For beekeepers, honey quality isn’t just about taste—it’s a matter of shelf life, marketability, and profitability. The difference between premium-grade honey and a fermented batch often comes down to one critical factor: moisture content. This guide unpacks the science, tools, and techniques to help you measure and maintain optimal moisture levels reliably.
The Critical Role of Moisture Control in Beekeeping
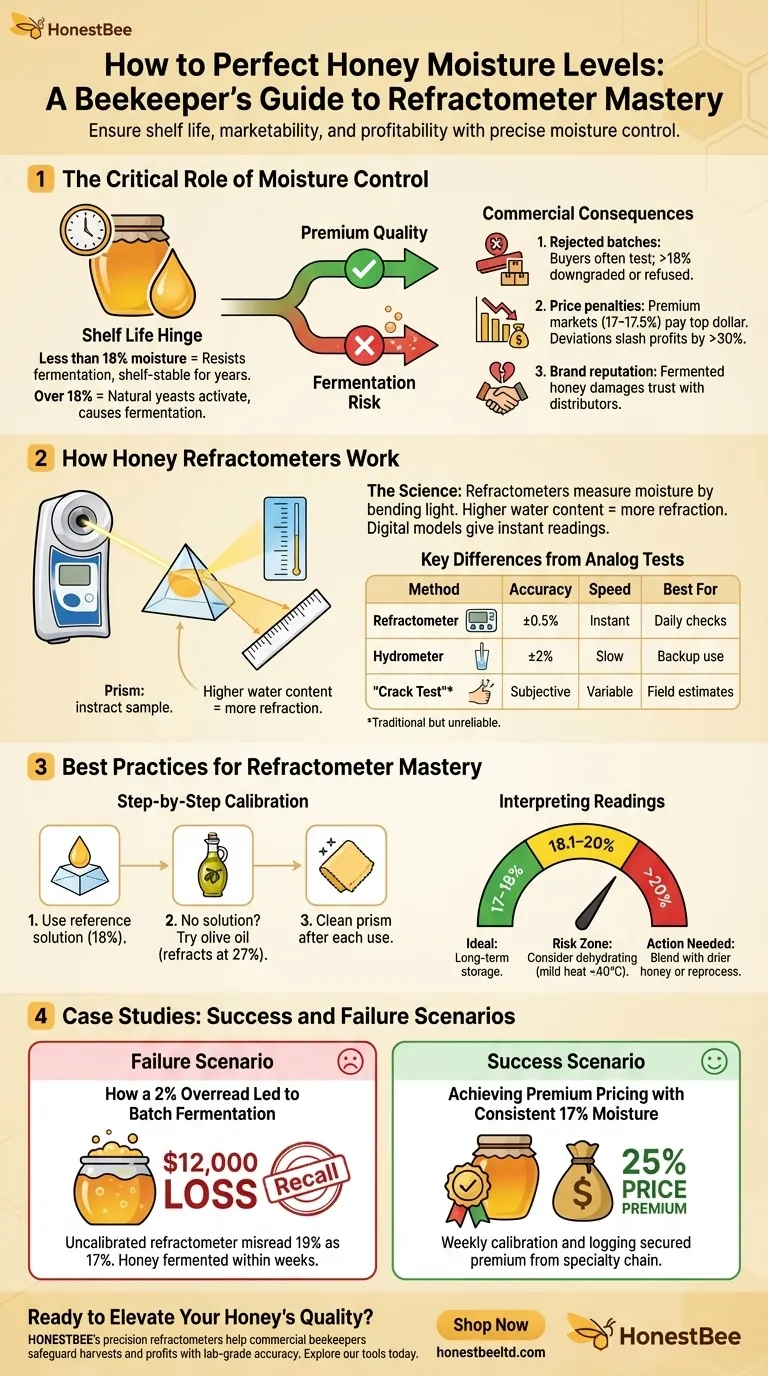
Why Moisture Content Determines Honey Shelf Life
Honey’s longevity hinges on its water content. Research shows that honey with less than 18% moisture resists fermentation and crystallization, staying shelf-stable for years. Exceed this threshold, and natural yeasts activate, turning your harvest into a bubbly, acidic mess.
Commercial Consequences of Improper Measurements
- Rejected batches: Buyers often test moisture levels, and honey over 18% may be downgraded or refused.
- Price penalties: Premium markets (e.g., organic or gourmet sectors) pay top dollar for honey with consistent 17–17.5% moisture, while deviations can slash profits by over 30%.
- Brand reputation: Fermented honey damages trust with distributors and consumers alike.
How Honey Refractometers Work
The Science Behind Optical Refraction
Refractometers measure moisture by bending light through a honey sample. The higher the water content, the more the light refracts. Digital models provide instant readings, while analog versions require manual calibration.
Key Differences from Analog Moisture Tests
| Method | Accuracy | Speed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refractometer | ±0.5% | Instant | Daily checks |
| Hydrometer | ±2% | Slow | Backup use |
| "Crack Test"* | Subjective | Variable | Field estimates |
*Squeezing honey to observe viscosity—a traditional but unreliable method.
Best Practices for Refractometer Mastery
Step-by-Step Calibration for Accuracy
- Use the reference solution included with your refractometer (typically labeled for 18% moisture).
- No solution? Try olive oil: It refracts at 27% moisture—adjust your device accordingly.
- Clean the prism after each use to avoid residue skewing results.
Interpreting Readings: From Theory to Action
- 17–18%: Ideal for long-term storage.
- 18.1–20%: Risk zone—consider dehydrating with mild heat (under 40°C).
- Over 20%: Immediate action needed (e.g., blending with drier honey or reprocessing).
Case Studies: Success and Failure Scenarios
How a 2% Overread Led to Batch Fermentation
A commercial apiary lost $12,000 when their uncalibrated refractometer misread 19% moisture as 17%. The honey fermented within weeks, forcing a recall.
Achieving Premium Pricing with Consistent 17% Moisture
By calibrating weekly and logging readings, a Colorado beekeeper secured a 25% price premium from a specialty grocery chain.
Ready to Elevate Your Honey’s Quality?
HONESTBEE’s precision refractometers help commercial beekeepers and distributors safeguard their harvests—and profits—with lab-grade accuracy. Explore our tools today and turn moisture control into a competitive edge.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Digital Honey Refractometer for Precision Measurement of Optimal Honey Quality
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Plastic Hand Crank 2 Frame Honey Extractor Low Price
- 6 Frame Manual Stainless Steel Honey Extractor Beekeeping Equipment
Related Articles
- How Honey Refractometers Protect Profits: A Science-Backed Guide to Harvest Timing and Quality Control
- The Unseen Architecture of Trust: Calibrating the Honey Refractometer
- The Professional’s Guide to Honey Refractometer Calibration: Ensuring Quality, Protecting Profit
- From Profit to Spoilage: The One Number Every Commercial Beekeeper Must Know
- How Beekeepers Prevent Honey Spoilage Through Precision Moisture Control




















