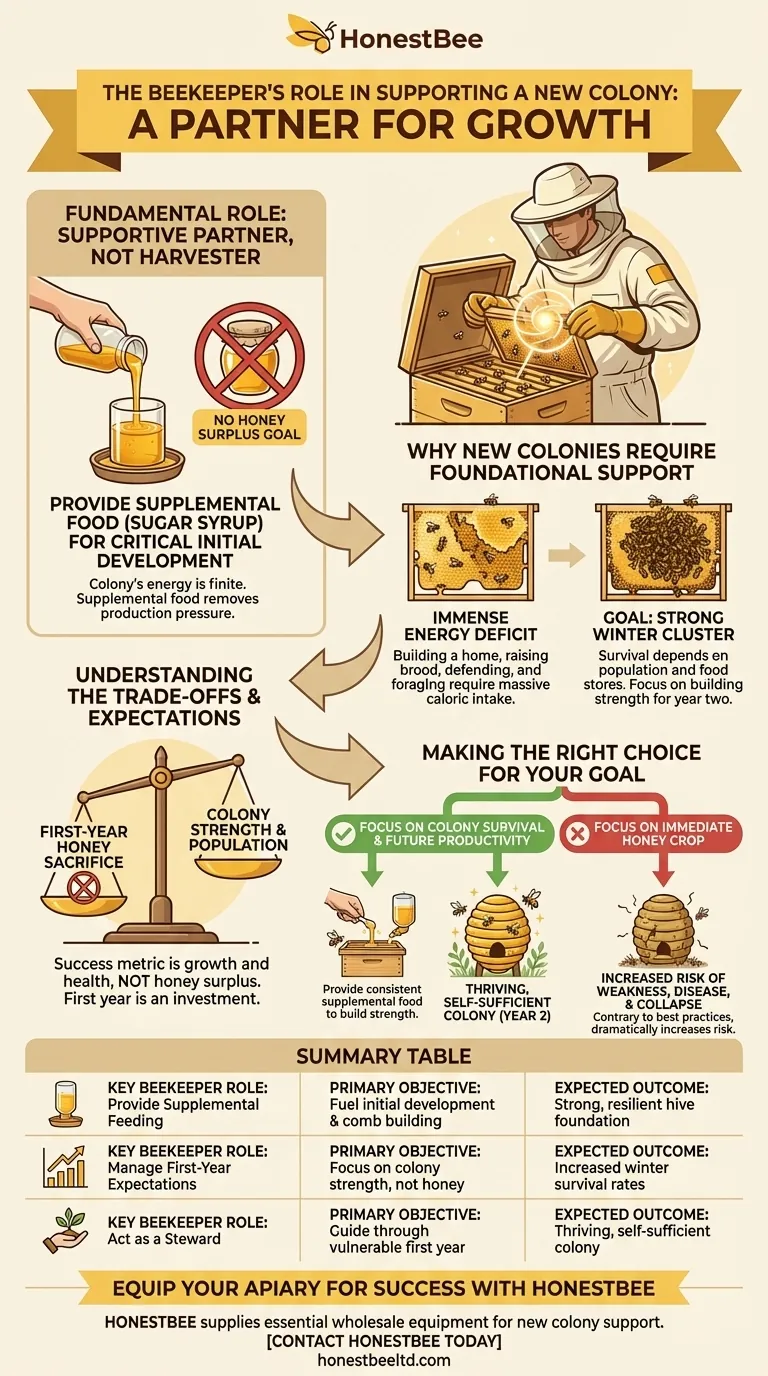
The fundamental role of a beekeeper for a new colony is not that of a harvester, but of a supportive partner. Your primary responsibility is to ensure the colony has an abundant and consistent food source, typically sugar syrup, to fuel its critical initial development.
A new colony's energy is a finite resource. By providing supplemental food, the beekeeper removes the pressure of producing a honey surplus, allowing the bees to invest everything into building a strong, resilient foundation for long-term survival and future productivity.
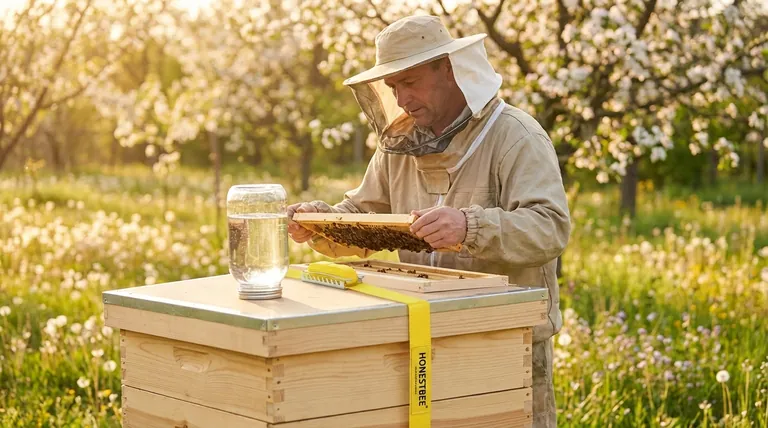

Why New Colonies Require Foundational Support
A new bee colony, whether from a package or a nucleus hive, is starting from behind. It faces an immense energy deficit that it must overcome to survive its first year, especially the first winter.
The Energetic Cost of Establishment
Building a new home is incredibly demanding. The bees must produce wax, draw out comb cell by cell, raise a new generation of brood (young bees), and defend the hive, all while foraging for nectar and pollen.
This initial construction and population growth requires a massive caloric intake.
Removing the Pressure of Production
In an established hive, bees can rely on existing comb and large honey stores. A new colony has neither.
By providing sugar syrup, you give them a readily available energy source. This allows them to focus their efforts on building the internal structure and population of the hive, rather than dedicating the majority of their foragers to a desperate search for nectar.
The Goal: A Strong Winter Cluster
A colony's ability to survive winter depends entirely on its population size and its food stores.
A well-fed colony will build its population faster and be better prepared for the cold months. The goal in the first year is not a honey crop for you, but a strong, healthy colony that can thrive in year two.
Understanding the Trade-offs
This supportive approach is an investment in the colony's future, but it requires patience and a shift in expectations from the beekeeper.
The First-Year Honey Sacrifice
The most significant trade-off is forgoing a honey harvest in the first year. Any surplus honey the colony produces should be considered their own vital winter food.
Taking honey from a first-year colony severely jeopardizes its chances of survival.
Focusing on Strength, Not Surplus
Your success metric for the first year should be the colony's growth, health, and population size—not the amount of honey in the supers.
A strong colony entering winter is the true harvest of your first season. It sets the stage for significant honey production in subsequent years.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your management strategy for a new colony should be directly aligned with the goal of ensuring its long-term viability.
- If your primary focus is colony survival and future productivity: Provide consistent supplemental food, like sugar syrup, throughout the first year to help the bees build strength and prepare for winter.
- If your primary focus is an immediate honey crop: You must understand that this is contrary to best practices for a new colony and dramatically increases the risk of weakness, disease, and colony collapse.
Ultimately, your role is to be a steward, guiding the colony through its vulnerable first year to become a thriving, self-sufficient force of nature.
Summary Table:
| Key Beekeeper Role | Primary Objective | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Provide Supplemental Feeding | Fuel colony's initial development and comb building | Strong, resilient hive foundation |
| Manage First-Year Expectations | Focus on colony strength, not honey surplus | Increased winter survival rates |
| Act as a Steward | Guide the colony through its vulnerable first year | Thriving, self-sufficient colony in year two |
Equip your apiary for new colony success with HONESTBEE.
As a commercial apiary or beekeeping equipment distributor, your success depends on strong, thriving colonies. HONESTBEE supplies the essential beekeeping supplies and equipment—from feeders and hive components to protective gear—needed to properly support new colonies through their critical first year.
Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable, high-quality equipment required to build resilient foundations for long-term productivity. Let us help you become the supportive partner your bees need.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale supply needs and set your new colonies up for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
- Professional Engraved Round Hive Number Tags for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of using cam buckle straps? Secure Your Load Fast with Simple, Safe Tensioning
- What is the best length for straps used around beehives? Why 12 Feet is the Industry Standard
- What are the two styles of hive straps? Choose the Right Strap for Your Hive Security
- What are hive straps and why are they used? Secure Your Hives Against Wind, Predators, and Transport
- How can a beehive be physically secured against harsh winter weather? Expert Winterizing Strategies for Your Apiary



















