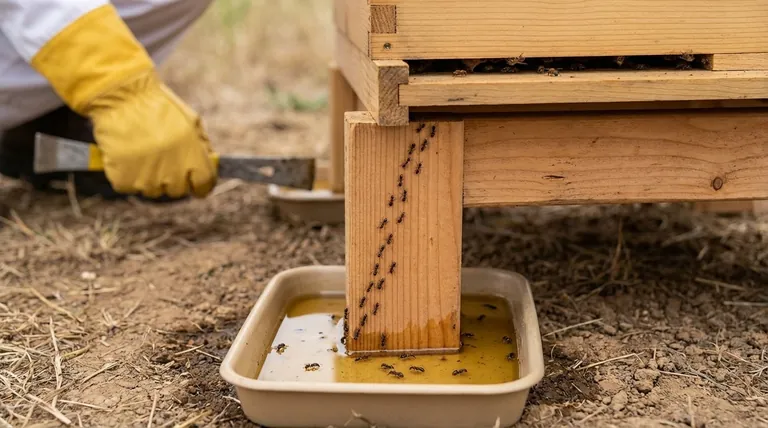
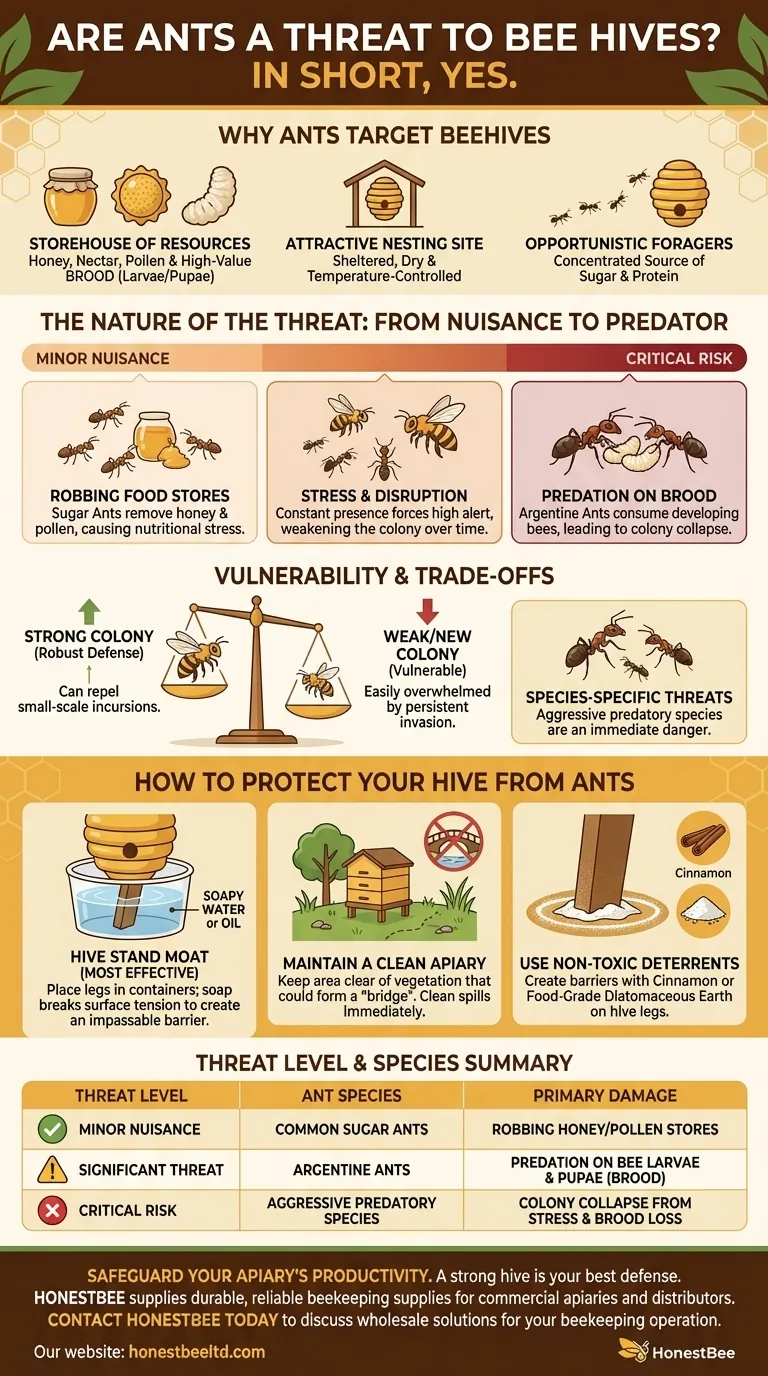
In short, yes. While a minor nuisance in some cases, certain ant species can pose a significant threat to a honey bee colony. The primary danger comes from predatory ants that are capable of overwhelming a hive's defenses to steal food stores and, most critically, prey upon the developing bee larvae and pupae (brood).
The core issue is one of resources and vulnerability. Ants are attracted to the concentrated sugar, protein, and shelter of a beehive, and while a strong colony can often defend itself, a weak or new colony can be quickly overwhelmed by a persistent ant invasion.

Why Ants Target Beehives
Ants are opportunistic foragers, and a beehive represents an almost perfect concentration of resources. Understanding their motivation is the first step to managing them effectively.
A Storehouse of Resources
A hive contains everything ants need to thrive: honey and nectar (carbohydrates), pollen (protein), and a ready supply of bee brood, which is a high-value food source for predatory ant species.
An Attractive Nesting Site
The hive itself provides a sheltered, dry, and temperature-controlled environment. Some ant species will attempt to establish a nest within the hive's lid or bottom board, creating constant stress for the colony.
The Nature of the Threat: From Nuisance to Predator
The level of threat depends entirely on the ant species and the strength of the bee colony. The damage can range from minor resource theft to the complete destruction of the hive.
The Primary Damage: Predation on Brood
The most severe threat comes from predatory species like the Argentine ant. These ants will enter the hive, carry away bee larvae and pupae, and consume them. This loss of future bees can quickly cripple a colony's population, leading to its collapse.
Robbing Food Stores
Even non-predatory "sugar ants" can cause significant problems. A constant stream of ants removing honey and pollen creates nutritional stress, forcing the bees to expend more energy guarding resources and less time foraging.
Stress and Disruption
The constant presence of invaders forces guard bees into a state of high alert and diverts worker bees from their normal tasks of nursing brood, cleaning the hive, and foraging. This chronic stress weakens the entire colony over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Vulnerabilities
Effective management requires recognizing that not every ant is a crisis, but every colony has a breaking point. Your intervention should be based on a clear assessment of the risk.
Colony Strength is the Best Defense
A strong, populous honey bee colony has a robust defense system. They can effectively guard the entrance and repel small-scale incursions from most ant species. Weak, small, or newly established colonies are far more vulnerable and can be overrun.
Species-Specific Threats
The specific type of ant in your area is the most critical factor. Small, common sugar ants might be a minor nuisance, but large, aggressive species known for predation are a direct and immediate threat that requires intervention.
The Limits of Bee Defense
While individual bees can sting and bite, they are often ineffective against a mass of small ants. The ants' sheer numbers can overwhelm the guards, especially if they find an unguarded crack or crevice to enter the hive.
How to Protect Your Hive from Ants
Prevention is simple, effective, and far better than trying to eradicate an established infestation. The most reliable methods create a physical barrier the ants cannot cross.
The Hive Stand Moat
This is the most common and effective solution. Place each leg of your hive stand into a small container filled with soapy water or oil. This creates a "moat" that ants cannot cross to climb into the hive. The soap breaks the water's surface tension, ensuring they cannot walk across it.
Maintain a Clean Apiary
Keep the area around your hives clear of tall grass, weeds, and branches that could form a "bridge" for ants to bypass your hive stand's defenses. Clean up any honey or syrup spills immediately, as this will attract scouts.
Use Non-Toxic Deterrents
For an added layer of defense, you can create a barrier by drawing a thick line of cinnamon or food-grade diatomaceous earth on the legs of the hive stand. While less permanent than a moat, these can be effective deterrents.
Making the Right Choice for Your Hive's Defense
Your approach to ant control should be proactive and tailored to the specific risk level in your apiary.
- If your primary focus is proactive prevention: Implement hive stand moats from day one and maintain a clean apiary to deny ants any easy access.
- If you are managing a weak or new colony: Be especially vigilant, as these hives are the most vulnerable and require robust, well-maintained physical barriers.
- If you already see a trail of ants on your hive: Act immediately to establish a moat or other barrier and disrupt their trail to protect the colony from further damage.
By understanding the threat and implementing simple, physical barriers, you can effectively protect your bees from ant predation.
Summary Table:
| Threat Level | Ant Species | Primary Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Minor Nuisance | Common Sugar Ants | Robbing honey/pollen stores |
| Significant Threat | Argentine Ants | Predation on bee larvae & pupae (brood) |
| Critical Risk | Aggressive Predatory Species | Colony collapse from stress and brood loss |
Safeguard your apiary's productivity and protect your investment. A strong hive is your best defense, but it starts with the right equipment. HONESTBEE supplies durable, reliable beekeeping supplies and equipment designed for the demands of commercial apiaries and distributors. Ensure your colonies have the protection they need to thrive.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss wholesale solutions for your beekeeping operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Beekeeping Gloves Goatskin Leather with Long Cotton Sleeve for Beekeepers
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- 8-Cone Galvanized Steel Bee Robber Guard
- Professional Insulated Plastic Bee Hives
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does the design of multi-layer combination beehives affect the application process of honeybee pest control?
- How do specialized pesticides contribute to bee colony health? Boost Your Honey Yield with Precision Pest Control
- How do pest control consumables in organic beekeeping differ? Ensure Purity with Natural Biological Solutions
- What role do specialized bee medicines and application tools play in honeybee disease and pest control? Protect Your Hive
- How do you protect a beehive from ants? A Proactive Guide to Effective, Long-Term Defense
- Why is high precision in temperature control essential for beekeeping disinfection equipment? Master AFB Eradication
- Why are specialized chemical application tools critical for honeybee pests? Maximize Hive Health & Minimize Loss
- How do environmental monitoring and physical protection equipment safeguard stingless bee colonies? Smart Hive Security



















