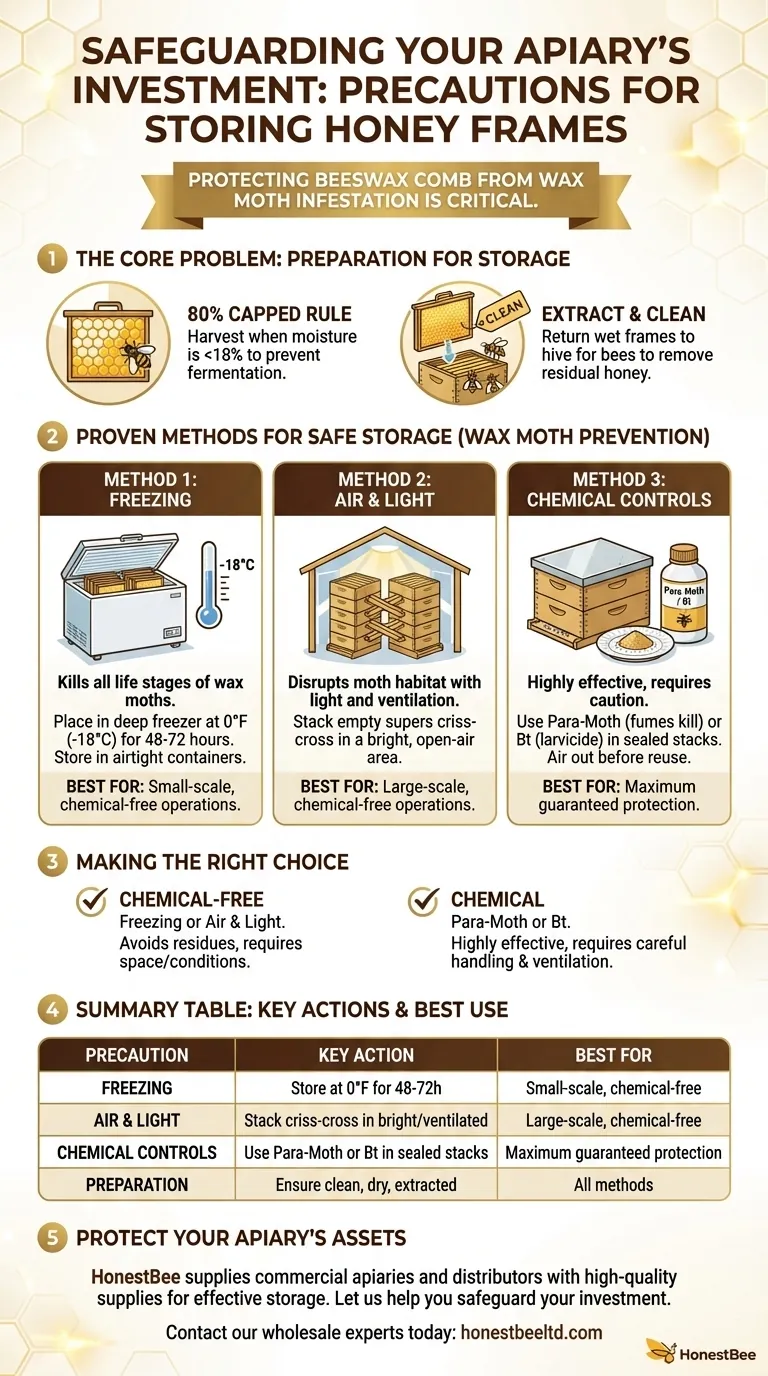
The most critical precaution when storing honey frames is to protect the beeswax comb from wax moth infestation. This is achieved by storing the frames in a moth-proof location after ensuring they are clean and dry, often using freezing or specific treatments as a preventative measure.
The goal of proper frame storage is not just about keeping things tidy; it's about preserving the bees' immense energy investment. A single frame of drawn comb is a valuable asset that gives your colony a significant head start for the next season.
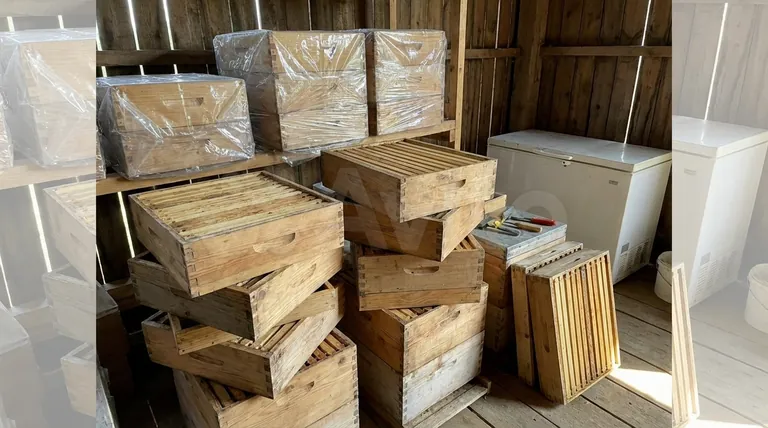

The Core Problem: Preparing Frames for Storage
Before you can store your frames, they must be properly prepared. This process begins the moment you decide to pull them from the hive.
The "80% Capped" Rule
The ideal time to harvest a frame is when at least 80% of the honey cells are capped with a clean, white-yellow layer of wax.
Bees only cap honey when its moisture content is below 18%. This prevents fermentation and ensures the honey is "ripe" and stable for long-term storage, both for the bees and for you.
Extracting and Cleaning
Once harvested, the honey must be extracted. After extraction, the frames are "wet" with residual honey.
Putting these wet supers back on the hive for a short period allows the bees to clean them thoroughly. This removes the remaining honey, making the frames far less attractive to pests like ants and wax moths during storage.
Proven Methods for Safe Storage
The primary enemy of stored comb is the wax moth. The moths lay eggs in the beeswax, and their larvae hatch and tunnel through the comb, consuming wax, pollen, and honey, leaving behind a destructive mess of webbing and waste.
Method 1: Freezing
The most effective, chemical-free way to eliminate wax moths and their eggs is freezing.
Place your frames in a deep freezer at 0°F (-18°C) for 48 to 72 hours. This kills all life stages of the pest. After freezing, store the frames in sealed, heavy-duty plastic bags or airtight tubs to prevent re-infestation.
Method 2: Air and Light
Wax moths thrive in dark, warm, and poorly ventilated spaces. You can use this to your advantage.
Stack your empty supers criss-cross or perpendicular to each other in a very bright, well-ventilated area like an open-air shed or barn. This "light stack" creates a wind tunnel effect that moths dislike, offering a simple and effective deterrent.
Method 3: Chemical Controls
For beekeepers with a large number of frames, chemical controls are a common option.
The most widely used product is Para-Moth (paradichlorobenzene). This chemical is placed on a paper plate on top of a sealed stack of supers. Its fumes are heavier than air and sink downwards, killing moths. Crucially, frames must be aired out for several days before being placed back on a hive.
Another option is Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis), sold as Xentari or B401. This is a naturally occurring bacterium that is safe for bees and humans but lethal to wax moth larvae when they ingest it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a storage method involves balancing effectiveness, effort, and philosophy. There is no single "best" answer for every beekeeper.
Chemicals vs. Chemical-Free
Using products like Para-Moth is highly effective but requires careful handling and thorough ventilation before reuse. Many beekeepers prefer to avoid any chemical use in their operation, making freezing or air-stacking more attractive options.
Space and Scale
Freezing is foolproof but demands significant freezer space, which can be a major constraint for anyone with more than a few hives. The air and light method is excellent for large numbers of frames but requires a secure, sheltered location protected from weather and rodents.
The Cost of Inaction
The biggest pitfall is doing nothing. Storing frames in a dark, sealed shed without any pre-treatment is an open invitation for wax moths. The result is almost always the complete destruction of your valuable drawn comb.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal storage method depends on the size of your operation and your management preferences.
- If your primary focus is simplicity with a few hives: Freeze your frames for 48 hours and then store them in airtight plastic totes.
- If your primary focus is a large-scale, chemical-free approach: Use the "light and air" stacking method in a secure, open-air structure.
- If your primary focus is maximum guaranteed protection: Freeze the frames first to kill existing pests, then store them in a sealed stack with a product like Para-Moth.
Protecting your frames is a direct investment in the health and productivity of your bees for the coming year.
Summary Table:
| Precaution | Key Action | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Freezing | Store at 0°F (-18°C) for 48-72 hours | Small-scale, chemical-free operations |
| Air & Light | Stack supers criss-cross in a bright, ventilated area | Large-scale, chemical-free operations |
| Chemical Controls | Use Para-Moth or Bt in sealed stacks | Maximum guaranteed protection |
| Preparation | Ensure frames are clean, dry, and extracted (80% capped rule) | All storage methods |
Protect your apiary's most valuable assets with the right supplies.
Proper frame storage is crucial for the health of your colony and the success of your next season. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, durable supplies needed to implement these storage methods effectively—from heavy-duty storage totes to essential hive components.
Let us help you safeguard your investment. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your specific needs and ensure your operation is equipped for long-term success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Sectional Comb Honey Frame with 250g Cassette System for Beekeeping
- JZBZ Langstroth Queen Rearing Frame for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Triangle Support Honey Strainer and Filters
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- Heavy-Duty Stainless Steel Clip-On Frame Perch
People Also Ask
- What are the components and purpose of a frame in a beehive? Essential Guide for Better Hive Management
- In what way does a movable frame system enable non-destructive honey harvesting? Boost Efficiency and Colony Health
- What is the purpose of using a Gridded Wooden Frame? Unlock Precise Data for Brood and Honey Measurement
- What are section comb honey supers? Master Specialized Comb Honey Production with 4 5/8" Equipment
- How do standardized frames contribute to colony maintenance? Optimize Pre-Winter Feeding for Better Survival



















