The standard technique for semen mixing in honey bee artificial insemination is the direct pooling of semen from multiple drones into a syringe, followed by physical agitation. This method is designed to mimic the genetic diversity a queen would acquire during natural mating flights. While other methods have been explored, this simple and effective protocol remains the industry standard.
The core objective of semen mixing is not just to combine sperm, but to replicate the genetic diversity of natural mating. The most reliable and widely used technique is the physical pooling and mixing of semen from 8-12 different drones directly within the insemination instrument.
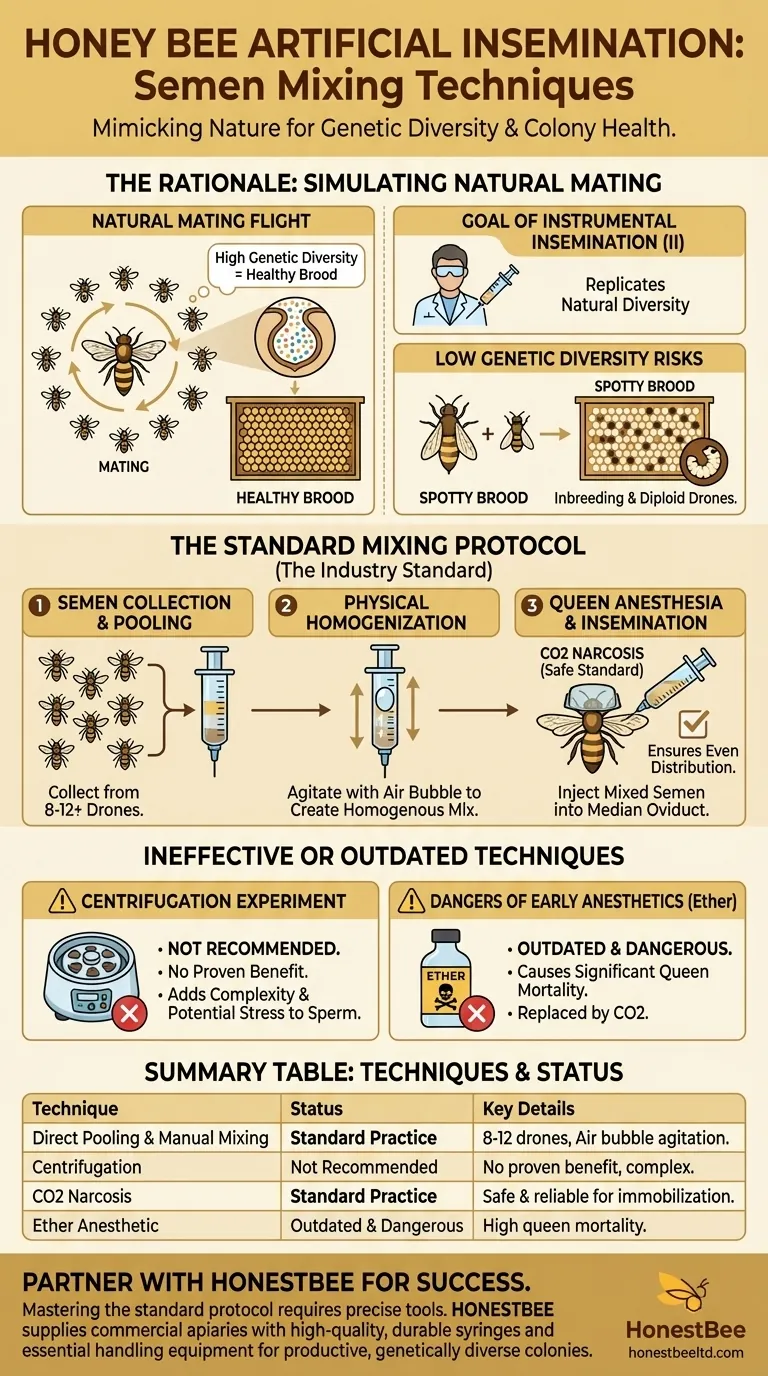
The Rationale: Simulating Natural Mating
The Queen's Mating Flight
In nature, a virgin queen embarks on one or more nuptial flights where she mates with an average of 12 to 20 different drones. This process ensures a high degree of genetic diversity within the sperm she stores in her spermatheca.
The Goal of Instrumental Insemination (II)
Instrumental insemination (II) must replicate this genetic diversity to be successful. A queen inseminated with semen from a single drone or only a few drones will produce a colony with low genetic variation.
Preventing Inbreeding and "Spotty Brood"
Low genetic diversity leads to a high percentage of diploid drones—males that develop from fertilized eggs. Worker bees identify and cannibalize these larvae, resulting in a "spotty brood" pattern with empty cells. This severely reduces the colony's population growth and overall productivity.
The Standard Mixing and Insemination Protocol
Step 1: Semen Collection and Pooling
The process begins by collecting semen from multiple mature, healthy drones. Typically, semen from 8 to 12 drones is collected sequentially and drawn into the tip of the insemination syringe.
Each drone's semen is carefully layered on top of the previous sample within the glass or plastic capillary tube.
Step 2: Physical Homogenization
Once the full volume of semen is collected, it must be mixed. The most common and effective method is to repeatedly draw and expel a small air bubble through the column of semen.
This action churns the semen, breaking up the individual strata from each drone and creating a homogenous mixture. This ensures that the sperm from all drones are evenly distributed.
Step 3: Queen Anesthesia and Insemination
During the procedure, the queen is immobilized using an anesthetic. The current, safe standard is carbon dioxide (CO2) narcosis. The mixed semen is then carefully injected into the queen's median oviduct.
Understanding Ineffective or Outdated Techniques
The Centrifugation Experiment
In the past, some practitioners experimented with centrifugation to mix the semen. The hypothesis was that spinning the semen in a centrifuge could create a more perfectly homogenous sample.
However, there is little to no scientific evidence that this complex step provides any benefit over simple physical mixing within the syringe. It adds time, requires specialized equipment, and may create unnecessary stress on the sperm. For these reasons, it is not a recommended practice.
The Dangers of Early Anesthetics
Early attempts at instrumental insemination used ether for anesthesia. This practice was quickly abandoned due to the significant mortality it caused in queens.
The adoption of CO2 narcosis was a critical advancement that made the procedure much safer and more reliable, highlighting the importance of adhering to modern, proven protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Following the correct protocol is essential for producing healthy, viable queens. Your specific goal may add minor considerations, but the core technique remains the same.
- If your primary focus is commercial queen production: Adhere strictly to the standard protocol of pooling semen from 8-12 drones and mixing it manually within the syringe to maximize genetic diversity and colony health.
- If your primary focus is breeding or genetic research: Your diligence must occur before collection. Keep meticulous records of drone parentage before pooling their semen, as the mixing process makes it impossible to trace individual contributions afterward.
Ultimately, mastering this fundamental process of pooling and mixing is the key to producing genetically robust and productive honey bee colonies.

Summary Table:
| Technique | Status | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Pooling & Manual Mixing | Standard Practice | Semen from 8-12 drones is collected and mixed via air bubble agitation in a syringe. |
| Centrifugation | Not Recommended | Lacks proven benefit over manual mixing; adds complexity and potential sperm stress. |
| Anesthetic: CO2 Narcosis | Standard Practice | Safe and reliable for queen immobilization during the procedure. |
| Anesthetic: Ether | Outdated & Dangerous | Causes high queen mortality; replaced by CO2. |
Produce Genetically Robust Queens with the Right Equipment
Mastering the standard semen mixing protocol is fundamental for successful instrumental insemination. Using high-quality, reliable supplies ensures the health of your drones and queens, leading to productive, genetically diverse colonies.
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the precise tools needed for this critical work, from durable syringes to essential handling equipment.
Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss how our beekeeping supplies can support your queen-rearing and breeding programs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Queen Bee Artificial Insemination Instrument Equipment for Instrumental Insemination
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- HONESTBEE 15-in-1 Beekeeper Multi-Tool with Hammer and Pliers for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the standard semen dose for AI of a honey bee queen? Master the 8-10 µl Precision for Longevity
- What is the procedure for collecting semen from subsequent drones? Master the Expel-to-Connect Method
- How should the syringe tip be maintained during semen collection? Prevent Sample Dilution and Osmotic Shock
- How should the mucus present during semen collection be handled? Avoid Clogs and Ensure Sample Quality
- What are the key steps involved in the artificial insemination of queen bees? Achieve Absolute Genetic Control



















