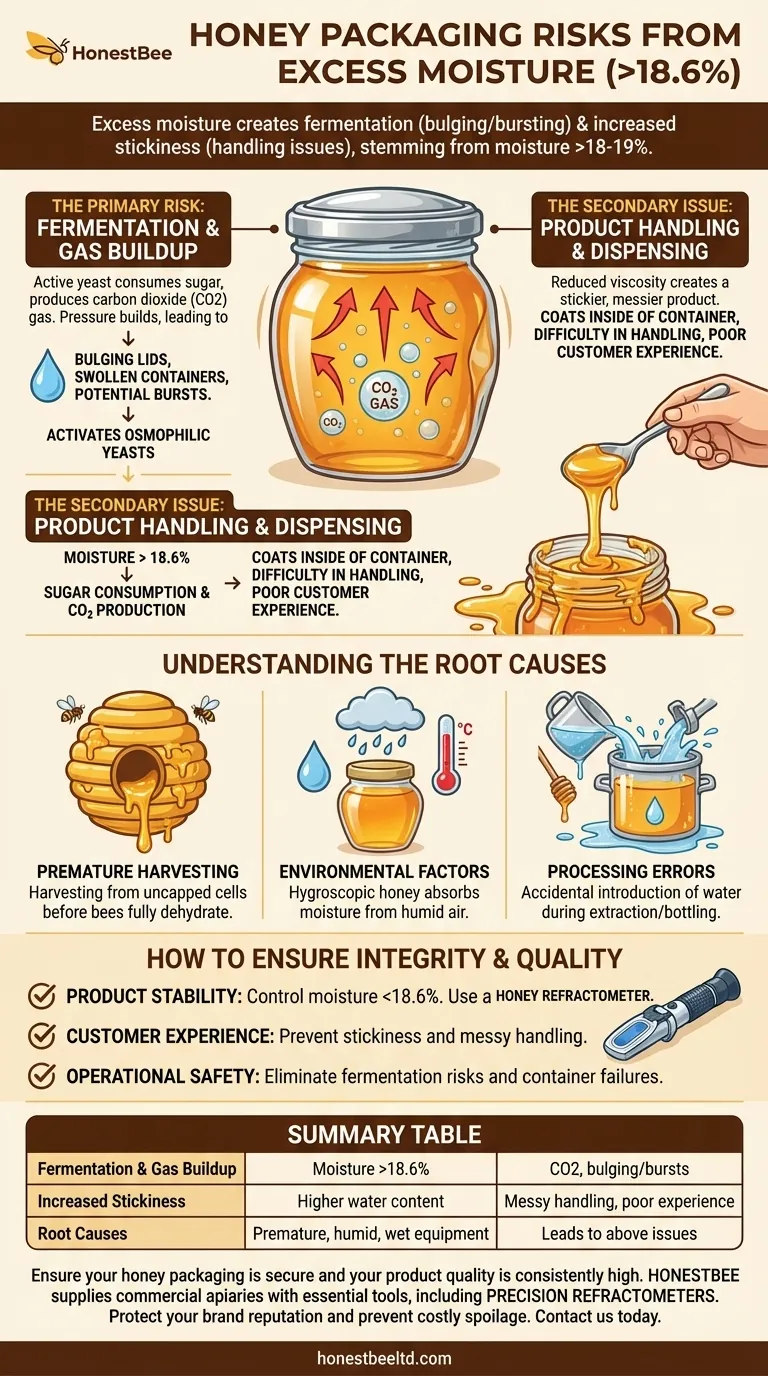
Excess moisture in honey creates two primary packaging risks: it enables fermentation that can cause containers to bulge or burst, and it increases the product's stickiness, which complicates handling and dispensing. These issues stem from moisture levels rising above the stable threshold of 18-19%.
The central challenge with high-moisture honey is not just its physical behavior in the container, but its chemical instability. Moisture levels above the natural threshold activate dormant yeasts, leading to fermentation, product spoilage, and inevitable packaging failure.

The Primary Risk: Fermentation and Gas Buildup
The most severe packaging issue caused by excess moisture is fermentation. This process directly compromises the integrity of any sealed container.
Why Moisture Triggers Fermentation
Honey naturally contains osmophilic yeasts, which are yeasts that can survive in high-sugar environments.
The extremely low water content of properly cured honey (typically below 18.6%) creates high osmotic pressure, keeping these yeasts dormant and harmless.
When water content rises, it dilutes the sugars and reduces this pressure, allowing the yeasts to activate, multiply, and metabolize the honey's sugars.
The Impact on Packaging
Active yeast consumes sugar and produces byproducts, most notably alcohol and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.
In a sealed container, this gas has nowhere to escape. The internal pressure begins to build steadily as fermentation continues.
Signs of Container Failure
This pressure buildup manifests in predictable ways. You may observe bulging lids on jars or swollen plastic containers.
If the pressure becomes too great, it can cause lids to pop off, seals to break, or containers to leak. In extreme cases, glass jars can burst, creating a significant safety hazard.
The Secondary Issue: Product Handling and Dispensing
While less destructive than fermentation, excess moisture also degrades the physical properties of honey, affecting its interaction with packaging and the user's experience.
The Problem of Stickiness
Excess moisture reduces honey's viscosity, making it runnier. While this might seem beneficial, it often results in a product that is more difficult to manage.
The honey tends to coat the inside of the container and lid, creating a sticky, messy residue that makes handling and dispensing difficult for the consumer.
Customer Experience Degradation
This stickiness and messiness can lead to product waste and frustration. A consumer struggling with a sticky, leaking jar perceives the product as being of lower quality, regardless of its taste.
Understanding the Root Causes of Excess Moisture
To prevent these packaging issues, it is essential to understand where the excess moisture originates.
Premature Harvesting
Bees cure honey in the hive, fanning their wings to evaporate water until it reaches a stable moisture content. They then cap the honeycomb cell with wax.
Harvesting honey from uncapped cells often means the honey has not been fully dehydrated and will have a high moisture content.
Environmental Factors
Honey is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture directly from the air.
Harvesting or storing honey in highly humid climates or during wet seasons can increase its water content if it is left exposed.
Processing Errors
Water can be accidentally introduced during the extraction and bottling process. Using wet equipment or rinsing tools without thoroughly drying them can easily contaminate a batch and raise its moisture level.
How to Ensure Packaging Integrity and Product Quality
Your approach to moisture control will dictate the success of your product from both a safety and a quality perspective.
- If your primary focus is product stability and shelf life: Meticulously control moisture content to stay below 18.6%, using a honey refractometer for an accurate measurement before packaging.
- If your primary focus is customer experience: Ensure proper moisture levels to prevent the excessive stickiness and difficult handling that signal a low-quality product.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Prevent moisture contamination to eliminate the risk of fermentation, gas buildup, and containers failing during storage or transport.
Ultimately, controlling honey's moisture content is the single most critical factor in guaranteeing both the integrity of its packaging and the quality of the product within.
Summary Table:
| Issue | Cause | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Fermentation & Gas Buildup | Moisture >18.6% activates yeast | CO2 production, bulging lids, potential container bursts |
| Increased Stickiness | Higher water content reduces viscosity | Messy handling, difficult dispensing, poor customer experience |
| Root Causes | Premature harvesting, humid environment, wet processing equipment | Leads to the above issues if not controlled |
Ensure your honey packaging is secure and your product quality is consistently high. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the essential tools for success, including precision refractometers for accurate moisture testing. Protect your brand reputation and prevent costly spoilage—contact our experts today to discuss your wholesale supply needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hexagonal Glass Honey Jars with Metal Lug Caps Elegant Versatile Packaging
- Classic Drum Shaped Glass Honey Jar with Airtight Lid
- Classic Honey Bear Jars with Flip Top Dispensing Cap for Liquid Sweeteners
- Inverted Squeezable Honey Jar with No Drip Flip Top Cap for Easy Pouring
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
People Also Ask
- How many jars of honey do you get from a hive? Unlock Sustainable Harvesting Secrets
- Why is it necessary to use storage containers with tight-fitting lids? Prevent Honey Spoilage and Loss
- What is the best way to jar honey? Preserve Quality with the Right Container
- What are the primary functional benefits of high-standard glass packaging for honey? Protect Purity and Brand Value
- How does the appearance of glass jar packaging affect the sales and perception of honey? Boost Your Premium Brand Value



















