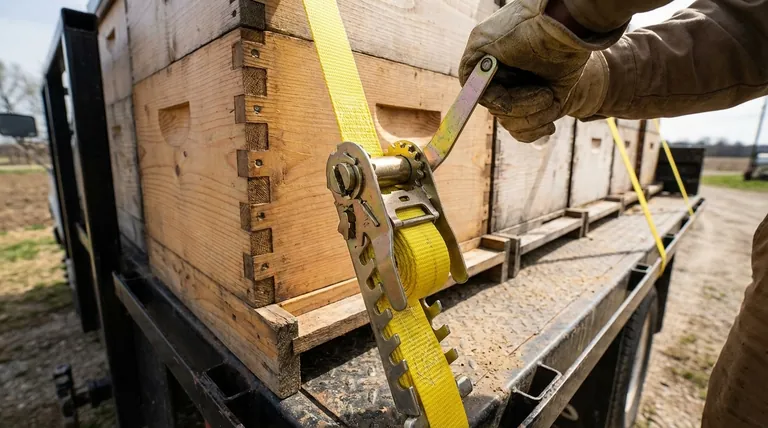
At its core, a ratchet strap works by using a simple lever and a geared spool to convert a back-and-forth handle motion into a powerful, one-way pulling force. The internal mechanism, called a pawl and gear system, allows you to incrementally tighten the webbing with significant mechanical advantage, ensuring the strap only gets tighter until you intentionally release it.
A ratchet strap's primary function is to provide mechanical advantage. It allows a user to apply immense tension to a strap with minimal physical effort, and its locking design ensures that tension is held securely without slipping.

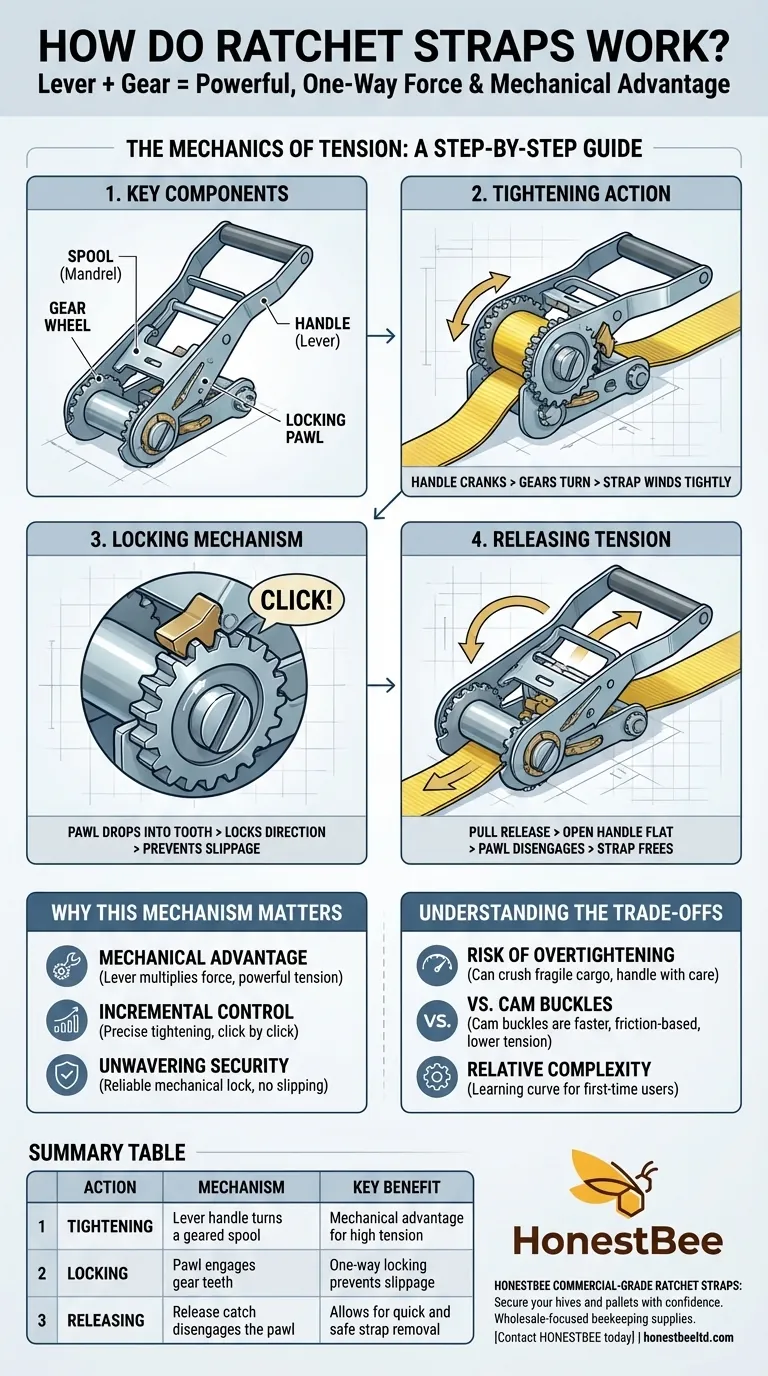
The Mechanics of Tension: A Step-by-Step Guide
To understand how a ratchet strap functions, it's best to break it down into its core components and actions. The design is elegantly simple once you see the parts at work.
### The Key Components
The mechanism consists of a spool (or mandrel) that the strap winds around, a gear wheel attached to that spool, and a locking pawl (a small metal catch) that engages the gear's teeth. The handle acts as a lever to turn this system.
### The Tightening Action
When you crank the handle, it engages the gear wheel, forcing the spool to rotate. This rotation pulls in the loose end of the webbing, winding it tightly around the spool.
### The Locking Mechanism
Each time you complete a pull and return the handle, the locking pawl drops into a tooth on the gear wheel. This acts as a one-way gate, preventing the spool from spinning backward and releasing the tension you just created. The "clicking" sound you hear is this pawl setting itself into the next tooth.
### Releasing the Tension
To release the strap, you typically pull a release catch and open the handle to a fully flat, 180-degree position. This action completely disengages the locking pawl from the gear, allowing the spool to spin freely and the strap to be pulled out.
Why This Mechanism Matters
The ratcheting design isn't just for convenience; it provides distinct advantages over simpler tie-down methods.
### The Power of Mechanical Advantage
The handle acts as a lever, multiplying the force you apply. This is why you can get a load significantly tighter with a ratchet strap than you could by simply pulling on a rope or a cam buckle strap.
### Incremental and Precise Control
Because the tightening happens in small increments with each "click," you have very fine control over the final tension. This allows you to secure a load until it is perfectly immobile.
### Unwavering Security
Once the locking pawl is engaged, the tension is set. Unlike a knot that can slip or a friction-based buckle that can give way, the mechanical lock of a ratchet is exceptionally reliable when used correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the ratchet mechanism is not the perfect solution for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging its potential downsides.
### Risk of Overtightening
The same mechanical advantage that provides security can also be a liability. It is very easy to apply too much force and damage or crush fragile cargo. Always tighten with care and check your load.
### Comparison to Cam Buckles
For lighter-duty tasks, a cam buckle is often faster. A cam buckle works on friction—you pull the strap tight by hand and a spring-loaded buckle bites down to hold it. It's quicker to use but cannot achieve the high tension of a ratchet strap.
### Relative Complexity
For a first-time user, threading the webbing through the spool and learning the release action can be confusing. It requires a moment of learning, whereas simpler straps are more intuitive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your tie-down method based on the specific demands of your cargo.
- If your primary focus is maximum security for heavy or large loads: The ratchet strap's superior mechanical advantage is the correct and safer choice.
- If your primary focus is speed and protecting fragile items: A simpler cam buckle strap is often a better tool, as it is faster and greatly reduces the risk of accidental overtightening.
- If your primary focus is frequent, light-duty securing: The quick, pull-to-tighten action of a cam buckle will likely be more efficient for your needs.
Ultimately, understanding the ratchet mechanism transforms it from a potentially confusing tool into a powerful and reliable partner for securing your most important cargo.
Summary Table:
| Action | Mechanism | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tightening | Lever handle turns a geared spool. | Mechanical advantage for high tension. |
| Locking | Pawl engages gear teeth. | One-way locking prevents slippage. |
| Releasing | Release catch disengages the pawl. | Allows for quick and safe strap removal. |
Need Reliable, High-Tension Ratchet Straps for Your Commercial Apiary or Distribution Business?
At HONESTBEE, we supply durable, commercial-grade beekeeping supplies and equipment, including heavy-duty ratchet straps designed for securing hives and pallets. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the quality and reliability your business depends on.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs and secure your loads with confidence!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Endless Loop Ratchet Hive Strap
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How should a cam buckle strap be installed for optimal performance? Master the Leverage for Maximum Tension
- What is the proper method for installing a cam buckle strap on a beehive? Secure Your Hives for Maximum Stability
- What is the best length for straps used around beehives? Why 12 Feet is the Industry Standard
- What are the types of Emlocks available? Choose the Right Strap for Hive Security
- What are the two styles of hive straps? Choose the Right Strap for Your Hive Security



















