. It ensures that no bacteria, dust, or other foreign matter can enter the container between the time of filling and the first use by the customer.
Primary Sealing Technologies Explained
While the end result looks simple, the technology used to create the seal is precise. The two most common methods are induction sealing and heat-shrink banding.
Induction Sealing: The Industry Standard
This is the most common method for creating a hermetic seal on plastic and glass bottles. The cap is manufactured with a multi-layered liner inside.
After the bottle is filled and the cap is screwed on, it passes under an induction sealer. This machine generates an electromagnetic field, which heats a foil layer within the liner.
This heat melts a polymer film on the bottom of the liner, causing it to fuse directly onto the rim of the container. The result is a strong, airtight seal that is independent of the cap itself.
Heat-Shrink Bands: Visible Tamper Evidence
This technology addresses tamper evidence directly and is what many people picture when they think of a "safety seal." It involves a pre-formed plastic sleeve or band.
The plastic band is placed over the capped bottle, covering both the cap and the neck of the container.
The bottle then passes through a heat tunnel or is exposed to another heat source. The heat causes the band to shrink tightly, conforming to the shape of the cap and neck. To open the bottle, this band must be torn or removed, providing clear evidence of entry.
Pressure-Sensitive Liners: A Simpler Approach
This method uses a foam liner coated with a special adhesive. The liner is placed inside the cap, and no special sealing equipment is needed.
When the cap is tightened onto the container, the torque and pressure activate the adhesive, causing the liner to stick to the bottle's rim over a period of about 24 hours. This method is simpler and cheaper but provides a less robust seal compared to induction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sealing technology is a balance of cost, security requirements, and the nature of the product being protected.
Security vs. Cost
Induction sealing provides the highest level of security, offering both a hermetic seal and tamper evidence. However, it requires a significant investment in specialized machinery.
Pressure-sensitive liners are the lowest-cost option, requiring no equipment beyond a standard capping machine, but they offer the weakest seal and are generally only suitable for dry products.
Hermetic Seal vs. Tamper Evidence
An induction seal excels at both. It creates a truly airtight barrier while also showing if it's been punctured.
A heat-shrink band, when used alone, provides excellent tamper evidence but does not create an airtight, hermetic seal on the bottle's opening. For this reason, it is often used in addition to an induction seal for maximum protection.
Material Compatibility
Not all seals work with all containers. The material of the liner must be chemically compatible with the bottle's material (e.g., PET, HDPE, glass) to create a successful and permanent bond. Mismatched materials will result in a failed seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right seal is a critical decision based on your product's specific needs for preservation and security.
- If your primary focus is product preservation and maximum security: Induction sealing is the definitive choice for creating a strong, hermetic barrier.
- If your primary focus is visible tamper-evidence at a lower cost: Heat-shrink bands provide a clear, external indicator that a product is unopened.
- If your primary focus is sealing dry goods with minimal equipment investment: Pressure-sensitive liners are a viable, entry-level solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct sealing technology is a foundational decision in protecting both your product and your customer.
Summary Table:
| Sealing Technology | Primary Function | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Sealing | Hermetic seal & tamper evidence | Maximum security & preservation | Requires specialized equipment |
| Heat-Shrink Bands | Tamper evidence | Visible consumer safety | Does not create an airtight seal |
| Pressure-Sensitive Liners | Basic seal for dry goods | Low-cost, minimal equipment | Weaker seal; not for liquids |
Secure Your Products with Professional Sealing Solutions
As a leading supplier to commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE understands that product integrity is non-negotiable. Whether you're packaging honey, supplements, or other sensitive products, the right sealing technology protects your brand reputation and ensures customer trust.
Our wholesale-focused operations provide commercial-grade sealing equipment and supplies that deliver:
- Guaranteed freshness with hermetic seals that prevent contamination
- Clear tamper evidence that builds consumer confidence
- Scalable solutions designed for high-volume production environments
Let us help you implement the perfect sealing system for your specific needs. Contact our packaging specialists today for expert guidance and competitive wholesale pricing on reliable sealing solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi-Automatic Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine by HONESTBEE
- HONESTBEE Professional Benchtop Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine Capper
- Semi Automatic Electric Bottle Capping Machine
- Automatic Inline Spindle Bottle Capping Machine for Honey Production
- Professional Water Cooled Induction Sealing Machine for Bottles and Containers
People Also Ask
- What types of caps can capping machines handle? Find the Right Solution for Your Bottling Line
- What is the role of a capping scratcher in the uncapping process? The Essential Tool for Maximum Honey Yield
- How does a bottle capping machine work? Unlock Efficient, Consistent Sealing for Your Production Line
- What is the purpose of bottle capping equipment and what types are available? Professional Sealing Solutions
- Which machine is used for sealing of bottles? Choose the Right Capper for Your Production Line



















