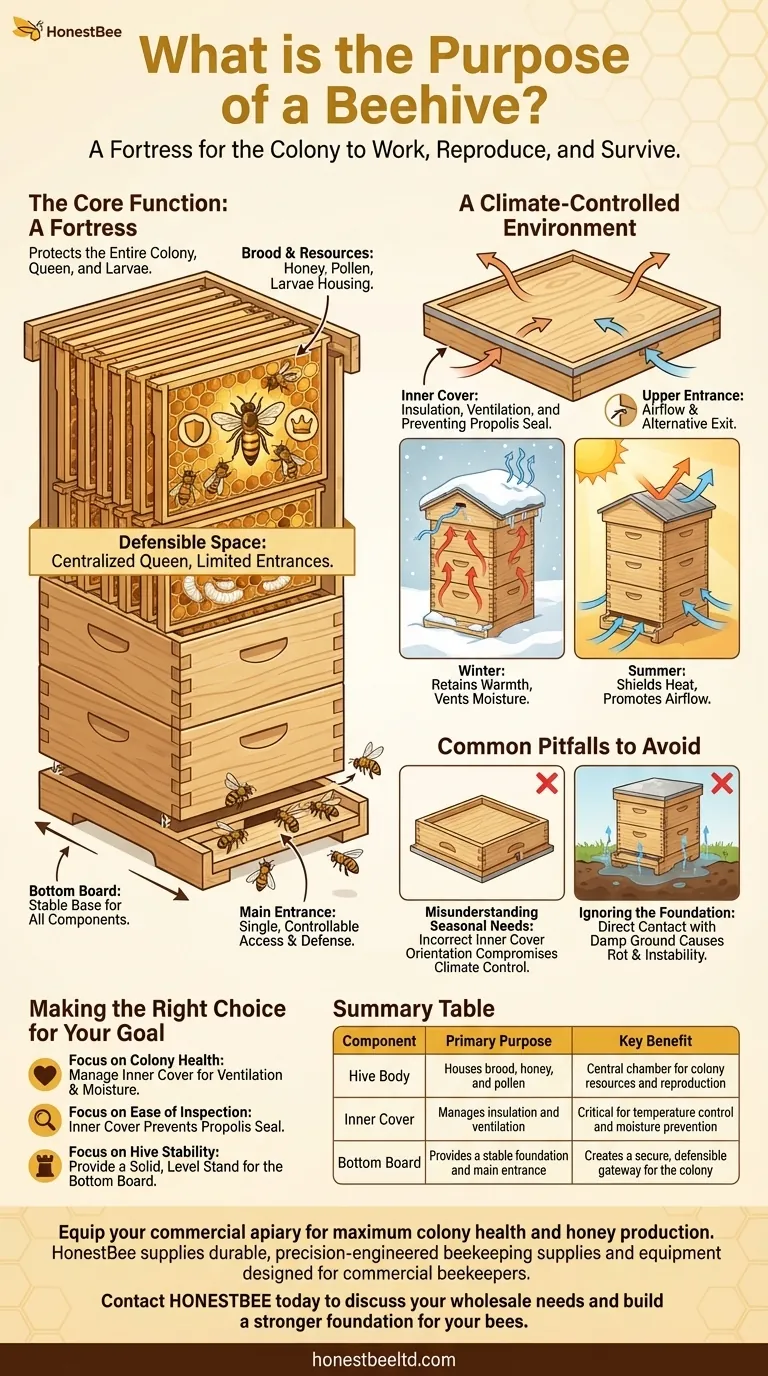
At its core, a beehive serves one primary function: to act as a home that protects the entire bee colony, its single queen, and its developing young, known as larvae. It is a structure designed to be a defensible fortress that enables the colony to work, reproduce, and survive through changing seasons.
While the surface purpose of a beehive is to provide shelter, its true function is best understood as an integrated system. Each component is specifically engineered to manage ventilation, temperature, access, and defense, creating a stable environment for the colony to thrive.

The Core Function: A Fortress for the Colony
A beehive's design is entirely centered on providing a safe, controlled space where the colony can efficiently manage its resources and raise the next generation of bees.
Housing the Brood and Resources
The main hive body is the central chamber of the operation. This is where the bees build out their wax combs on frames, creating a complex of hexagonal cells to store honey, pollen, and to house the developing larvae.
Defending the Queen and Larvae
The entire structure is a defensible space. By centralizing the queen and brood deep within the hive, the colony can focus its defensive efforts on a limited number of entrances, protecting its most valuable assets from predators and the elements.
A Climate-Controlled Environment
A successful colony depends on maintaining a stable internal environment. Key components of the hive are dedicated entirely to managing temperature, humidity, and airflow.
The Crucial Role of the Inner Cover
The inner cover is a thin board that sits directly on top of the uppermost box, just beneath the main roof. It is a multi-purpose tool vital for climate control.
It provides a dead air space for insulation, shielding the colony from the direct heat of the sun in summer and helping retain warmth in the winter.
Crucially, it also prevents the bees from gluing the main outer cover to the hive body with propolis (a resinous bee glue), which would make inspections nearly impossible.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
The inner cover is essential for managing moisture. In winter, warm, moisture-laden air from the bees' respiration rises. The inner cover helps this moisture vent properly, preventing it from condensing and dripping back down onto the bees, which can be fatal in cold weather.
Many inner covers also feature a small notch, providing an upper entrance or exit. This helps with airflow and gives bees an alternative path if the main entrance is blocked by snow or debris.
The Foundation and Gateway
Like any well-built structure, a beehive relies on a solid base to function correctly. This is the role of the bottom board.
Providing a Stable Base
The bottom board is the floor of the hive. It provides a solid foundation for all the other components that are stacked on top of it, ensuring the entire structure is stable.
Creating the Main Entrance
When the first hive body is placed on the bottom board, a gap is created that serves as the primary entrance and exit for the colony. This single, controllable opening is where foragers come and go and where guard bees are stationed to defend the hive.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the purpose of individual parts is critical, as incorrect assembly can undermine the hive's entire function and harm the colony.
Misunderstanding Seasonal Needs
The inner cover often has two sides: a "winter" side with a deeper recess and a "summer" side. Using the wrong side can compromise the hive's insulation and ventilation, leading to overheating in summer or excessive moisture in winter.
Ignoring the Hive's Foundation
Placing a hive directly on damp ground will cause the wooden bottom board to rot and destabilize the entire structure. A hive should always be placed on a firm, level stand to ensure its longevity and provide a clear, defensible entrance for the bees.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the purpose of each component is the key to effective beekeeping and supporting a healthy, productive colony.
- If your primary focus is colony health: Ensure the inner cover is correctly positioned for the season to manage ventilation and moisture effectively.
- If your primary focus is ease of inspection: Recognize that the inner cover is designed to prevent bees from sealing the top shut, making hive access predictable and less disruptive.
- If your primary focus is hive stability: Provide a solid, level stand for the bottom board to create a sound structure and a secure entrance.
By understanding how each component serves the colony's needs, you can better manage and support the complex life of the hive.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hive Body | Houses brood, honey, and pollen | Central chamber for colony resources and reproduction |
| Inner Cover | Manages insulation and ventilation | Critical for temperature control and moisture prevention |
| Bottom Board | Provides a stable foundation and main entrance | Creates a secure, defensible gateway for the colony |
Equip your commercial apiary for maximum colony health and honey production. A properly functioning beehive is the foundation of a successful operation. HONESTBEE supplies durable, precision-engineered beekeeping supplies and equipment designed for the demands of commercial beekeepers and distributors. From hive bodies to inner covers, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable equipment you need to support thriving colonies. Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and build a stronger foundation for your bees.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Professional Engraved Round Hive Number Tags for Beekeeping
- Assembled Wooden Bee Frames with Beeswax Foundation Ready to Use by HONESTBEE
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What are the technical and maintenance characteristics of the Top Bar Hive in commercial beekeeping? Key Insights
- What is a horizontal top bar hive? Discover Natural and Ergonomic Beekeeping Benefits
- What are the ergonomic and management advantages of Horizontal Top-Bar Hives? Modern Beekeeping with Less Strain
- How does the top bar hive help control varroa mites? A Natural Approach to Mite Management
- How does the design of a top bar hive benefit beekeepers? Ergonomic & Natural Beekeeping for Hobbyists



















