To determine the expected output of a honey stick machine, you must calculate its production rate over a specific period, accounting for its operational efficiency. The core calculation involves multiplying the machine's speed (sticks per minute) by the total minutes it runs per shift, and then adjusting that number by a realistic efficiency percentage to account for stoppages like film changes, honey refills, and maintenance.
The theoretical output stated by a manufacturer is only a starting point. Your actual, predictable output is a direct result of balancing the machine's speed against the practical realities of your specific operation, including honey viscosity, operator skill, and maintenance downtime.
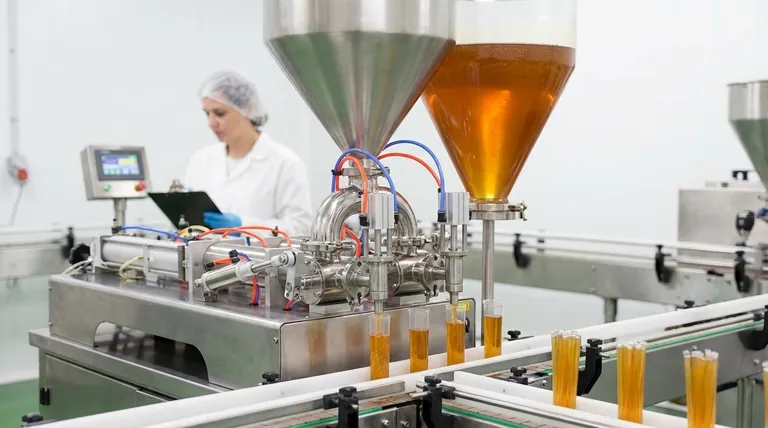

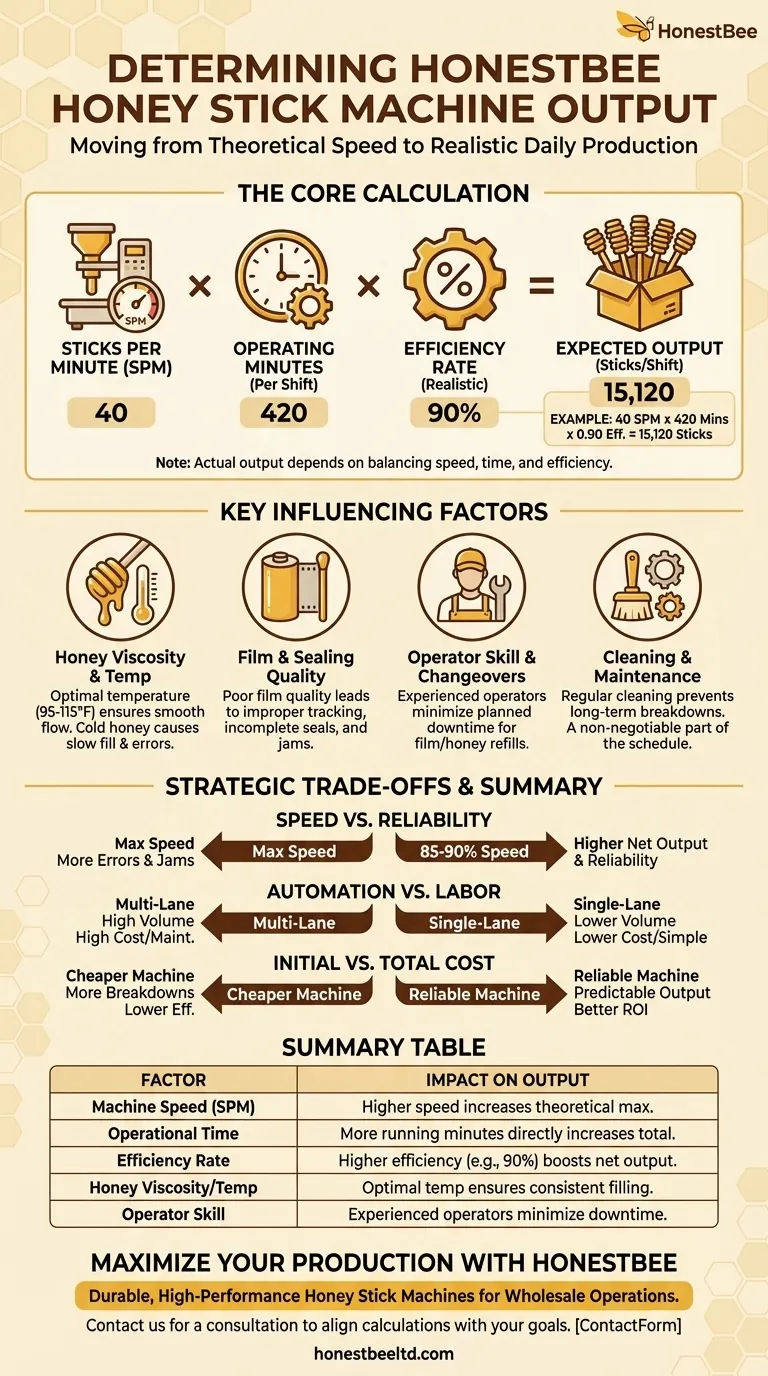
The Core Calculation: From Machine Speed to Daily Output
Calculating your expected output is a straightforward process. It begins with the machine's specifications and ends with a realistic, on-the-floor production figure.
Start with Sticks Per Minute (SPM)
Every honey stick machine has a rated speed, typically expressed as Sticks Per Minute (SPM) or pieces per minute. This is the theoretical maximum output under ideal conditions. For example, a machine might be rated at 40 SPM.
Factor in Operational Time
Next, determine the actual number of minutes the machine will be running. Do not simply use the total length of a work shift. You must subtract scheduled breaks, cleaning time, and other planned stoppages.
For an 8-hour (480-minute) shift with two 15-minute breaks and 30 minutes for end-of-day cleaning, your operational time would be 480 - 30 - 30 = 420 minutes.
Introduce the Reality: The Efficiency Rate
No machine runs perfectly without interruption. Unplanned downtime from film roll changes, honey hopper refills, or fixing jams is inevitable. This is captured by the efficiency rate.
A well-run operation might achieve a 90-95% efficiency rate. A new or less optimized process might be closer to 80-85%. It is critical to be realistic here.
The Final Formula
With these three variables, you can calculate your expected output.
Expected Output = (Sticks per Minute) x (Operating Minutes) x (Efficiency Rate)
Using our example: 40 SPM x 420 Minutes x 0.90 Efficiency = 15,120 sticks per shift.
Key Factors That Influence Your Real-World Output
The variables in the formula are not static. Several operational factors can dramatically impact your final numbers, forcing you to adjust machine speed or hurting your efficiency rate.
Honey Viscosity and Temperature
Honey that is too cold is thick and flows slowly. This can cause inconsistent filling volumes and may force you to run the machine at a lower SPM to compensate. Most operations use a heated, jacketed tank to keep the honey at an optimal, consistent temperature (typically 95-115°F or 35-46°C) for smooth flow.
Film and Sealing Quality
The quality and consistency of your plastic film roll are crucial. Poor quality film can track improperly or fail to seal, causing machine jams and product waste. This directly lowers your efficiency rate by increasing unplanned downtime.
Operator Skill and Changeovers
An experienced operator can perform routine tasks—like splicing a new roll of film or refilling the honey hopper—much faster than a novice. These changeover times are a primary source of planned downtime, and minimizing them is a key lever for increasing output.
Cleaning and Maintenance
A honey stick machine requires rigorous daily cleaning. This is non-negotiable downtime that must be factored into your schedule. Ignoring preventative maintenance may offer a short-term boost in operating minutes but will inevitably lead to longer, more costly breakdowns and a much lower overall efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and operating a machine involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making sound business decisions.
Speed vs. Reliability
Pushing a machine to its maximum rated SPM often increases the frequency of errors, such as incomplete seals or inaccurate fills. This leads to more waste and more frequent stops to clear jams.
Often, the highest net output is achieved by running the machine at 85-90% of its maximum speed. This small reduction in speed can result in a significant increase in reliability and overall efficiency.
Automation vs. Labor
Highly automated, multi-lane machines offer the highest potential output, capable of producing hundreds of sticks per minute. However, they come with a high capital cost and require more sophisticated maintenance.
Smaller, semi-automatic, or single-lane machines have a lower output but are far less expensive and simpler to operate. This makes them a more practical choice for startups or businesses producing smaller batches of artisanal flavors.
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
A cheaper machine may seem attractive, but if it is built with lower-quality components, it may suffer from more frequent breakdowns and have a lower efficiency rate. Over its lifetime, the cost of lost production and repairs can easily exceed the initial savings. A reliable, well-built machine delivers more predictable output and a better return on investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this understanding to align your calculations and equipment choice with your specific business objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production volume: Invest in a reliable, multi-lane machine and meticulously control your honey temperature and operator training to achieve a high efficiency rate (>90%).
- If your primary focus is starting a new business: Choose an affordable, single-lane machine and base your projections on a conservative efficiency rate (e.g., 85%) to ensure your business model is sound.
- If your primary focus is improving an existing operation: Begin tracking downtime meticulously. Categorize every stoppage to identify your biggest bottlenecks and calculate your true, current efficiency rate.
Ultimately, determining your honey stick output is a process of moving from a theoretical formula to a data-driven operational reality.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Output |
|---|---|
| Machine Speed (SPM) | Higher speed increases theoretical maximum output. |
| Operational Time | More running minutes directly increases total output. |
| Efficiency Rate | Higher efficiency (e.g., 90% vs. 80%) reduces waste and downtime, boosting net output. |
| Honey Viscosity/Temp | Optimal temperature ensures smooth flow and consistent filling, preventing speed reductions. |
| Operator Skill | Experienced operators minimize changeover and troubleshooting time, increasing efficiency. |
Ready to Maximize Your Honey Stick Production?
Accurate output calculations are key to profitability. Whether you're a commercial apiary scaling up or a distributor supplying reliable equipment, the right machine makes all the difference.
HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-performance honey stick machines and beekeeping equipment designed for wholesale operations. We help you achieve predictable, high-volume output.
Contact HONESTBEE today for a consultation to find the perfect machine for your production goals and operational needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Precision Automated Packaging Turntable Honey Spoon Filling Sealing Packing Machine
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
People Also Ask
- What role do automated honey-filling machines play in trade standards? Ensure Global Export Compliance & Consistency
- Why is a specialized honey filling machine necessary? Meet International Standards and Preserve Premium Honey Quality
- How do industrial honey filling machines ensure compliance? Master Quality Control for Global Export
- What is the primary function of industrial filling equipment? Maximize Honey Profitability and Market Access
- What role do automated honey filling machines play? Elevate Efficiency & Standardization in Honey Processing



















