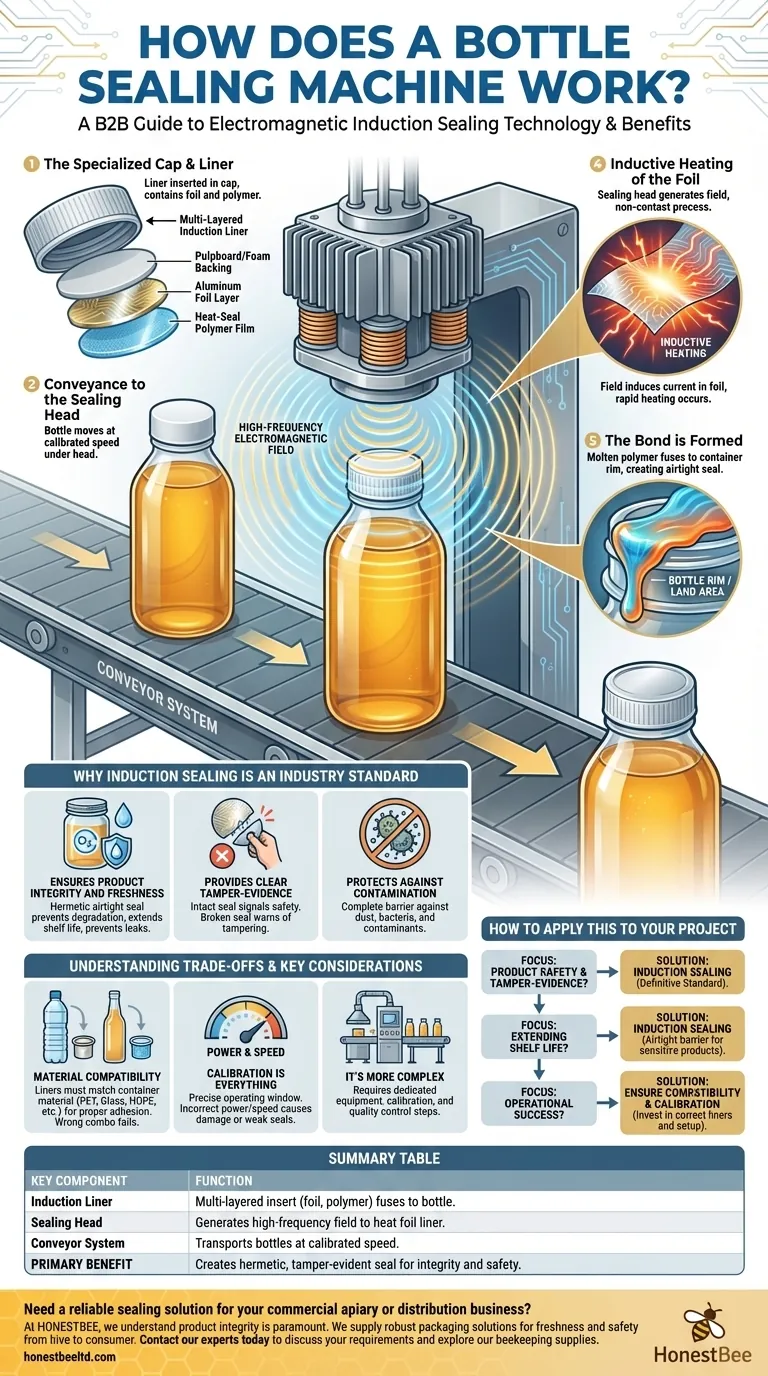
At its core, a bottle sealing machine uses electromagnetic induction to create a hermetic, tamper-evident seal without direct contact. After a bottle is filled and capped with a special lid containing a foil liner, it passes under a sealing head. This head generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field, which heats the foil inside the cap, causing a heat-seal layer to melt and fuse to the rim of the container.
The purpose of a bottle sealing machine extends beyond simply closing a container. It employs a precise physical process—electromagnetic induction—to create an airtight and tamper-evident barrier that is fundamental to product safety, integrity, and shelf life.
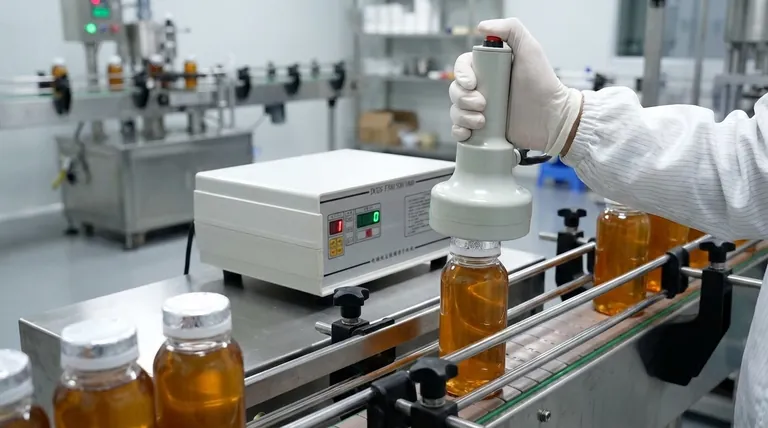

The Induction Sealing Process Deconstructed
To understand how a secure seal is formed, we must look at the components and the sequence of events on a typical packaging line. The magic happens in a fraction of a second, but it relies on a perfectly coordinated system.
Step 1: The Specialized Cap and Liner
The process begins before the bottle even reaches the sealer. A cap is applied that contains a multi-layered induction liner.
This liner typically consists of a foil layer, a heat-seal polymer film, and a pulpboard or foam backing that stays in the cap after sealing.
Step 2: Conveyance to the Sealing Head
Once capped, the container moves along a conveyor belt. It passes directly underneath an induction sealing head or "tunnel."
The speed of this conveyor is a critical variable that must be calibrated with the power of the sealer to ensure a perfect seal.
Step 3: Electromagnetic Field Generation
As the bottle passes through, the sealing head generates a controlled, high-frequency electromagnetic field.
This is the "non-contact" part of the process. The machine never physically touches the cap or bottle to apply heat.
Step 4: Inductive Heating of the Foil
The electromagnetic field passes through the plastic cap and induces an electrical current in the aluminum foil layer of the liner.
This current causes the foil to heat up rapidly—a principle known as induction heating.
Step 5: The Bond is Formed
The heat generated by the foil melts the heat-seal polymer film on the bottom of the liner.
This molten polymer fuses directly onto the rim (or "land area") of the bottle or jar, creating a strong, airtight bond as it cools. The seal is now complete.
Why Induction Sealing is an Industry Standard
The adoption of induction sealing is driven by three primary benefits that directly address the core needs of product manufacturers and consumers.
Ensures Product Integrity and Freshness
The primary function of the seal is to be hermetic, meaning it is airtight. This prevents oxygen and moisture from entering the container, preserving the product's freshness and extending its shelf life. It also prevents product leakage.
Provides Clear Tamper-Evidence
For a consumer, a perfectly intact foil seal is a clear sign that the product is safe and has not been opened or tampered with. A broken or missing seal immediately signals a potential problem.
Protects Against Contamination
By creating a complete barrier between the product and the outside world, the seal is a critical defense against dust, bacteria, and other contaminants that could compromise the product's safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While highly effective, implementing an induction sealing process requires careful attention to detail to avoid common pitfalls.
Material Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
Induction liners are designed for specific container materials. A liner formulated for a PET plastic bottle will not properly adhere to a glass or HDPE bottle. Using the wrong liner-container combination is a leading cause of seal failure.
Calibration is Everything
The "operating window" for a perfect seal is precise. Too much power from the sealing head or a conveyor that is too slow can overheat the liner, damaging the seal, cap, or even the bottle itself. Too little power or a fast conveyor will result in a weak, incomplete seal.
It's More Complex Than a Simple Lid
While far superior, induction sealing is a more involved process than simply screwing on a cap or using a basic pressure-sensitive liner. It represents an additional step on the packaging line that requires its own equipment, calibration, and quality control.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing and implementing a sealing solution depends entirely on your product's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum product safety and tamper-evidence: Induction sealing is the definitive standard for creating a verifiable, hermetic barrier that protects consumers.
- If your primary focus is extending shelf life: The airtight seal created by induction heating is essential for preventing degradation from oxygen and moisture, especially for sensitive food, beverage, or pharmaceutical products.
- If your primary focus is operational success: You must ensure perfect compatibility between your containers and liners, and invest time in calibrating the sealer's power and conveyor speed for a consistent, reliable outcome.
Understanding this technology empowers you to make informed decisions that safeguard your product, your customers, and your brand's reputation.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Induction Liner | Multi-layered cap insert (foil, polymer, backing) that fuses to the bottle. |
| Sealing Head | Generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field to heat the foil liner. |
| Conveyor System | Transports bottles at a calibrated speed under the sealing head. |
| Primary Benefit | Creates a hermetic, tamper-evident seal for product integrity and safety. |
Need a reliable sealing solution for your commercial apiary or distribution business?
At HONESTBEE, we understand that the integrity of your honey and related products is paramount. Our wholesale-focused operations supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the robust packaging solutions they need to ensure product freshness and safety from the hive to the consumer.
Let us help you select the right sealing equipment to protect your brand and meet industry standards. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and explore our range of beekeeping supplies and equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Handheld Induction Sealing Machine for Tamper Evident Packaging
- Professional Water Cooled Induction Sealing Machine for Bottles and Containers
- Semi Automatic Round Bottle Labeling Machine
- Automatic Continuous Heat Sealing Machine
- Automated Rotary Bottle Unscrambler for Honey Production Line
People Also Ask
- How does professional gift customization equipment enhance brand value? Elevate Honey Products into Premium Merchandise
- What is the function of an induction sealing machine in packaging? Secure Your Brand with Tamper-Evident Seals
- What is the significance of induction sealing equipment in honey packaging? Protect Your Brand and Product Integrity
- What is the function of sealing machines? Ensure Product Integrity and Extend Shelf Life
- What is the purpose of induction sealing in honey packaging? Ensure Quality & Build Consumer Trust



















