Selecting the right honey filling machine requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, adaptability to product variations, and long-term cost efficiency. This guide breaks down critical factors—from production capacity to compliance standards—to help commercial apiaries and distributors optimize their packaging operations.
Technical Specifications for Production Efficiency
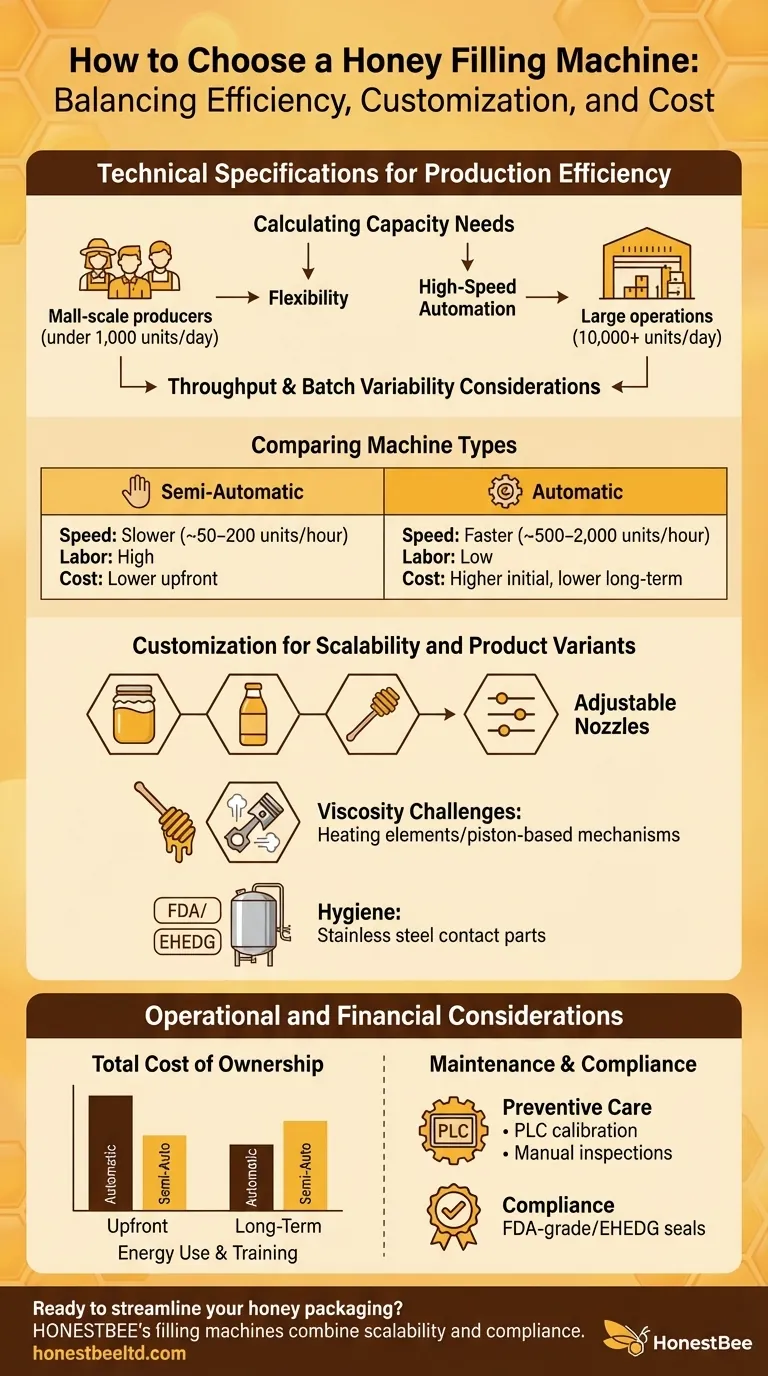
Calculating Capacity Needs Based on Output Goals
Your honey filling machine’s capacity should align with both current demand and future growth. Small-scale producers (under 1,000 units/day) may prioritize flexibility, while large operations (10,000+ units/day) need high-speed automation.
Key considerations:
- Throughput: Automatic machines fill hundreds of containers per hour; semi-automatic models require manual intervention, slowing output.
- Batch variability: If producing multiple honey types (e.g., raw, creamed), opt for machines with quick-change components.
Comparing Machine Types: Automatic vs. Semi-Automatic Systems
| Feature | Semi-Automatic | Automatic |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower (~50–200 units/hour) | Faster (~500–2,000 units/hour) |
| Labor Dependency | High (manual loading/sealing) | Low (PLC-controlled workflows) |
| Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher initial cost, lower labor expenses long-term |
Example: A commercial apiary expanding to retail honey sticks might start with semi-automatic fillers but transition to automatic systems as orders grow.
Customization for Scalability and Product Variants
Modern honey fillers adapt to:
- Container types: Jars, bottles, or sticks, with adjustable nozzles for precise fills.
- Viscosity challenges: Heating elements or piston-based mechanisms handle crystallized honey.
- Hygiene: Stainless steel contact parts meet FDA/EHEDG standards, critical for export compliance.
Operational and Financial Considerations
Total Cost of Ownership: Upfront vs. Long-Term Expenses
While automatic machines cost 2–3x more than semi-automatic models, they reduce labor costs by ~30–50% over five years. Factor in:
- Energy use: Automated systems often include energy-efficient pumps.
- Training: Semi-automatic machines require less specialized training.
Maintenance Requirements and Downtime Mitigation
- Preventive care: Automatic machines need quarterly PLC calibration; semi-automatic models require manual part inspections.
- Spare parts: Ensure suppliers (like HONESTBEE) offer access to seals and pistons.
Compliance with Food Safety and Industry Certifications
Look for:
- Material safety: FDA-grade stainless steel prevents contamination.
- Certifications: EHEDG seals validate suitability for viscous foods like honey.
Ready to streamline your honey packaging? HONESTBEE’s filling machines combine scalability and compliance, helping commercial beekeepers and distributors meet demand without compromising quality. Explore solutions tailored to your production scale.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Fully Automatic Honey Filling Packaging Machine for Processing Line
- Manual Honey Filling Machine Bottling Machine for Honey
- Automatic Honey Filling and Filtering Machine for Beekeeping Bottle Filling
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
Related Articles
- The 40°C Rule: How Gentle Heat Protects the Soul of Your Honey
- HonestBee Top & Bottom Bar Forming Machine: Precision Manufacturing for Beehive Frames
- The Hive's Silent Architect: Engineering Efficiency with Beeswax Foundation
- Why Your Honey Filling Line is Failing—And It's Not the Machine's Fault
- How to Make Bee Frames in a Factory: The Ultimate Guide to High-Volume Production with HONESTBEE Bee Frame Machines




















