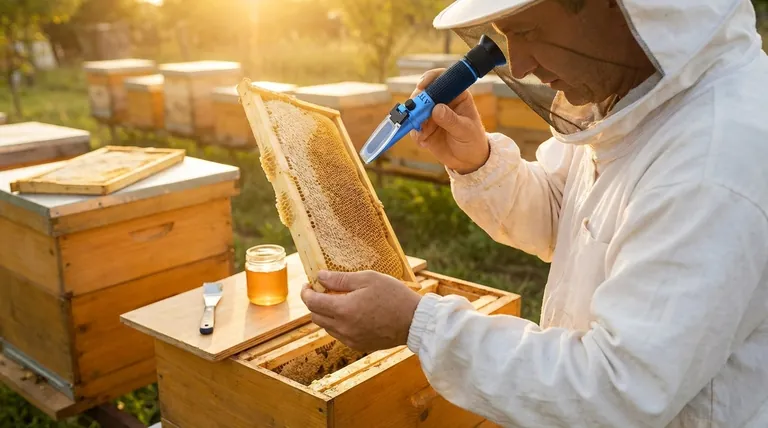
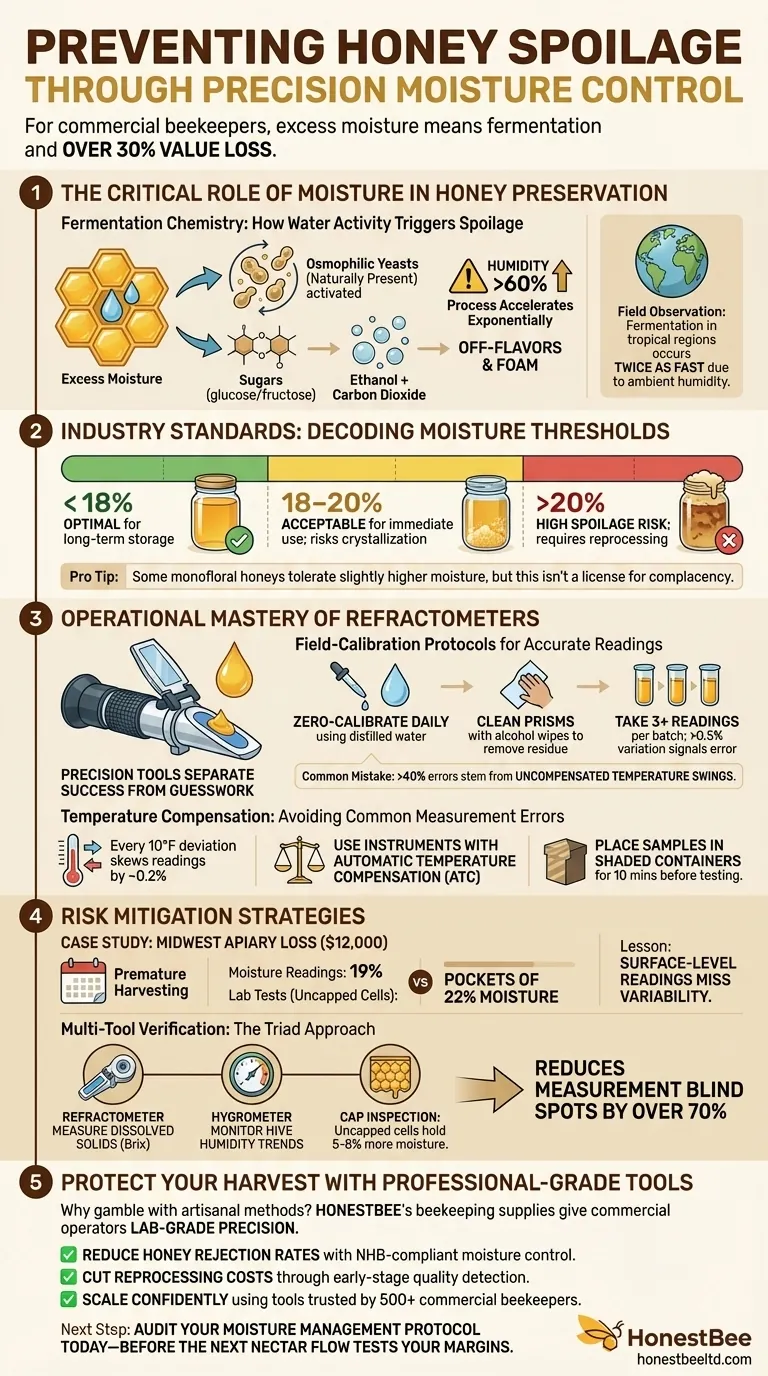
For commercial beekeepers, honey spoilage isn't just a quality issue—it's a direct threat to profitability. Research shows that improperly stored honey with excess moisture can lose over 30% of its market value due to fermentation. This guide breaks down the science of moisture control and field-tested techniques to preserve honey quality at scale.
The Critical Role of Moisture in Honey Preservation
Honey’s shelf stability hinges on one factor: keeping water activity below fermentation thresholds.
Fermentation Chemistry: How Water Activity Triggers Spoilage
When honey absorbs moisture:
- Osmophilic yeasts (naturally present in honey) activate
- Sugars convert to ethanol and carbon dioxide—creating off-flavors and foam
- The process accelerates exponentially in humidity above 60%
Field observation: Beekeepers in tropical regions report fermentation occurring twice as fast as in arid climates due to ambient humidity.
Industry Standards: Decoding 17-20% Brix Scale Thresholds
The National Honey Board’s research confirms:
- <18% moisture: Optimal for long-term storage
- 18-20%: Acceptable for immediate use but risks crystallization
- >20%: High spoilage risk; requires reprocessing
Pro Tip: Some monofloral honeys (e.g., black locust) tolerate slightly higher moisture without fermenting—but this isn’t a license for complacency.
Operational Mastery of Refractometers
Precision tools separate successful operations from guesswork.
Field-Calibration Protocols for Accurate Readings
- Zero-calibrate daily using distilled water
- Clean prisms with alcohol wipes to remove sugar residues
- Take 3+ readings per batch—variation >0.5% signals measurement errors
Common Mistake: Over 40% of refractometer errors stem from uncompensated temperature swings.
Temperature Compensation: Avoiding Common Measurement Errors
- Every 10°F deviation from calibration temp skews readings by ~0.2%
- Use instruments with automatic temperature compensation (ATC)
- Field fix: Place samples in shaded containers for 10 mins before testing
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Case Study: Financial Losses from Premature Harvesting
A Midwest apiary lost $12,000 in 2022 by harvesting frames during a humid spell. Their moisture readings showed 19%—but later lab tests revealed pockets of 22% moisture in uncapped cells.
Lesson: Surface-level readings miss variability within the hive.
Multi-Tool Verification: Combining Refractometers with Hygrometers
- Refractometers: Measure dissolved solids (Brix)
- Digital hygrometers: Monitor hive humidity trends
- Cap inspection: Uncapped cells often hold 5-8% more moisture
This triad approach reduces measurement blind spots by over 70% compared to single-tool reliance.
Protect Your Harvest With Professional-Grade Tools
Why gamble with artisanal methods when HONESTBEE’s beekeeping supplies give commercial operators lab-grade precision in the field? Our wholesale-focused equipment helps distributors and large apiaries:
✅ Reduce honey rejection rates with NHB-compliant moisture control
✅ Cut reprocessing costs through early-stage quality detection
✅ Scale confidently using tools trusted by 500+ commercial beekeepers
Next Step: Audit your moisture management protocol today—before the next nectar flow tests your margins.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- Natural Wood Honey Dipper for Tea Coffee and Desserts
- Modern Honeycomb Pattern Wooden Honey Dipper for Stirring and Drizzling
Related Articles
- Mastering Honey Refractometer Basics: A Guide to Precision and Profitability
- How to Accurately Test Honey Readiness: Science-Backed Methods for Beekeepers
- The Second Half of the Measurement: Protecting the Integrity of Your Honey Refractometer
- From Profit to Spoilage: The One Number Every Commercial Beekeeper Must Know
- From Ambiguity to Certainty: The Practical Case for Digital Honey Refractometers




















