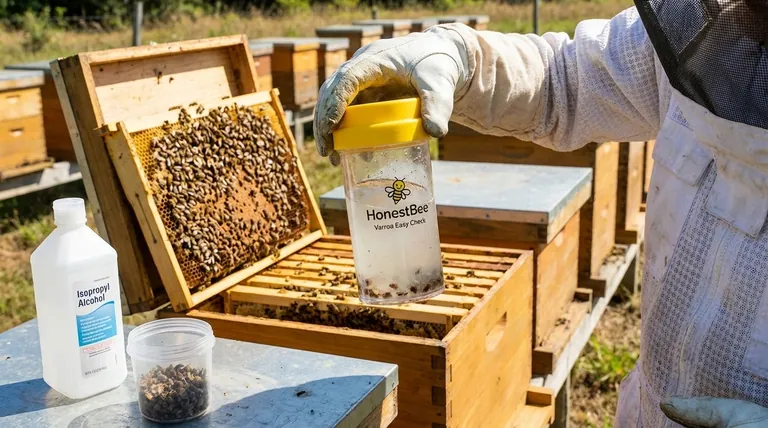
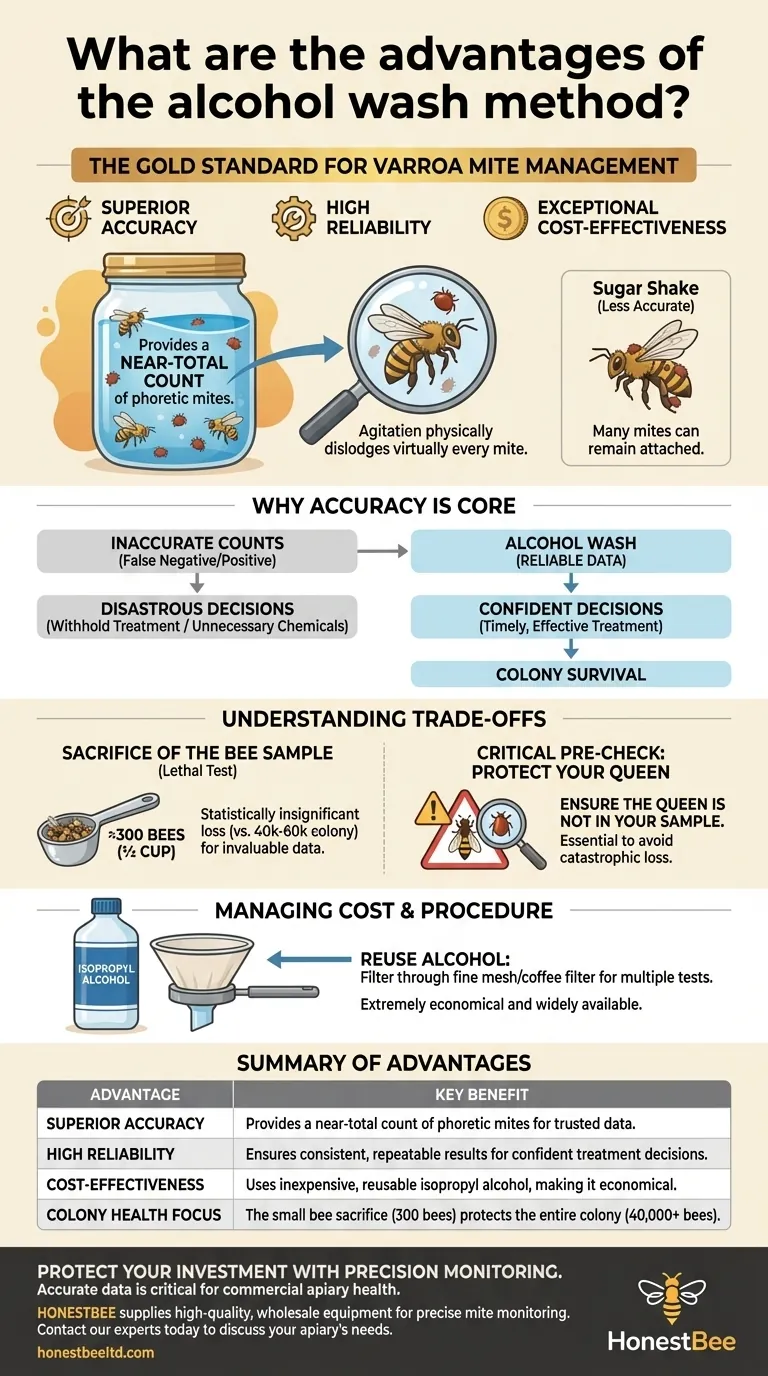
When it comes to managing Varroa mites, the alcohol wash method is considered the gold standard for a clear reason. Its primary advantages are superior accuracy, high reliability, and exceptional cost-effectiveness, making it the most dependable tool for assessing a honey bee colony's health.
The alcohol wash method requires sacrificing a small sample of bees to gain the most precise data on your colony's mite infestation. This trade-off is essential for making timely, effective treatment decisions that can save the entire colony from collapse.

Why Accuracy is the Core Advantage
The entire purpose of mite monitoring is to get data you can trust. Inaccurate counts can lead to disastrous decisions, and the alcohol wash method is specifically designed to minimize this risk.
How the Method Ensures High Accuracy
An alcohol wash provides a near-total count of the phoretic mites on your sample bees. By immersing the bees in isopropyl alcohol, the solution quickly kills both the bees and the mites.
The subsequent agitation physically dislodges virtually every mite from the bees' bodies, allowing for a complete and visible count. This is far more effective than methods like the sugar shake, where many mites can remain attached to the bees.
The Impact of a Reliable Count
Reliability means you get consistent, repeatable results. An inaccurate test that gives you a low count (a false negative) might lead you to withhold treatment when it's desperately needed.
Conversely, a false high count could cause you to treat a colony unnecessarily, wasting time, money, and exposing your bees to chemicals without cause. The alcohol wash removes this guesswork.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While highly effective, the method is not without its considerations. Acknowledging them is key to using it responsibly.
The Sacrifice of the Bee Sample
The most significant drawback is that the test is lethal to the sampled bees. A standard sample requires approximately 300 bees (about a ½ cup measure).
Putting the Loss in Perspective
While sacrificing any bees is regrettable, it's crucial to contextualize this loss. A healthy summer colony contains 40,000 to 60,000 bees and naturally loses hundreds, if not thousands, of workers each day.
The loss of 300 bees is statistically insignificant to the colony's population but provides invaluable data that is critical for the survival of the other 99.5%+.
Managing Cost and Procedure
The alcohol wash is extremely economical. Isopropyl alcohol is inexpensive and widely available.
Furthermore, you can reuse the alcohol for multiple tests by filtering it through a very fine mesh screen or coffee filter to remove the mites and debris from the previous test, further reducing costs.
The Critical Pre-Check: Protecting Your Queen
The single most important procedural step is to ensure the queen is not in your sample. Before collecting bees, inspect the frame thoroughly to locate and secure her. Accidentally including the queen in the sample would be catastrophic for the colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of monitoring method should align directly with your beekeeping objectives.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the most precise data to protect your colony: The alcohol wash is the definitive choice and should be your standard method for monitoring mite loads.
- If your primary focus is cost and efficiency: The alcohol wash remains the most economical and reliable option, particularly because the alcohol can be filtered and reused.
- If your primary focus is avoiding any bee loss: You can use non-lethal methods like the sugar shake, but you must acknowledge that the results are less accurate and may require more frequent testing to build confidence.
Ultimately, adopting the alcohol wash method is a proactive investment in the long-term health and survival of your colonies.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Accuracy | Provides a near-total count of phoretic mites for trusted data. |
| High Reliability | Ensures consistent, repeatable results for confident treatment decisions. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Uses inexpensive, reusable isopropyl alcohol, making it economical. |
| Colony Health Focus | The small bee sacrifice (300 bees) protects the entire colony (40,000+ bees). |
Protect Your Investment with Precision Monitoring
Accurate Varroa mite data is critical for the health of your commercial apiary. The alcohol wash method provides the reliable information you need to make timely, effective treatment decisions and avoid colony collapse.
HONESTBEE supplies beekeepers and distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused equipment required for precise mite monitoring and effective hive management.
Contact our experts today to discuss your apiary's needs and discover how our beekeeping supplies can help you achieve superior colony health and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
- Professional Stainless Steel J-Hook Hive Tool
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- How do specialized Varroa mite detection equipment and alcohol function in the alcohol wash method? Master Mite Control
- How does a shake jar containing 70% alcohol facilitate assessment of Varroa mite infestation rates? Industry Insights
- How is the powdered sugar shake method performed to detect Varroa mite levels? Protect Your Bees with This Guide
- What is the importance of the alcohol wash method? Master Varroa Mite Monitoring for Commercial Apiaries
- What are the components of the three-part monitoring tool designed for Varroa alcohol washes? Optimize Bee Health



















