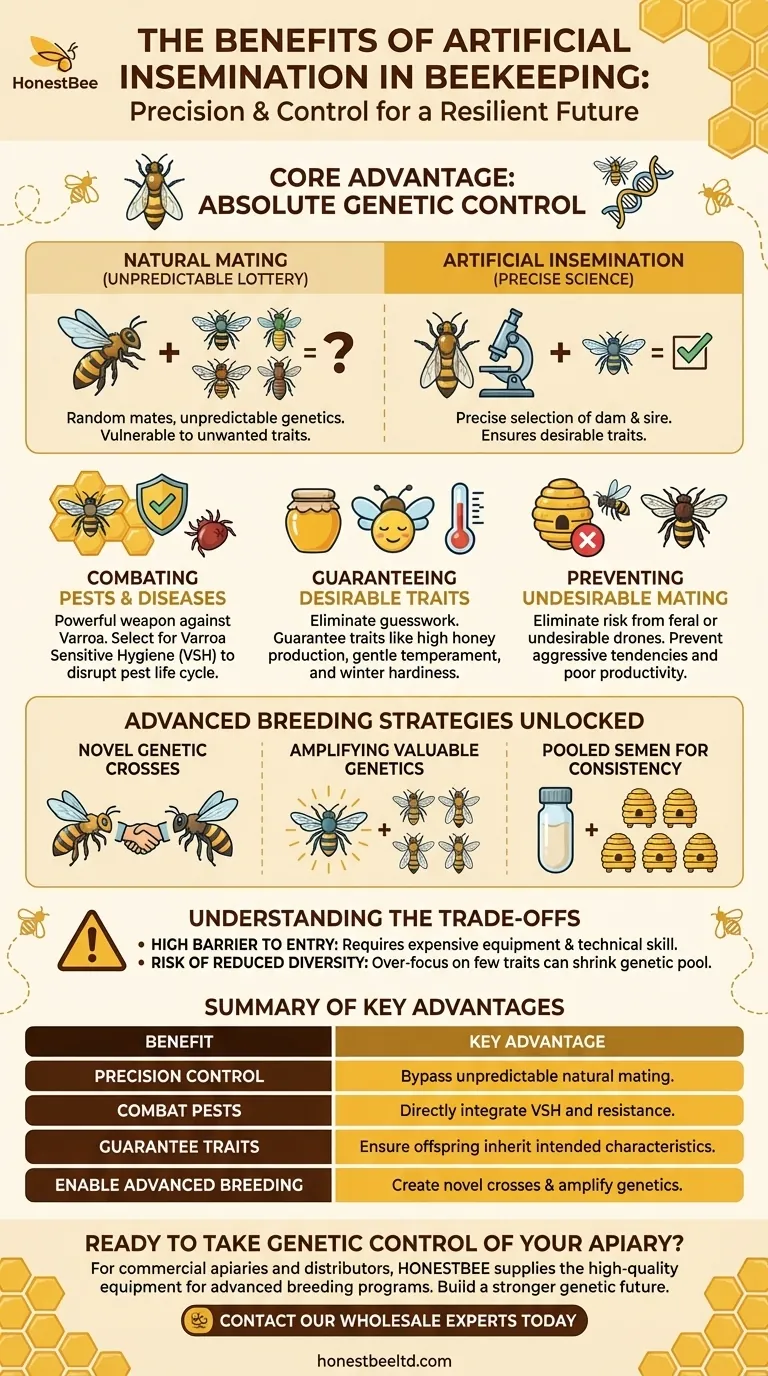
At its core, artificial insemination (AI) in beekeeping grants the beekeeper absolute control over honey bee genetics. This technique allows for the precise selection of both the queen (dam) and the drones (sires), ensuring that desirable traits like disease resistance and productivity are passed to the next generation while preventing random, unwanted mating.
The true value of artificial insemination is not merely breeding a "better bee," but gaining a strategic tool to combat systemic threats like pests and diseases. It transforms hive management from a reactive process into a proactive, long-term genetic improvement program.

The Core Advantage: Precision Genetic Control
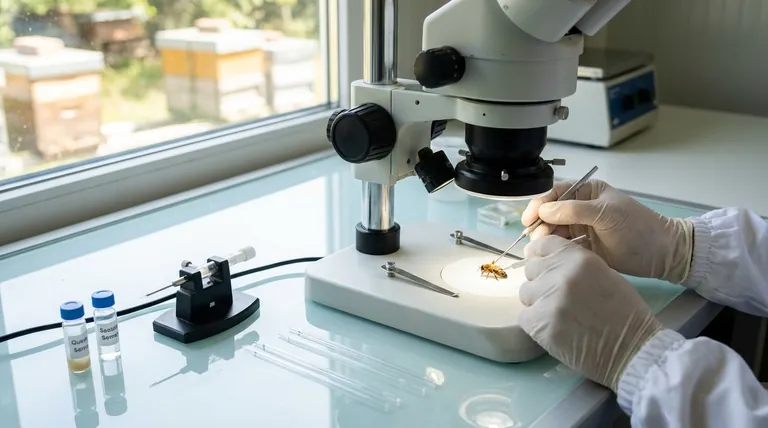
Artificial insemination bypasses the chaotic and unpredictable nature of a queen's natural mating flight. During a natural flight, a queen mates with 10-20 different drones from various colonies in a "drone congregation area," making the genetic outcome a lottery. AI turns this lottery into a precise science.
Combating Pests and Diseases
The Varroa destructor mite is the single greatest threat to honey bee colonies worldwide. AI is a powerful weapon in this fight.
By using AI, breeders can specifically select drones from colonies that exhibit Varroa Sensitive Hygiene (VSH). This behavioral trait causes bees to detect and remove mite-infested pupae, disrupting the pest's life cycle and creating a naturally resilient colony.
Guaranteeing Desirable Traits
Every beekeeper has a different goal. Some prioritize honey production, others seek gentle temperament for easier hive inspections, and some need bees that overwinter well in harsh climates.
AI ensures the queen is inseminated only with sperm from drones that carry these specific genetic markers. This removes the guesswork and guarantees the resulting offspring will inherit the intended characteristics.
Preventing Undesirable Mating
Natural mating leaves the queen vulnerable to mating with drones from feral colonies or less desirable apiaries. This can introduce aggressive tendencies, poor productivity, or a low tolerance for disease into your apiary.
Instrumental insemination takes place in a controlled lab environment, completely eliminating the risk of a queen mating with drones of unknown or undesirable genetic origin.
Advanced Breeding Strategies Unlocked by AI
Beyond simple trait selection, AI enables sophisticated breeding programs that are impossible to achieve through natural mating.
Creating Novel Genetic Crosses
AI allows breeders to cross bee subspecies or lines from different continents that would never meet in nature. This expands the genetic toolkit available for developing new, robust stocks of bees.
Amplifying Valuable Genetics
If a single drone displays exceptionally valuable traits, his genetics can be maximized. His semen can be collected and used to inseminate multiple queens, rapidly propagating his superior genes throughout a large number of colonies.
Ensuring Consistency with Pooled Semen
For large-scale queen producers, consistency is key. AI allows for the semen of hundreds or even thousands of desirable drones to be collected, mixed, and homogenized.
Inseminating a batch of queens with this pooled semen creates a consistent and genetically diverse baseline, ensuring uniform performance across all the new colonies they produce.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, artificial insemination is not a universal solution. It requires a clear understanding of its limitations and significant investment.
The High Barrier to Entry
The procedure requires expensive, specialized equipment, including a stereomicroscope, insemination device, and tools for handling queens and drones.
Furthermore, it is a highly technical skill that demands significant training, practice, and a very steady hand. It is not a technique for a casual or beginner beekeeper.
Risk of Reduced Genetic Diversity
If breeding programs become too focused on a handful of traits, the overall genetic diversity of the population can shrink. This "genetic bottleneck" can inadvertently make the population more vulnerable to a new disease or environmental stressor that wasn't part of the initial selection criteria.
Is Artificial Insemination Right for Your Operation?
The decision to use AI depends entirely on your goals, scale, and resources.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial breeding or research: AI is an indispensable tool for developing and maintaining superior genetic lines with verifiable consistency.
- If your primary focus is combating specific, persistent threats like Varroa mites: AI allows you to rapidly integrate critical resistance traits like VSH into your apiary's gene pool.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist or small-scale beekeeping: The high costs and technical skill required likely outweigh the benefits compared to simply purchasing instrumentally inseminated queens from a reputable breeder.
Ultimately, artificial insemination provides a level of strategic control that can safeguard the future health and productivity of honey bee populations.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Precision Genetic Control | Bypass unpredictable natural mating; select for specific traits like disease resistance and honey production. |
| Combat Pests & Diseases | Directly integrate Varroa Sensitive Hygiene (VSH) and other resistance traits into your breeding stock. |
| Guarantee Desirable Traits | Ensure offspring inherit intended characteristics like gentle temperament or winter hardiness. |
| Enable Advanced Breeding | Create novel genetic crosses and amplify valuable genetics from a single superior drone. |
Ready to take genetic control of your apiary?
For commercial apiaries and distributors, the strategic use of artificial insemination is key to building resilient, productive, and profitable operations. HONESTBEE supplies the high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment necessary to support advanced breeding programs.
Let us help you build a stronger genetic future. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your equipment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Plastic Chinese Queen Grafting Tool for Bee Queen Rearing
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
People Also Ask
- How should beekeepers handle bees when using a hive tool? Master Calm, Deliberate Techniques
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- What are the primary functions of a stainless steel hive tool? Essential Equipment for Professional Beekeeping
- Why is it important to compare the progress of different hives? A Beekeeper's Key Diagnostic Tool
- What is the hole in a hive tool for? A Multi-Tool for Apiary Repairs and Maintenance



















