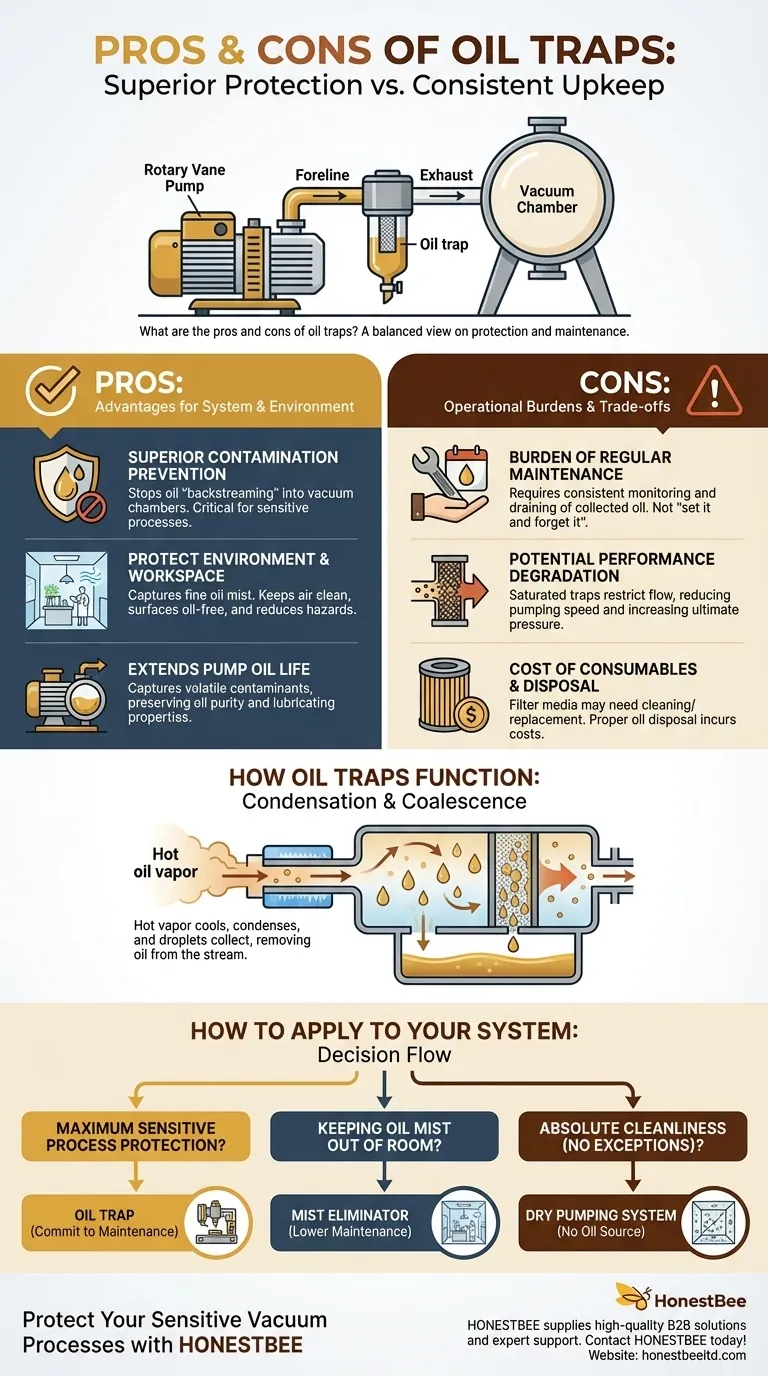
The primary advantage of an oil trap is its high effectiveness in capturing oil vapor and mist from a vacuum pump's exhaust. This prevents contamination of your system or the surrounding environment. The main disadvantage is the need for regular, hands-on maintenance to drain the collected oil and ensure the trap functions correctly.
Choosing an oil trap is a commitment to superior protection at the cost of consistent upkeep. The decision hinges on whether the value of that protection outweighs the operational burden of its maintenance.
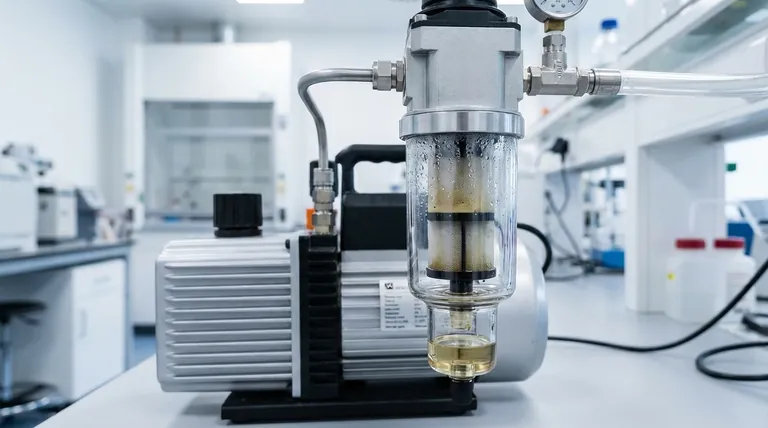

How Oil Traps Function
An oil trap, often called a foreline trap or exhaust filter, is a simple but critical component in many vacuum systems that use oil-sealed rotary vane pumps. Its operation is based on a straightforward physical principle.
The Principle of Condensation and Coalescence
Hot, oil-laden vapor and mist exit the pump and enter the larger, cooler body of the trap. This change in temperature and volume causes the oil vapor to condense into liquid droplets.
Capturing and Collecting Oil
These droplets then coalesce on internal surfaces or a filter medium (like stainless steel wool) within the trap. Gravity pulls the collected liquid oil down into a reservoir at the bottom, effectively removing it from the exhaust gas stream.
The Core Advantages of Using an Oil Trap
The benefits of a properly maintained oil trap are directly related to controlling the oil that is essential to the pump's operation but detrimental to the vacuum system or workspace.
Superior Contamination Prevention
The primary benefit is preventing oil "backstreaming." An oil trap stops oil vapor from migrating from the pump back into your vacuum chamber, which is critical for sensitive processes like surface analysis, microscopy, or thin-film deposition where molecular contamination can ruin results.
Protecting the Environment and Workspace
Oil traps capture the fine oil mist that would otherwise be exhausted from the pump. This keeps your lab or workshop air clean, prevents oily residue from coating nearby surfaces, and reduces potential inhalation hazards.
Extending Pump Oil Life
When placed on the inlet (foreline) side, a trap can also capture volatile contaminants from the system before they enter the pump. This helps preserve the purity and lubricating properties of the vacuum pump oil, extending its useful life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
The effectiveness of an oil trap is not without its operational costs. These are practical considerations that must be factored into any decision.
The Burden of Regular Maintenance
This is the most significant drawback. An oil trap is not a "set it and forget it" device. The collected oil must be regularly monitored and drained from the reservoir. Forgetting this step will render the trap useless.
Potential for Performance Degradation
If the trap becomes saturated with oil, it can become a flow restriction for the vacuum pump. This reduces the effective pumping speed and can increase the ultimate pressure achievable by the system. A poorly maintained trap can hurt performance more than it helps.
Cost of Consumables
While the trap housing is a one-time purchase, the internal filter media may need periodic cleaning or replacement. The captured oil must also be disposed of properly, which can have associated costs and procedural requirements.
How to Apply This to Your System
Your choice depends entirely on the sensitivity of your application and your capacity for routine maintenance.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection for a sensitive process: An oil trap is often the superior choice for preventing backstreaming, provided you can commit to the maintenance schedule.
- If your primary focus is simply keeping oil mist out of the room: A simpler exhaust mist eliminator (a coalescing filter) may be a more practical, lower-maintenance solution.
- If your primary focus is absolute cleanliness with no exceptions: The best long-term strategy is to invest in an oil-free "dry" pumping system, eliminating the source of contamination entirely.
Ultimately, understanding these trade-offs allows you to select a contamination solution that aligns with your operational reality, not just your technical specifications.
Summary Table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Superior oil vapor & mist capture | Requires regular, hands-on maintenance |
| Prevents system backstreaming | Can degrade pump performance if saturated |
| Protects lab/workshop environment | Consumable filter media & disposal costs |
| Extends vacuum pump oil life | Operational burden for consistent upkeep |
Protect Your Sensitive Vacuum Processes with HONESTBEE
Choosing the right contamination control solution is critical for your commercial apiary or beekeeping equipment distribution. HONESTBEE supplies the high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to maintain a clean, efficient operation.
Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable products and expert support required to protect your investments. Let us help you find the right solution for your specific needs.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your requirements and enhance your system's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reusable Wasp Trap Bottle Converter
- Gourd Shaped Hanging Wasp Trap Professional Wasp Catcher
- Compact Multi-Funnel Hanging Wasp Trap
- Professional Bucket Style Wasp and Moth Pheromone Trap
- Solar Powered LED Wasp Trap
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a Langstroth brood box for hornet traps? Use Biological Mimicry for Superior Hive Defense
- What role does the color configuration of a hornet trap play? Harness Chromotropism for Maximum Capture Efficiency
- What is the role of bait traps in the integrated management of wasps at a commercial apiary? Boost Hive Productivity
- How do high-resolution infrared hunting cameras assist in monitoring wasp activity at a bee apiary? Enhance Your Defense
- How can traps be used effectively to manage yellow jacket populations around beehives? Proven Apiary Defense Strategies



















