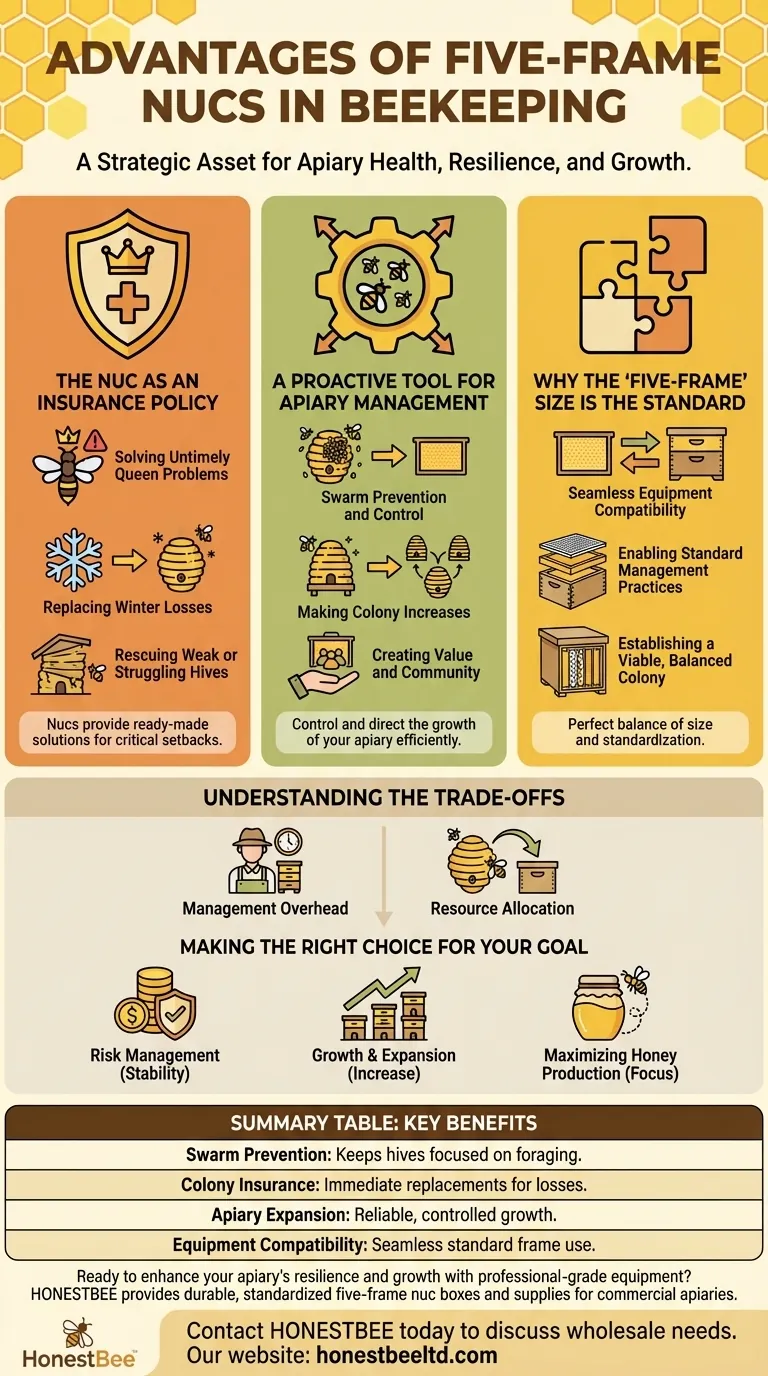
In beekeeping, the primary advantage of the five-frame nuc is its perfect balance of size and standardization. This specific configuration is large enough to support a viable, self-sustaining colony while remaining fully compatible with the standard frames and equipment used in full-sized ten-frame hives, making it an exceptionally versatile management tool.
A five-frame nucleus colony, or "nuc," is more than just a small beehive. It is a strategic asset that allows a beekeeper to proactively manage colony health, prevent swarms, and ensure the long-term resilience of their entire apiary.

The Nuc as an Insurance Policy
For any beekeeper, losing a colony is a significant setback. Nucs act as a powerful insurance policy, providing ready-made solutions to the most common and costly apiary problems.
Solving Untimely Queen Problems
A hive that unexpectedly loses its queen is in critical danger. A nuc with a laying queen provides an immediate fix. You can transfer the queen—or the entire nuc—to save the queenless colony, especially during times of the year when buying a replacement queen isn't an option.
Replacing Winter Losses
Many beekeepers create several nucs during the summer and overwinter them. These "spares" serve as immediate replacements for any full-sized production colonies that may die during the winter, allowing you to start the next season at full strength.
Rescuing Weak or Struggling Hives
A weak hive may not have the population to build up on its own. By transferring a frame of capped brood from a strong nuc into the weak hive, you can provide a massive population boost, helping the colony recover and thrive.
A Proactive Tool for Apiary Management
Beyond serving as a backup, the five-frame nuc is a fundamental tool for proactive and efficient hive management. It allows you to control and direct the growth of your apiary.
Swarm Prevention and Control
As a colony becomes crowded, its natural impulse is to swarm, which drastically reduces your honey-producing workforce. You can alleviate this congestion by pulling a few frames of brood, bees, and resources out of the strong hive to create a nuc. This relieves the pressure and keeps the production colony focused on foraging.
Making Colony Increases
Nucs are the most reliable method for expanding your apiary. By "splitting" a strong hive into one or more nucs, you can create new, healthy colonies, effectively doubling your stock or growing at a controlled pace.
Creating Value and Community
Well-managed nucs are valuable assets. If all your colonies survive the winter, these extra nucs can be sold to other beekeepers for profit or shared to help new beekeepers get started, strengthening your local beekeeping community.
Why the 'Five-Frame' Size Is the Standard
While nucs can come in various sizes, the five-frame configuration has become the industry standard for clear, practical reasons.
Seamless Equipment Compatibility
The most significant advantage is that five-frame nucs use the exact same frames as standard eight or ten-frame Langstroth hives. This allows you to interchange frames of brood, honey, or pollen between any of your colonies without any special equipment.
Enabling Standard Management Practices
This compatibility extends to other equipment. You can place a standard queen excluder on top of a booming five-frame nuc and add a honey super. This allows you to harvest honey from a nuc without worrying about brood in the honey frames, just as you would with a full-sized hive.
Establishing a Viable, Balanced Colony
A five-frame nuc is the ideal size to contain all the elements of a healthy colony: a queen, multiple frames of brood in all stages, and frames of pollen and honey for food. This balance makes it self-sufficient and poised for rapid growth, unlike smaller mating nucs which are more fragile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, incorporating nucs into your operation requires a clear understanding of the investment.
Management Overhead
A nuc is a living colony that requires its own inspections, feeding, and pest management. Maintaining several nucs adds to your overall workload.
Resource Allocation
The bees, brood, and food used to create a nuc are resources that are being diverted from a production hive. This is a strategic trade-off, investing in future stability at the cost of some immediate honey production potential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrating nucs into your apiary should align with your specific beekeeping objectives.
- If your primary focus is risk management and apiary stability: Use nucs to overwinter spare queens and have immediate replacements for any colony losses.
- If your primary focus is growth and expansion: Make nucs by splitting your strongest hives to steadily increase your colony count with local, adapted genetics.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Use nucs as a swarm-control method to keep your production hives populous and focused on foraging.
Ultimately, integrating five-frame nucs transforms your beekeeping from simple maintenance to strategic apiary management.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit for Beekeepers |
|---|---|
| Swarm Prevention | Keeps production hives focused on foraging by relieving congestion. |
| Colony Insurance | Provides immediate replacements for winter losses or queen failures. |
| Apiary Expansion | Enables reliable, controlled growth by splitting strong hives. |
| Equipment Compatibility | Uses standard Langstroth frames for seamless hive management. |
Ready to enhance your apiary's resilience and growth with professional-grade equipment?
As a trusted wholesale supplier, HONESTBEE provides commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, standardized five-frame nuc boxes and supplies needed to implement these strategic advantages. Let us help you build a more stable and profitable operation.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover our full product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 5 Frame Wooden Nuc Box for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Automatic Honey Flow Beehive 4 Frame Mini Hive for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
People Also Ask
- How should the nuc be installed in the apiary? Ensure Colony Success from Day One
- What are the benefits of starting a new bee colony in a nuc box? Boost Colony Success with Efficient Beekeeping
- What is a common feature of many 5-frame nuc boxes? The Integrated Feeder for Efficient Colony Growth
- What feeding feature is common in 5-frame nuc boxes? Explore Top-Feeding Innovation for Colony Growth
- When can nucleus colonies (nucs) be created? Optimal Timing for Apiary Growth and Survival



















