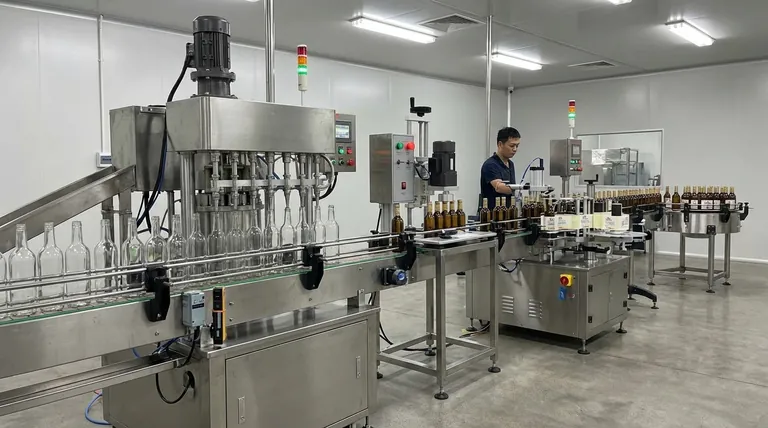
At its core, a bottle packing machine is an automated system that uses a conveyor to move containers through a sequence of stations. These stations perform specific tasks such as filling, capping, and labeling in a precise, repeatable manner. The entire process is orchestrated by sensors and controllers that ensure each step happens at the correct time.
A bottle packing machine isn't a single device, but rather a synchronized production line. The fundamental principle is to deconstruct the manual process of packaging into a series of simple, automated tasks executed with speed and precision.

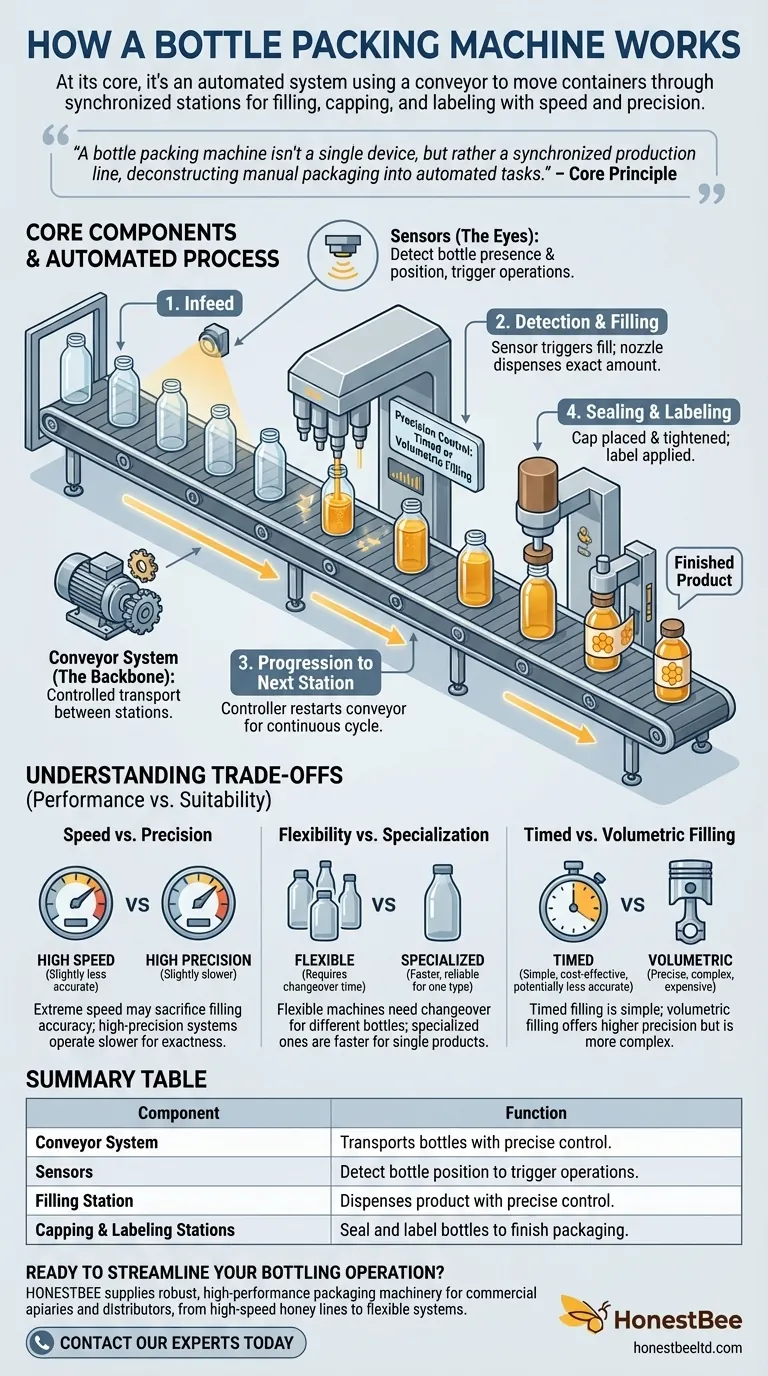
The Core Components of a Packing Line
To understand how the machine works, you must first understand its key components. Each part has a distinct role in moving the product from an empty container to a finished good ready for shipment.
The Conveyor System: The Backbone of the Line
The conveyor belt is the transport system for the entire line. It is driven by a motor that moves containers from one station to the next.
The speed and movement of the conveyor are not constant. They are controlled to start and stop precisely, ensuring bottles are perfectly positioned for each operation.
Sensors: The Eyes of the System
Sensors are the eyes and ears of the machine. They detect the presence and position of bottles on the conveyor.
When a sensor detects a bottle at a station, it sends a signal to the machine's controller. This signal is the trigger that stops the conveyor and initiates the station's specific task, such as filling or capping.
The Filling Station: Precision and Control
The filling station is where the product is dispensed into the bottle. It consists of one or more filling nozzles connected to a product reservoir.
When a bottle is in position, a precise shut-off valve opens to fill the container. The amount of product dispensed is controlled either by time (the valve stays open for a set number of seconds) or by volume (a meter measures the exact amount).
Capping and Labeling: The Final Steps
After filling, the conveyor moves the bottle to the capping station. Here, a cap is automatically placed and tightened, sealing the product.
Finally, the labeling station applies a product label. This completes the packaging process, and the finished bottle exits the line.
The Automated Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The magic of a bottle packing machine lies in the seamless coordination of its components. The process follows a logical, linear sequence.
Step 1: Infeed and Positioning
Empty bottles are loaded onto the conveyor system at the beginning of the line, a process known as infeed. The conveyor then transports them toward the first active station.
Step 2: Detection and Filling
As a bottle arrives at the filling station, a sensor detects its presence and signals the controller to stop the conveyor. The filling nozzle descends or activates, dispensing the product into the bottle. Once filling is complete, the valve closes.
Step 3: Progression to the Next Station
The controller signals the conveyor motor to restart, moving the newly filled bottle away from the filling station. Simultaneously, this brings the next empty bottle into position, allowing the cycle to repeat continuously.
Step 4: Sealing and Labeling
The filled bottle continues down the line to the capping and labeling stations, where it is sealed and branded. It then exits the machine as a finished product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, these machines are not one-size-fits-all. The design of any packing line involves critical trade-offs that impact its performance and suitability for a given task.
Speed vs. Precision
Extremely high-speed lines may sacrifice a small degree of filling accuracy. Conversely, systems designed for high-precision filling, especially for high-value products, may operate at a slightly slower pace to guarantee accuracy.
Flexibility vs. Specialization
A machine built for a single bottle and product type will be exceptionally fast and reliable. A more flexible machine that can handle various bottle sizes and shapes will require "changeover" time to adjust guides, nozzles, and other components, reducing overall throughput.
Timed Filling vs. Volumetric Filling
Timed filling, where a valve opens for a set duration, is simple, robust, and cost-effective. However, it can be less accurate if the product's flow rate changes. Volumetric filling, which uses a piston or flowmeter, is far more precise but also more complex and expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Understanding the mechanics of a bottle packing machine allows you to select a system that aligns directly with your production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a single product: Prioritize a specialized, high-speed line with minimal changeover requirements and robust, simple controls.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for small batches: Look for a machine designed for quick changeovers with adjustable guides and easily swappable parts.
- If your primary focus is product value and fill accuracy: Invest in a system with volumetric or level-sensing fillers over simpler, time-based mechanisms.
By breaking down the system into its core principles, you can make an informed decision that enhances your operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Conveyor System | Transports bottles between stations with precise control. |
| Sensors | Detect bottle position to trigger machine operations. |
| Filling Station | Dispenses product into bottles with precise volume or time control. |
| Capping & Labeling Stations | Seal bottles and apply labels to finish the packaging process. |
Ready to streamline your bottling operation?
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with robust, high-performance packaging machinery. Whether you need a high-speed line for honey production or a flexible system for various product sizes, our wholesale-focused solutions are designed to maximize your throughput and accuracy.
Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal bottle packing machine for your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Electric Bottle Capping Machine
- Semi Automatic Round Bottle Labeling Machine
- Automatic In-Line Flat Surface Labeling Machine
- HONESTBEE Professional Benchtop Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine Capper
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
People Also Ask
- How does the feeding system work in automated honey filling machines? A Guide to Viscosity & Volume
- What are the application advantages of honey filling machines? Elevate Precision and Hygiene in Your Production Chain
- What role do automatic honey-filling machines play? Enhancing Honey Purity and Commercial Sustainability
- How can Arrhenius model parameters improve honey filling? Optimize Precision in Industrial Honey Machinery
- How does an Automatic Viscous Liquid Filling Machine function? Master High-Speed Precision for Honey Production
- What causes jamming or blockage of film in honey stick machines? Prevent Costly Downtime
- What are equipment used for filling? Match Your Product to the Perfect Filling Machine
- What are the benefits of utilizing professional honey filling machines? Scale Your Production with Precision



















