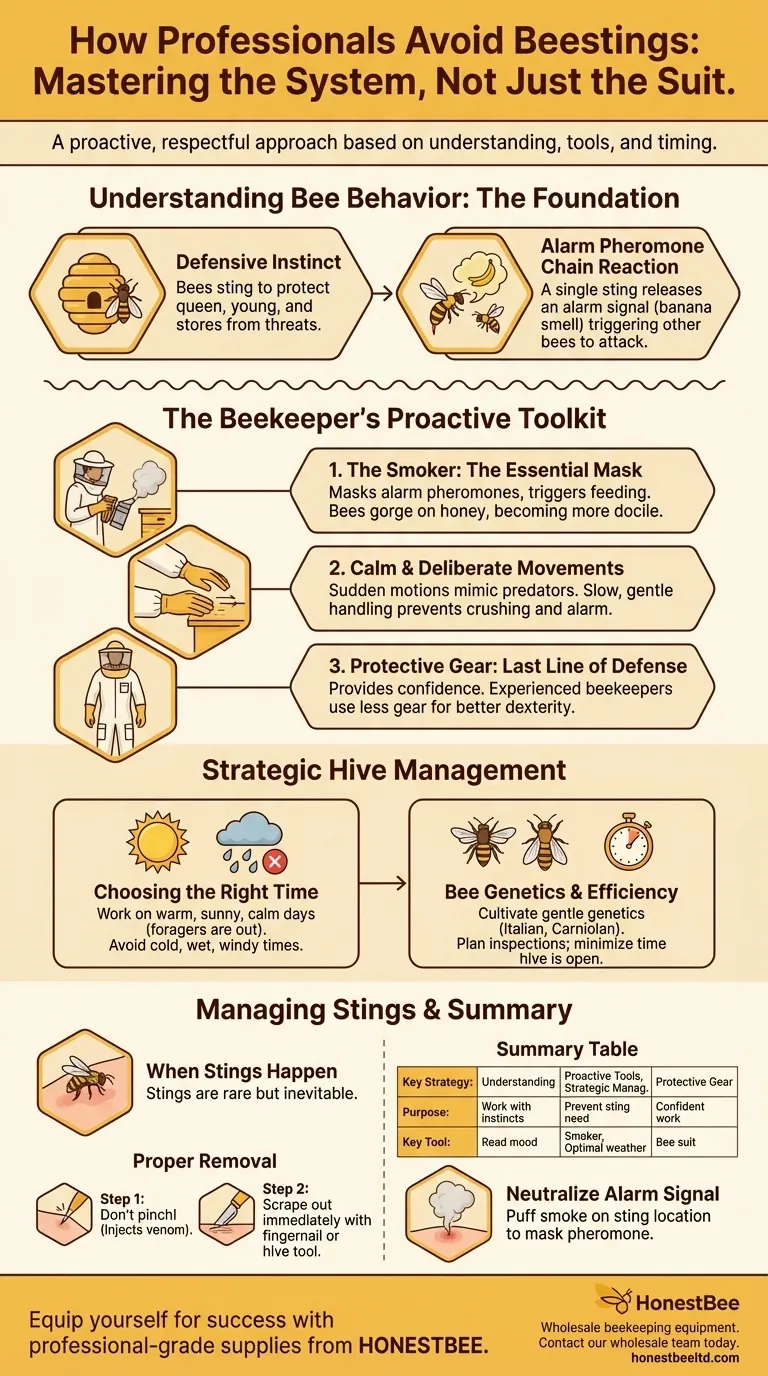
At its core, professional beekeeping is not about being immune to stings, but about mastering a system that makes them a rare event. Professionals avoid stings by understanding bee behavior, using specific tools to prevent alarm within the hive, and choosing the right time and manner for every interaction. It is a proactive and respectful approach, not a reactive one.
The professional beekeeper's primary goal is not to block stings, but to prevent the bees from ever feeling the need to sting in the first place. This is achieved by managing the hive’s defensive instincts through technique, timing, and tools.
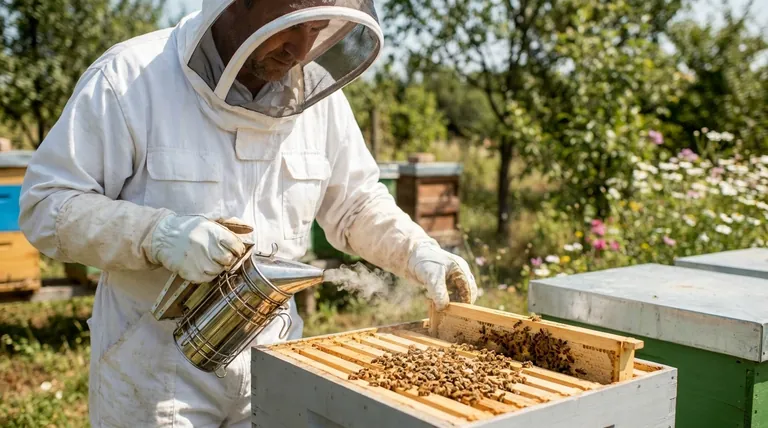

It Starts with Understanding Bee Behavior
The foundation of safe beekeeping is a deep respect for the colony's social structure and defensive triggers. A professional works with the bees' nature, not against it.
The Hive's Defensive Instinct
Bees are not inherently aggressive; they are defensive. They sting to protect their queen, their young, and their food stores (honey) from perceived threats. A beekeeper entering a hive is a massive disruption, and every action is interpreted by the bees as either benign or hostile.
Reading the Colony's Mood
Professionals learn to "listen" to the hive. A calm hive has a steady, low hum. An agitated hive will have a higher-pitched, louder buzz. Bees may also issue warning signs by bumping into your veil or flying directly at your face. These are signals to slow down or reassess your approach.
The Role of Alarm Pheromones
When a bee stings, it releases an alarm pheromone that smells like bananas. This chemical signal alerts other bees in the vicinity to the threat, inciting them to sting the same target. A single sting can quickly trigger a chain reaction, which is why preventing that first sting is paramount.
The Beekeeper's Proactive Toolkit
A beekeeper's most important tools are not their suit or gloves, but the techniques and equipment used to keep the bees calm.
The Smoker: The Most Important Tool
The smoker is not for driving bees away. Its primary functions are to mask the alarm pheromone and trigger a feeding response. The smoke scrambles the bees' ability to communicate danger, and it also encourages them to gorge on honey. A bee with a full stomach is less likely to be able to flex its abdomen to sting, making it more docile.
Calm and Deliberate Movements
Sudden, jerky movements mimic predators like bears or skunks. Professionals move slowly and deliberately when opening and inspecting a hive. Tools are never dropped, and frames are lifted and replaced with gentle, steady hands to avoid crushing bees, which also releases alarm pheromones.
Protective Gear: The Last Line of Defense
A bee suit, veil, and gloves provide critical protection, but professionals see them as the final line of defense, not the first. This gear provides the confidence to work calmly and deliberately. As beekeepers gain experience and confidence, they may opt for less gear, such as working without gloves to improve dexterity.
Strategic Hive Management
Where, when, and how a beekeeper works are just as important as the tools they use.
Choosing the Right Time to Work
Professionals meticulously choose their timing. They work hives on warm, sunny, and calm days. On these days, a large portion of the colony's foragers are out gathering nectar and pollen, meaning fewer bees are inside the hive to defend it. Conversely, they avoid inspections on cold, rainy, or windy days when the entire population is at home and more defensive. Hives are never opened at night.
The Importance of Bee Genetics
Not all honeybees are the same. Professional beekeepers often cultivate colonies with gentle genetics. Breeds like Italian or Carniolan bees are known for their docile temperament. If a hive is consistently aggressive, a professional will often replace its queen with one from a gentler genetic line.
Efficient and Purposeful Inspections
A professional beekeeper opens a hive with a plan. They know what they are looking for—signs of disease, the queen's laying pattern, honey stores—and they perform their tasks efficiently. Minimizing the time the hive is open reduces the stress on the colony and limits the opportunity for defensive behavior to escalate.
Understanding the Inevitable: Managing Stings
Even with perfect technique, stings are an occasional part of beekeeping. How a professional responds is key to preventing more.
Stings Still Happen
Every professional beekeeper gets stung. It may be due to a simple mistake, an unusually defensive hive, or just bad luck. The goal is to reduce the frequency from dozens per inspection to a handful per year.
The Correct Way to Remove a Stinger
When a honeybee stings, its barbed stinger and venom sac are left behind. Pinching the stinger to pull it out will inject the remaining venom. Instead, professionals scrape it out immediately with a fingernail or a hive tool. This action removes the stinger without squeezing the venom sac.
Neutralizing the Alarm Signal
After removing the stinger, a professional will often puff a small amount of smoke on the sting location. This helps mask the alarm pheromone that was released, calming the nearby bees and preventing them from joining the attack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting a professional mindset means shifting your focus from fear of stings to a deep understanding of the hive.
- If you are a new beekeeper: Your absolute priority should be mastering the smoker and always wearing full protective gear to build confidence.
- If you are an experienced hobbyist: Focus on refining your hive inspection efficiency and consider requeening aggressive colonies with gentler genetics.
- If you are simply curious: Understand that a beekeeper's calm demeanor and knowledge of bee behavior are their most powerful tools for preventing stings.
Ultimately, avoiding stings is the natural result of a respectful and knowledgeable partnership with the bees.
Summary Table:
| Key Strategy | Purpose | Key Tool/Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding Bee Behavior | Work with the colony's instincts, not against them. | Reading hive mood, avoiding alarm pheromones. |
| Using Proactive Tools | Prevent bees from feeling the need to sting. | Smoker (masks pheromones, triggers feeding). |
| Strategic Hive Management | Minimize disruption and defensive triggers. | Choosing optimal weather, using gentle bee genetics. |
| Proper Protective Gear | Last line of defense for confident, calm work. | Bee suit, veil, gloves (for dexterity and safety). |
Equip yourself for success with the right tools and knowledge.
Whether you manage a commercial apiary or supply beekeeping equipment, the right gear is foundational to safe and efficient beekeeping. HONESTBEE supplies professional-grade beekeeping supplies and equipment—including reliable smokers, protective suits, and hive tools—to commercial apiaries and distributors through our wholesale-focused operations.
Let's discuss how our equipment can support your operation's safety and productivity.
Contact our wholesale team today to learn more about our products and pricing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- European Stainless Steel Bee Smoker for Honey Bee Hive
- Heavy Duty Manual Bee Smoker Blower for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
- Electric Bee Smoker European Style Bee Hive Smoker for Beekeeping
- Economy Galvanized Beekeeping Honey Bee Smoker for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- Do gloves need to be worn with a bee suit? Essential Protection for Beekeepers
- What types of protective beekeeping equipment are recommended? Essential Gear for Maximum Sting Resistance
- How should propolis and wax stains be treated on beekeeping apparel? Expert Cleaning Tips for Lasting Gear
- What is the function of professional beekeeping protective gear in api-tourism? Secure Your Commercial Success
- What are the advantages of using a bee jacket? Maximize Comfort and Efficiency in the Apiary
- What is the typical lifespan of a bee suit? Essential Tips to Extend Your Protective Gear's Durability
- How does industrial-grade beekeeping protective equipment facilitate professional colony management? Boost Apiary Yields
- Why is white the predominant color in bee suit designs? | Key to Hive Calm & Beekeeper Safety



















