In short, a beehive box is the central component of a modern beehive. Also known as a hive body or brood box, its primary purpose is to provide a protected, structured space for the queen bee to lay eggs and for the colony to raise its young (the brood). It serves as the main living quarters and nursery for the entire bee colony.
The beehive box is more than just a container; it is the heart of the colony. It's the dedicated space for reproduction and the core of the hive's social structure, directly influencing the colony's health, growth, and survival.

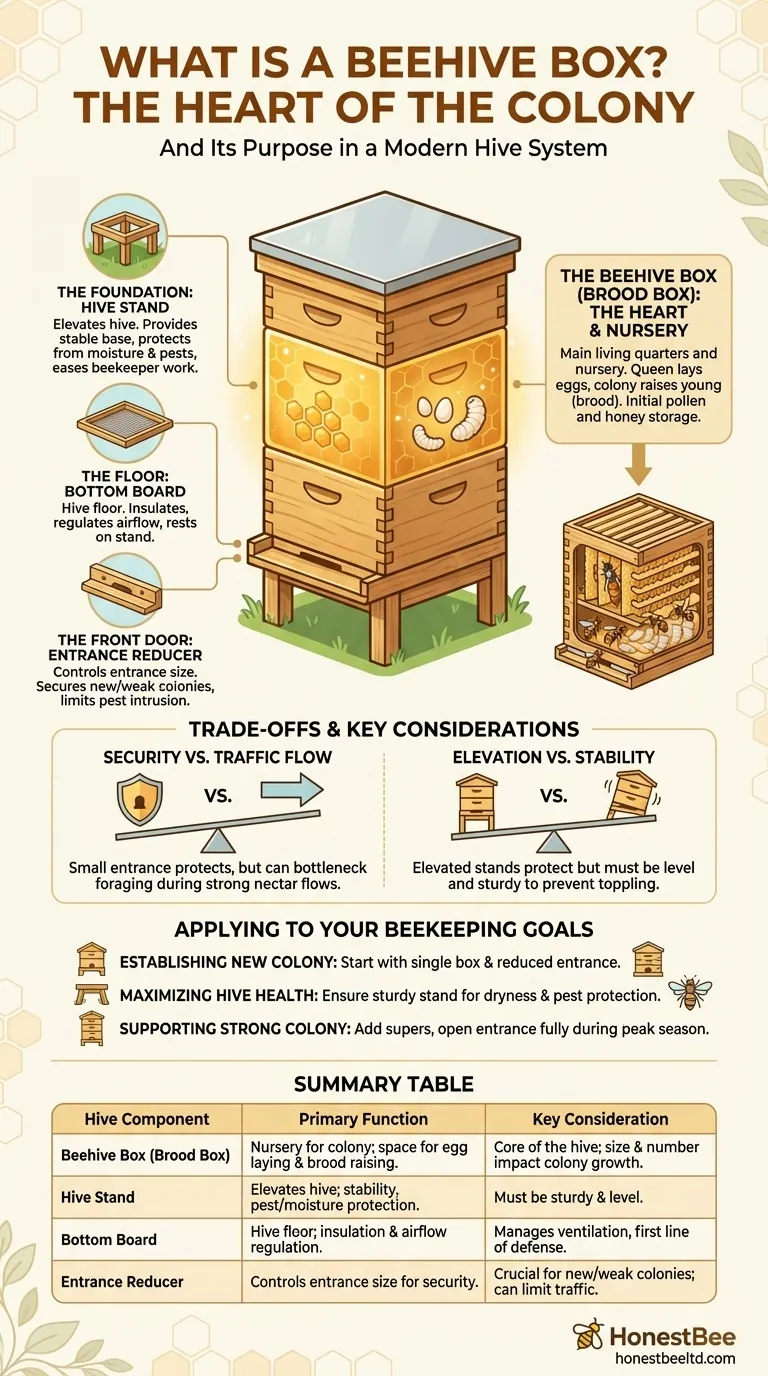
The Beehive Box in Context: Anatomy of a Hive
A beehive box does not function in isolation. It is part of a modular system where each component serves a critical role in maintaining a healthy, productive colony. Understanding these parts reveals how the hive functions as a whole.
The Foundation: The Hive Stand
A hive stand is the structure that elevates the entire beehive off the ground. It can be made of wood, metal, or plastic.
Its purpose is to provide a stable, level base. This elevation protects the hive from ground moisture, deters pests like skunks, and makes it easier for the beekeeper to work without excessive bending.
The Floor: The Bottom Board
Resting directly on the stand is the bottom board, which serves as the floor of the hive. This component provides insulation from the ground and helps regulate airflow. It is the base upon which the beehive boxes are stacked.
The Heart of the Colony: The Beehive Box
The beehive box, or brood box, sits directly on the bottom board. This is the largest section of the hive and is where the colony's life begins and is sustained.
Inside, the queen lays her eggs, and the worker bees raise the larvae. It also houses the initial stores of pollen and honey used to feed the developing bees and the queen.
The Front Door: The Entrance Reducer
An entrance reducer is a small, often wooden, cleat that fits into the opening on the bottom board. It allows a beekeeper to control the size of the hive's entrance.
For a new or weak colony, a smaller entrance is easier for the guard bees to defend against robber bees from other hives or pests like wasps.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While the concept is straightforward, the implementation of these components involves important decisions that impact the colony's well-being.
Security vs. Traffic Flow
Using an entrance reducer is critical for protecting a young colony. However, a small entrance can create a bottleneck for foraging bees during a strong nectar flow, potentially reducing the amount of honey they can bring in.
Elevation vs. Stability
A hive stand is essential for hive health, but it must be stable. A wobbly or unlevel stand can put the entire hive at risk, especially in high winds or if bumped by animals or equipment.
Protection vs. Ventilation
The hive must protect the bees from the elements, but it also needs adequate ventilation. The bottom board and the hive entrance are key to managing airflow, which is crucial for controlling temperature and humidity within the hive.
How to Apply This to Your Beekeeping Goals
Choosing and managing your hive components correctly is fundamental to success. Your priorities will guide your approach.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new colony: Start with a single beehive box and a reduced entrance to give the small population a secure, manageable space to defend and grow.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hive health: Ensure your setup includes a sturdy hive stand to protect the hive from dampness and pests, promoting a drier, healthier internal environment.
- If your primary focus is supporting a strong, established colony: Be prepared to add more boxes for honey storage (called "supers") and open the entrance fully during peak season to maximize foraging efficiency.
Understanding how each part supports the central function of the beehive box is the first step toward becoming a successful and responsible beekeeper.
Summary Table:
| Hive Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Beehive Box (Brood Box) | Nursery for the colony; space for the queen to lay eggs and raise brood. | The core of the hive; size and number directly impact colony growth. |
| Hive Stand | Elevates the hive off the ground for stability and pest/moisture protection. | Must be sturdy and level to prevent the hive from toppling. |
| Bottom Board | Acts as the hive floor, providing insulation and helping regulate airflow. | Manages ventilation and is the first line of defense against some pests. |
| Entrance Reducer | Controls the size of the hive entrance for security and defense. | Crucial for new/weak colonies but can limit traffic during heavy nectar flows. |
Ready to build a strong foundation for your apiary?
As a leading wholesale supplier, HONESTBEE provides commercial apiaries and equipment distributors with the durable, high-quality beehive boxes and components needed for thriving colonies. Our products are designed to support the health and productivity of your bees, season after season.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and get a quote. Let us help you equip your beekeeping operation for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Honey Bee Box Hive Boxes for Different Depths
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Portable Bee Mating Hive Boxes Mini Mating Nucs 8 Frames for Queen Rearing
- Professional Engraved Round Hive Number Tags for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How do frame sizes relate to the different types of Langstroth boxes? Master Hive Compatibility Today
- What are the sizes available for Langstroth boxes? A Guide to 8-Frame vs. 10-Frame & Depths
- How does a hive box work? A Guide to the Langstroth Hive System for Beekeepers
- How should hive boxes be aligned after reassembly? Ensure a Perfect Seal for Hive Health
- What is a hive body in a Langstroth hive? Essential Guide to Brood Chambers and Standard Dimensions



















