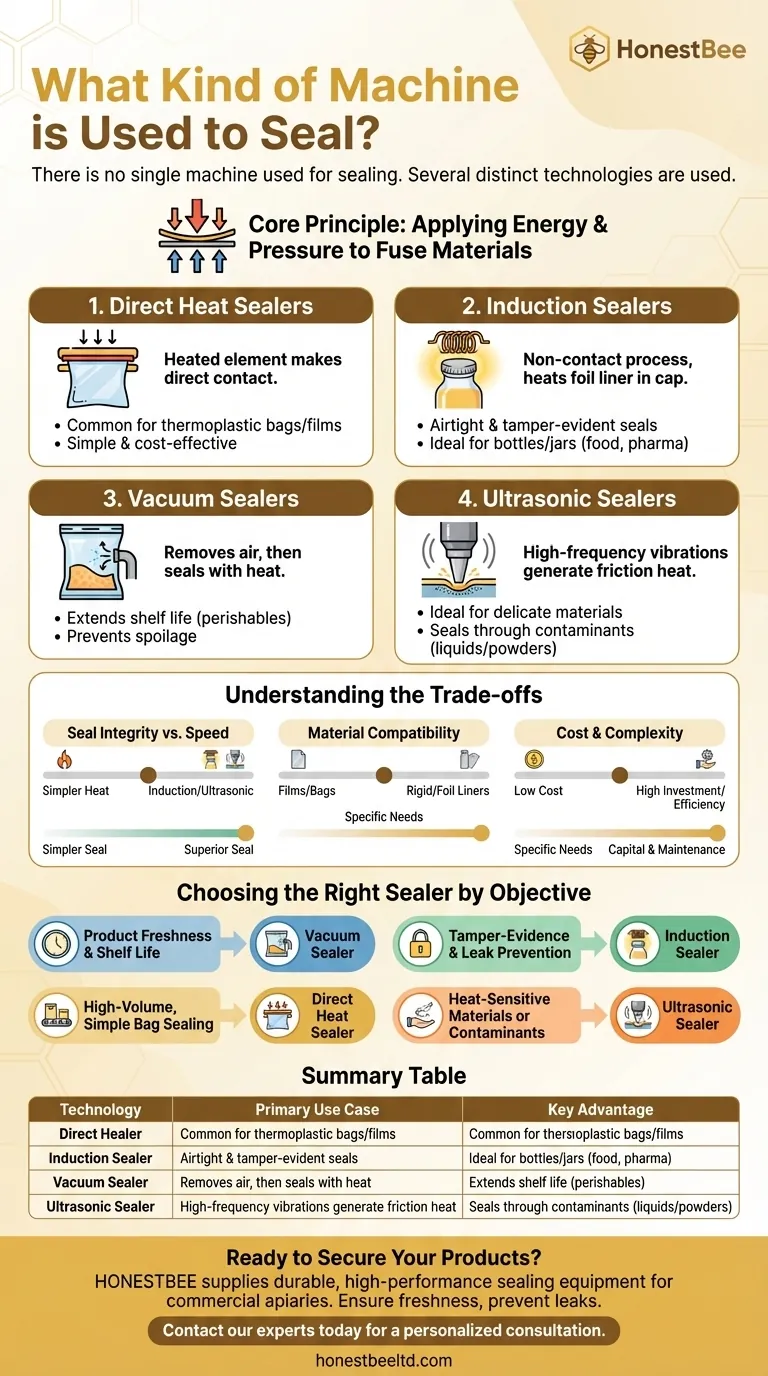
There is no single machine used for sealing. Instead, several distinct technologies are used, each designed for specific materials, container types, and operational goals. The most common types include direct heat sealers, vacuum sealers, induction sealers, and ultrasonic sealers, all of which work by applying energy to create a secure, often airtight, bond.
The critical insight is not to ask "what machine seals," but "what is my sealing objective?" The right technology depends entirely on whether your goal is product freshness, tamper-evidence, high-speed production, or compatibility with sensitive materials.

How Sealing Machines Fundamentally Work
All sealing machines operate on a core principle: applying a focused form of energy to fuse materials together. The method of energy delivery is what differentiates one type of machine from another.
The Role of Energy and Pressure
Most sealing processes use a combination of energy (typically heat) and pressure. The energy raises the temperature of the sealing surfaces to a molten or semi-molten state, and pressure ensures the materials meld together to form a uniform, permanent bond as they cool.
Key Types of Sealing Technologies
Understanding the four primary sealing methods will clarify which is appropriate for your needs. Each excels in different applications.
Direct Heat Sealers
This is the most straightforward sealing method. A heated element, such as a bar or a continuous band, makes direct physical contact with the material to be sealed.
These machines are common for sealing thermoplastic bags and films. Their simplicity makes them cost-effective and easy to operate for basic packaging tasks.
Induction Sealers
Induction sealing is a non-contact process used to create an airtight and tamper-evident seal on the opening of a bottle or jar. It is a cornerstone of product safety in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
The process uses an electromagnetic field to heat a foil liner inside the cap. This heat melts a polymer layer on the foil, which then fuses to the rim of thecontainer, creating a hermetic seal without heating the entire product.
Vacuum Sealers
Vacuum sealers perform a critical two-step function: first, they remove the air from a package, and second, they create a seal using a heated bar.
By removing oxygen, these machines dramatically extend the shelf life of perishable goods, especially food. They are essential for preventing spoilage and maintaining product freshness.
Ultrasonic Sealers
This advanced method uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create a seal. The vibrations cause intense friction between the materials, which generates localized heat almost instantly.
This process is ideal for delicate materials or products that are sensitive to external heat. It also works well through contaminants like powders or liquids that might be present in the seal area, something direct heat sealers struggle with.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sealing technology involves balancing speed, cost, and the specific requirements of your product and packaging.
Seal Integrity vs. Speed
Simpler direct heat sealers can be very fast for basic bag sealing. However, induction sealers provide a superior, tamper-evident hermetic seal that is critical for liquid products or those requiring a guarantee of safety.
Material Compatibility
Your packaging material dictates your choice. Induction sealing requires containers with a compatible foil liner in the cap. Ultrasonic sealing excels with rigid thermoplastics but may not work on all flexible films.
Cost and Complexity
Direct heat sealers are typically the least expensive and simplest to maintain. In contrast, ultrasonic and high-speed induction systems represent a larger capital investment but can offer greater efficiency, less waste, and higher-quality seals for demanding applications.
Choosing the Right Sealer for Your Application
Use your primary objective to guide your decision. Each technology is a tool designed for a specific job.
- If your primary focus is product freshness and shelf life: A vacuum sealer is the correct choice for removing corrosive oxygen before sealing.
- If your primary focus is tamper-evidence and leak prevention for bottles/jars: An induction sealer is the industry standard and the most effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, simple bag sealing: A direct heat sealer (either impulse or continuous band) offers the best balance of speed and cost.
- If your primary focus is sealing heat-sensitive materials or through contaminants: An ultrasonic sealer provides a precise, powerful bond without external heat.
Ultimately, selecting the right machine begins with a clear definition of your operational and product-related goals.
Summary Table:
| Sealing Technology | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Heat Sealer | Sealing bags and flexible films | Cost-effective and simple operation |
| Induction Sealer | Tamper-evident seals on bottles/jars | Creates airtight, hermetic seals |
| Vacuum Sealer | Extending shelf life of perishables | Removes oxygen to prevent spoilage |
| Ultrasonic Sealer | Heat-sensitive materials or contaminated areas | No external heat; precise, strong bonds |
Ready to Secure Your Products with the Right Sealing Solution?
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, high-performance sealing equipment needed to protect honey, beeswax, and other hive products. Ensure product freshness, prevent leaks, and maintain quality from your facility to your customers.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation on the best sealing machines for your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Handheld Induction Sealing Machine for Tamper Evident Packaging
- Automatic Continuous Heat Sealing Machine
- Professional Frame Preparation: The HONESTBEE Electric Wire Embedder
- 10L Stainless Steel Honey Wax Press Extractor for Wax Cappings
- HONESTBEE Adjustable Voltage Wire Embedder with Digital Display
People Also Ask
- Why is the proper sealing of honey jars considered a critical component in honey production? Protect Quality & Growth
- What advantages do vacuum sealing bags provide for the storage of dried bee pollen? Preserve Freshness and Potency
- What is a sealing machine called? Choose the Right Heat Sealer for Your Packaging
- What defines a 4-side seal on a package? Discover the Benefits of Total Perimeter Sealing for Maximum Security
- What are the causes and solutions for leakage in a stick pack seal? Fix Pressure, Temperature, and Hardware Issues
- How do I choose a heat sealer? A Guide to Matching the Right Machine to Your Needs
- How do modern honey packaging and sealing equipment enhance the commercial value of honey products? Boost Your ROI Today
- How does an induction sealing machine work? Enhance Honey Packaging with Hermetic Seals & Tamper Evidence



















