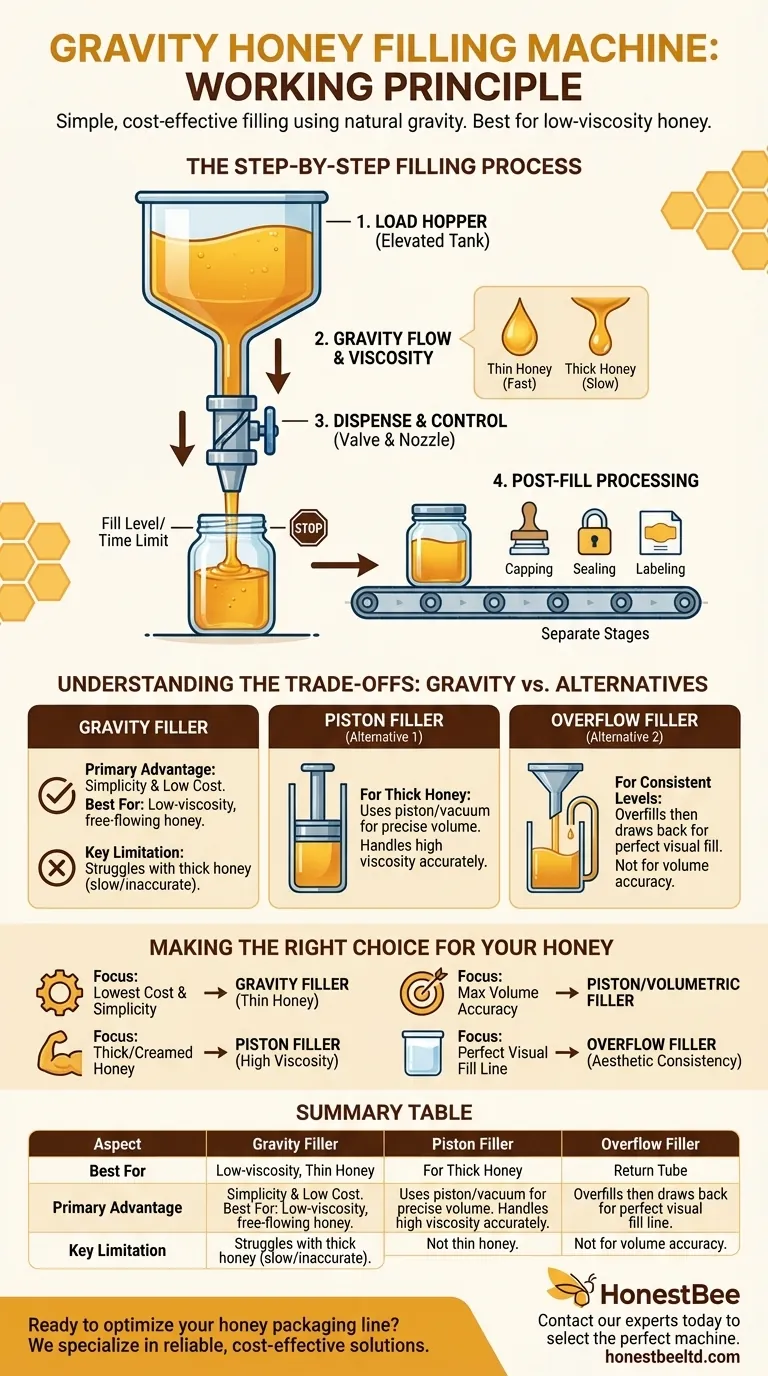
At its core, a gravity honey filling machine operates on the simple principle of using Earth's gravity to do the work. Honey is placed in an elevated tank or hopper, and it flows downward through a valve and into a nozzle to fill containers positioned below. The flow is controlled by a simple valve that opens to start the fill and closes once the container reaches the desired amount.
While gravity fillers offer unmatched simplicity and cost-effectiveness, their reliance on natural flow makes them best suited for thin, low-viscosity honey. The key decision is balancing this simplicity against the need to handle thicker products or achieve higher levels of precision.
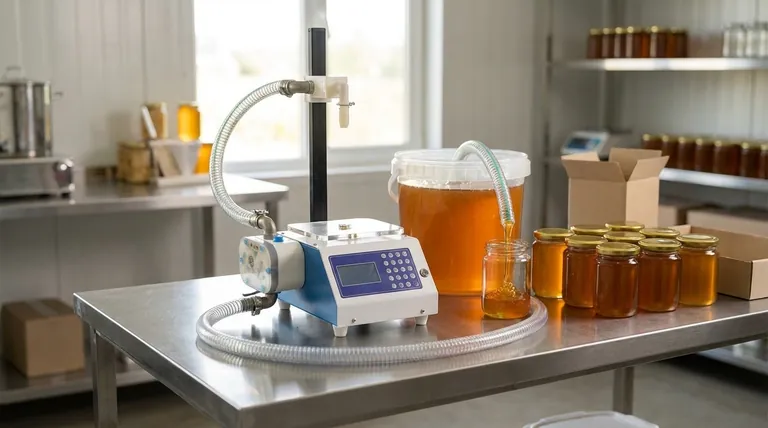

The Step-by-Step Filling Process
To understand a gravity filler, it's best to break its operation down into a few key stages. Each step is elegantly simple, relying on physics rather than complex machinery.
1. Loading the Hopper
The process begins by loading honey into a hopper or tank located at the highest point of the machine. This elevation is critical, as it creates the potential energy needed for gravity to initiate the flow.
2. The Role of Gravity and Viscosity
Once the valve is opened, gravity pulls the honey down towards the filling nozzle. The speed and consistency of this flow are directly influenced by the honey's viscosity (its thickness). Thinner, more liquid honey flows quickly and easily, while thicker honey will flow much more slowly.
3. Dispensing and Control
A valve acts as the gatekeeper between the hopper and the nozzle. When a container is in position, the valve opens, allowing honey to flow in. The system stops the flow once a predetermined limit—often based on fill time or level—is reached.
4. Post-Fill Processing
Once the container is filled, it moves on to subsequent stages like capping, sealing, and labeling. These are essential parts of the overall packaging line but are separate from the gravity filling principle itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gravity vs. Other Fillers
A gravity filler is not the right choice for every situation. Its effectiveness is defined by its limitations, which become clear when compared to other common filling technologies.
The Primary Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The main benefit of a gravity filler is its mechanical simplicity. With fewer moving parts than other systems, it is generally less expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain. This makes it an excellent entry-level choice for small-scale producers.
The Key Limitation: Honey Viscosity
Gravity fillers struggle with high-viscosity (thick) or creamed honey. The passive force of gravity may not be strong enough to produce a consistent or timely flow, leading to slow production rates and inaccurate fills.
Alternative 1: Piston Fillers for Thick Honey
A piston filler uses a cylinder and piston to create a vacuum, actively drawing a precise volume of honey from the hopper and then forcefully dispensing it into the container. This mechanism is ideal for thick products that won't flow easily on their own.
Alternative 2: Overflow Fillers for Consistent Levels
An overflow filler is designed to fill every container to the exact same visual level, regardless of minor volume variations in the containers. It overfills the container slightly, and the excess honey is drawn back to the hopper, ensuring a perfect cosmetic appearance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Honey
The best machine depends entirely on your product and operational goals. Use these points as a guide for your decision.
- If your primary focus is lowest cost and simplicity: Choose a gravity filler, especially if you work with free-flowing, low-viscosity honey.
- If your primary focus is handling thick or creamed honey: A piston filler is the superior choice, as its mechanism can actively move high-viscosity products accurately.
- If your primary focus is maximum filling accuracy by volume: Invest in a piston or volumetric filler that offers more precise control over the dispensed amount.
- If your primary focus is a perfect visual fill line: Consider an overflow filler, especially if you use clear containers where aesthetic consistency is crucial.
By understanding the fundamental principle of gravity and its limitations, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Gravity Filler | Piston Filler | Overflow Filler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Low-viscosity, free-flowing honey | Thick, creamed honey | Perfect visual fill level |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity & low cost | Handles high viscosity | Consistent cosmetic appearance |
| Key Limitation | Struggles with thick honey | Higher cost & complexity | Not for volume accuracy |
Ready to optimize your honey packaging line?
As HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying the right beekeeping equipment for commercial apiaries and distributors. Whether a simple gravity filler meets your needs or a more advanced piston system is required for thicker honey, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get reliable, cost-effective solutions.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific honey viscosity and production goals. Let us help you select the perfect filling machine to boost your efficiency and profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Economy Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Bottle Filler Packaging Machine
- Small Honey Filling Machine Sachet Packing Equipment Single Nozzle
- Commercial Rotary Honey Filling Machine for Production
- Precision Automated Packaging Turntable Honey Spoon Filling Sealing Packing Machine
- Double Wall Honey Heating Stirring Homogenizer Mixing Machine with Various Capacity
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of industrial filling equipment? Maximize Honey Profitability and Market Access
- What defines a Semi-automated honey filling machine? Precision and Efficiency for Scaling Apiaries
- Why is sachet packaging frequently utilized for honey distribution in institutional nutrition programs? Key Benefits
- How do large honey storage tanks and gravity fall filling systems improve honey packaging efficiency and safety?
- What are the advantages of automatic honey-filling machines? Scale Your Production with Industrial Precision
- What is the volumetric filling method? Achieve Precise, Consistent Product Dosing
- What is the purpose of using precision viscometers in honey filling design? Optimize Flow & Preserve Honey Quality
- How do professional processing equipment and industrial honey-filling machines improve the value of honey products?



















