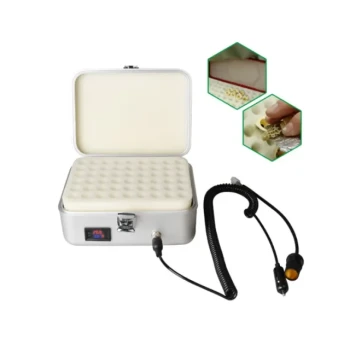
The primary role of a biochemical incubator in honey analysis is to provide a strictly controlled thermal environment essential for cultivating latent microorganisms. By maintaining precise temperatures—specifically 37°C for bacteria and 28°C for fungi—the device accelerates microbial growth to detectable levels. This capability allows analysts to perform accurate total viable counts, which serves as the fundamental metric for validating the hygiene of the honey harvesting and processing chain.
Reliable food safety testing depends on the ability to artificially replicate the conditions under which pathogens thrive. The biochemical incubator serves as the critical variable in this process, transforming a raw sample into a quantifiable dataset regarding bacterial and yeast contamination.
The Mechanism of Microbial Detection
Targeting Specific Organisms
Different microorganisms require distinct environmental triggers to multiply. A biochemical incubator is designed to hold specific temperatures with high precision to target these groups.
For bacterial cultivation, the device maintains a temperature of 37 degrees Celsius.
For yeast and fungal cultivation, the device is set to a lower temperature of 28 degrees Celsius.
Enabling Accurate Enumeration
Raw honey samples may contain microorganisms that are too few to detect immediately.
The incubator facilitates a specific incubation cycle, allowing these organisms to reproduce until they form visible colonies.
This growth is what allows for an accurate count of total viable bacteria and yeast, converting invisible contamination into measurable data.
Assessing Supply Chain Hygiene
Verifying Processing Standards
The data derived from incubation is not just about the final product; it is a diagnostic tool for the entire production line.
High microbial counts often indicate lapses in hygiene during the harvesting or processing stages.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Food safety standards dictate strict limits on permissible microbial load in honey.
The incubator provides the empirical evidence necessary to prove a product meets these food safety standards before it reaches the consumer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Calibration
The reliability of the test is entirely dependent on the machine's ability to maintain a constant temperature.
Even minor thermal fluctuations can inhibit growth or kill sensitive organisms, leading to false negatives.
Time dependency
Biochemical incubation is not an instantaneous test; it relies on biological time scales.
The "incubation cycle" represents a fixed waiting period, meaning safety clearance is always delayed by the time required for culture growth.
Ensuring Reliable Safety Standards
To effectively utilize a biochemical incubator for honey safety, align your settings with your specific testing goals:
- If your primary focus is Bacterial Detection: Ensure the incubator is calibrated strictly to 37°C to simulate the optimal environment for common bacterial pathogens.
- If your primary focus is Yeast and Mold: Adjust the environment to 28°C, as these organisms generally require cooler conditions to thrive and form countable colonies.
Precise temperature regulation is the only way to transform a biological sample into a verified safety certification.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Targeted Microorganism | Incubation Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 37°C Setting | Bacteria | Cultivation for total viable counts |
| 28°C Setting | Yeast & Fungi/Mold | Detection of fermentation and spoilage |
| Incubation Cycle | All latent microbes | Accelerate growth for visible enumeration |
| Thermal Stability | Sensitive Pathogens | Prevent false negatives through calibration |
Elevate Your Honey Quality Standards with HONESTBEE
Maintaining the highest hygiene levels is essential for commercial success in the honey industry. HONESTBEE specializes in supporting commercial apiaries and distributors by providing the professional-grade tools and machinery required to meet global safety standards.
Whether you are scaling your production with our honey-filling and hive-making machines or need a steady supply of essential industry consumables, we offer a comprehensive wholesale portfolio tailored to your growth.
Partner with us to secure your supply chain today:
- Expert Equipment: From specialized hardware to precision testing support.
- Wholesale Efficiency: High-quality beekeeping tools at scale.
- Brand Value: Unique honey-themed cultural merchandise for your storefront.
Contact HONESTBEE Today to Discuss Your Wholesale Needs
References
- Grace Oluwakemi Babarinde, Sinmilolu I. Ajayeoba. Effects of harvesting methods on physicochemical and microbial qualities of honey. DOI: 10.1007/s13197-011-0329-9
This article is also based on technical information from HonestBee Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Portable Queen Bee Incubator with 12V Car Adapter for Safe Transport
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
- HONESTBEE Professional Mini J-Hook Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Queen Catcher and Introduction Queen Cage
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial constant temperature and humidity incubator required for queen bee development? Ensure Vitality.
- What is the primary function of a constant temperature and humidity incubator in queen bee rearing? Optimize Emergence
- What biosecurity risks are associated with honeybee breeding tools? Protect Your Apiary from Transboundary Disease
- Why are high-precision constant temperature and humidity incubators necessary? Secure Your Queen Bee Emergence
- What is the purpose of using high-precision incubators in queen rearing? Ensure Superior Queen Vitality