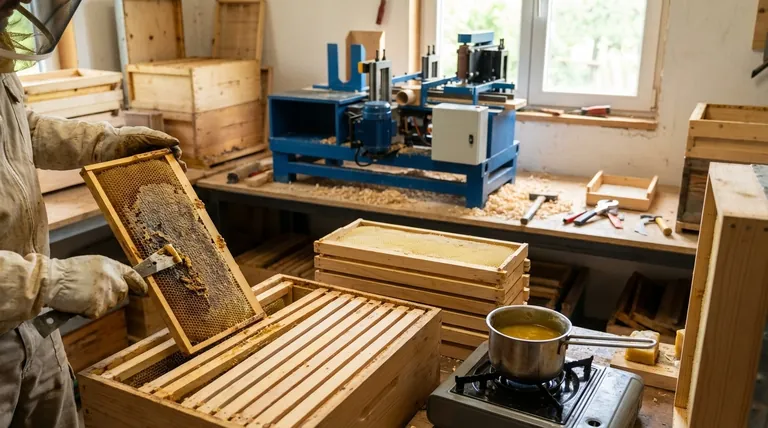
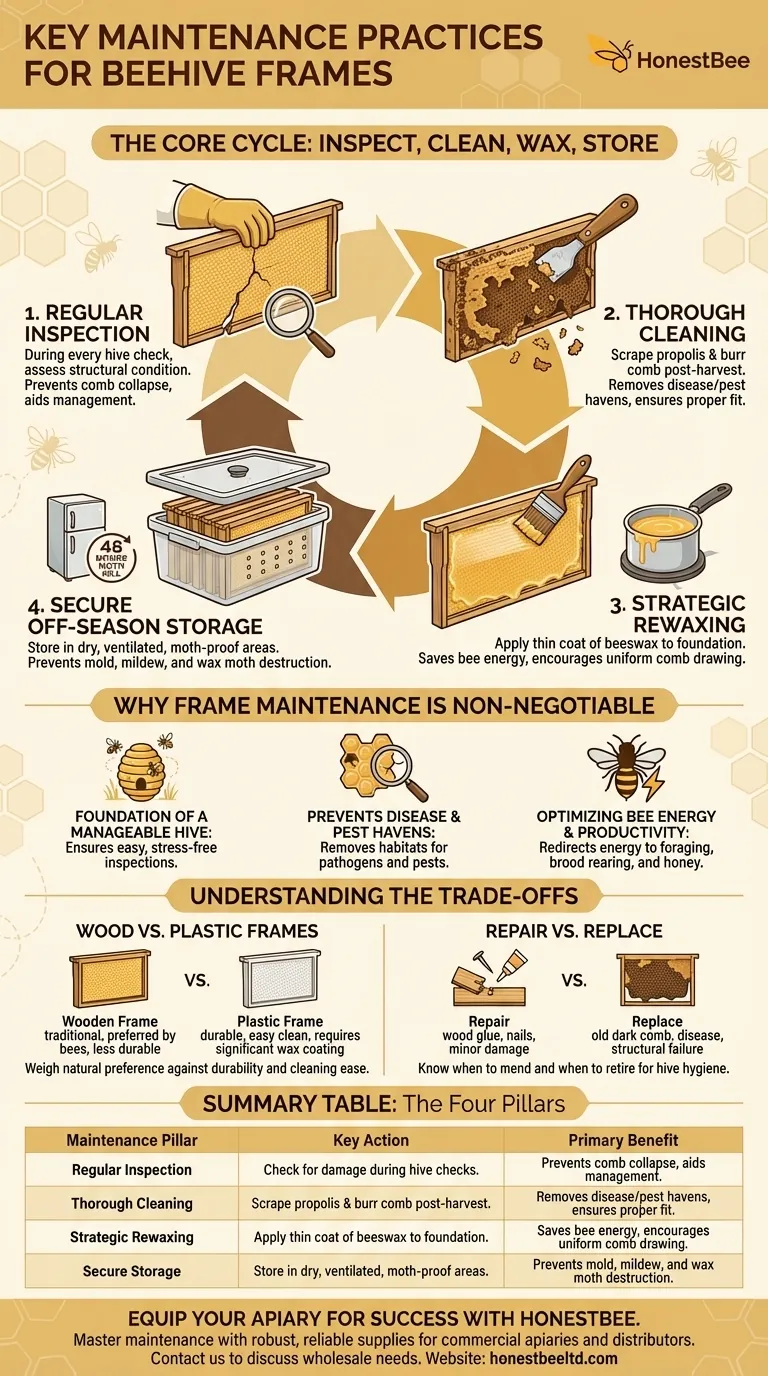
At its core, proper beehive frame maintenance is a straightforward cycle of inspection, cleaning, waxing, and storage. These practices are essential for ensuring the structural integrity of the hive, preventing the spread of pests and disease, and encouraging productive, healthy bees. Neglecting frames means neglecting the very foundation upon which your colony builds its home and stores its resources.
The central goal of frame maintenance extends beyond simple cleanliness. It is a proactive strategy to manage hive health, direct the colony's energy efficiently, and ensure the long-term viability and productivity of your apiary.

Why Frame Maintenance is Non-Negotiable
Frames are more than just wooden or plastic rectangles; they are the skeleton of your hive. Understanding their role clarifies why their upkeep is critical.
The Foundation of a Manageable Hive
Frames were designed to be removable, allowing a beekeeper to inspect a colony's health, brood pattern, and food stores without destroying the delicate wax comb. Damaged or stuck frames undermine this core principle, making inspections difficult and stressful for both the bees and the beekeeper.
Preventing Disease and Pest Havens
Old, dark comb and frames clogged with propolis or debris can harbor pathogens and pests. Pests like the wax moth thrive in poorly maintained or improperly stored equipment, capable of destroying drawn comb in a short period.
Optimizing Bee Energy and Productivity
Building wax comb is an energy-intensive process for bees. By providing clean frames with a fresh coat of wax, you give them a clear blueprint. This saves the colony significant energy, which can be redirected toward foraging, raising brood, and producing honey.
The Four Pillars of Frame Maintenance
A consistent maintenance routine can be broken down into four key activities performed at different points in the beekeeping season.
Pillar 1: Regular Inspection
During every hive check, take a moment to assess the condition of the frames themselves. Look for broken joints, splintering wood, or foundation that has become detached. A structurally sound frame prevents comb from breaking and falling, which can kill bees and disrupt the colony.
Pillar 2: Thorough Cleaning
After each honey harvest is the ideal time for deep cleaning. Use your hive tool to scrape off excess propolis and burr comb. This not only keeps the frames fitting properly within the hive body but also removes material that can harbor disease.
Pillar 3: Strategic Rewaxing
Frames, especially plastic ones or those with bare foundation, should be periodically rewaxed. Applying a thin, even layer of melted beeswax provides a guide and an incentive for bees to begin drawing out fresh comb quickly and uniformly.
Pillar 4: Secure Off-Season Storage
Proper storage is critical to protecting your investment. Frames must be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent mold and mildew. To protect against wax moths, ensure storage containers are moth-proof or place frames in a freezer for 48 hours to kill any existing eggs or larvae.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Making the right maintenance decisions often involves weighing the pros and cons of different approaches and materials.
Wood vs. Plastic Frames
Wooden frames are the traditional choice and what bees naturally prefer. However, they are more susceptible to damage and can be more difficult to clean thoroughly. Plastic frames are highly durable, easier to clean, and less prone to breaking, but they almost always require a substantial coat of beeswax to encourage bee acceptance.
Repair vs. Replace
Minor damage, like a loose joint on a wooden frame, can often be repaired with wood glue and a nail. However, you must know when to retire a frame. Frames with excessively old, dark comb, signs of disease, or significant structural damage should be replaced entirely. Removing them from the apiary is a crucial step in maintaining hive hygiene.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to frame maintenance should align with your primary beekeeping objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hive health: Prioritize replacing old, dark brood combs every few years to reduce the natural buildup of pathogens.
- If your primary focus is high honey production: Ensure your honey supers are always equipped with clean, well-waxed frames to encourage bees to draw comb and store honey efficiently.
- If your primary focus is long-term sustainability: Master the skills of cleaning and rewaxing frames to significantly extend the life of your equipment and reduce recurring costs.
Ultimately, diligent frame maintenance is one of the most impactful investments of time you can make for the health and productivity of your bees.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Pillar | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Check for damage during hive checks. | Prevents comb collapse and aids management. |
| Thorough Cleaning | Scrape propolis & burr comb post-harvest. | Removes disease/pest havens and ensures proper fit. |
| Strategic Rewaxing | Apply a thin coat of beeswax to foundation. | Saves bee energy, encourages uniform comb drawing. |
| Secure Storage | Store in dry, ventilated, moth-proof areas. | Prevents mold, mildew, and wax moth destruction. |
Equip Your Apiary for Success with HONESTBEE
Mastering frame maintenance is fundamental, but it starts with durable, high-quality equipment. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the robust, reliable supplies needed to build a thriving operation.
We understand that your success depends on the integrity of your hive components. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the equipment that stands up to rigorous maintenance cycles season after season.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our beekeeping supplies can form the solid foundation for a healthier, more productive apiary.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Bee Frame Side Bar Forming Machine Precision Engineered for High-Volume Production Bee Frame Machine
- Mini Desktop Bee Hive Frame Forming Making Machine
- Frame Eyelets Assembly Machine Bee Frame Eyelets Fitting Machine Eyelets Machine
- Automatic Pneumatic Bee Frame Machine for Eyelet Insertion
- Stainless Steel Jack Type Honey Comb Press Machine Wax and Honey Separator
People Also Ask
- What functionalities does the Beehive Frame Making Machine offer? A Complete Guide to Automated Frame Production
- How should wooden hive components be cared for before use? Essential Steps for Longevity & Bee Health
- What is an automatic sidebar forming machine? Automate High-Volume Beehive Frame Production
- How does industrial-grade woodworking machinery contribute to standardized beehive manufacturing? Precision at Scale
- What role does standardized wooden beehive manufacturing machinery play? Scale Your Apiary with Industrial Precision



















