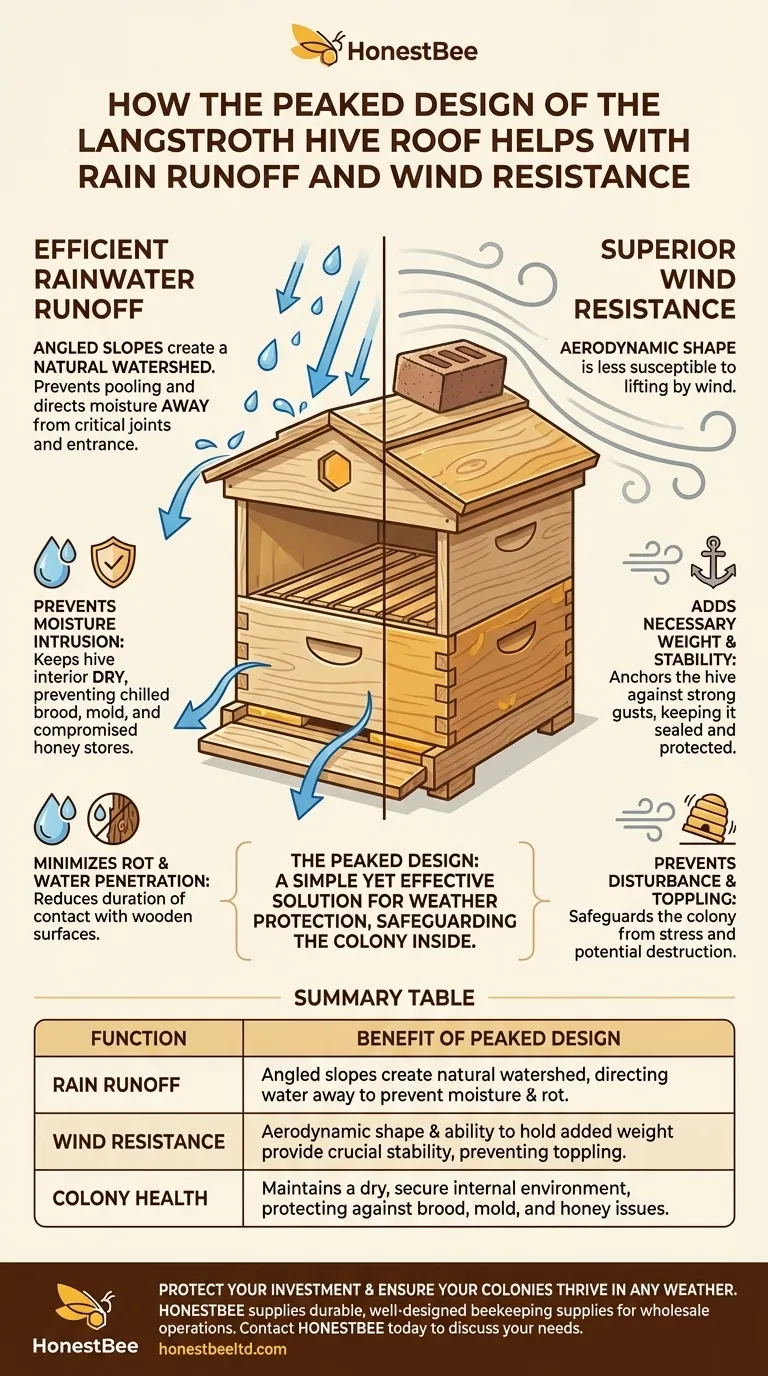
The peaked design of a Langstroth hive roof is a simple yet highly effective solution for weather protection. Its angled construction is engineered to channel rainwater away from the hive entrance and body, while its shape and weight provide crucial stability against strong winds, safeguarding the colony inside.
A hive roof is more than a simple cover; it is the colony's first line of defense against the elements. The peaked design's ability to manage rain and wind is fundamental to maintaining the stable, dry, and secure internal environment a honeybee colony needs to thrive.

The Purpose of a Protective Hive Roof
A hive is a finely balanced ecosystem. The roof's primary job is to protect that balance from external threats, specifically moisture and physical disturbance.
Preventing Moisture Intrusion
Moisture is a significant threat to a honeybee colony. A damp hive interior can lead to chilled brood, the growth of mold and mildew, and compromised honey stores.
The angled slopes of a peaked roof ensure that rainwater runs off immediately and is directed away from the hive body and its critical joints. This prevents water from seeping into cracks and compromising the wooden components.
Ensuring Structural Stability
Wind can easily disturb or even topple a hive, causing immense stress to the colony and potentially destroying it. The roof is the most exposed component.
A well-designed peaked roof adds necessary weight and presents a low-profile, aerodynamic shape that helps keep it securely in place during high wind gusts. This stability is essential for keeping the hive sealed and protected.
How the Peaked Design Works
The effectiveness of the peaked Langstroth roof lies in its straightforward application of basic physics to solve beekeeping challenges.
Efficient Rainwater Runoff
Unlike a flat top that allows water to pool, the peak creates a natural watershed. Water immediately flows down the slopes and off the edges, far from the hive entrance and the seams between hive boxes.
This design minimizes the duration of contact between water and the hive's wooden surfaces, drastically reducing the chances of rot and water penetration.
Superior Wind Resistance
The gentle slope of a peaked roof is less susceptible to being lifted by wind compared to a flat roof with extended edges that can act like a wing.
Furthermore, these roofs are often constructed to be heavier or are designed to accommodate a brick or rock on top, adding mass that anchors the entire hive structure against gusts.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While the design is effective, its performance depends on proper use and maintenance. Neglecting the roof can undermine its protective benefits.
The Risk of a Poor Seal
The roof must fit securely on the inner cover or top hive body. Any gaps can create a channel for wind-driven rain to enter the hive, defeating the roof's primary purpose.
Regularly check for warping or damage on both the roof and the top edge of your hive boxes to ensure a snug fit.
The Mistake of Inadequate Weight
In areas prone to high winds, the roof's inherent weight may not be enough. Many beekeepers place a heavy, flat rock or brick on top of the peaked roof.
This simple action dramatically increases the hive's stability and is a low-cost insurance policy against losing a roof—or an entire hive—in a storm.
Making the Right Choice for Your Colony
Choosing and maintaining your hive roof should be directly aligned with the goal of promoting colony health and equipment longevity.
- If your primary focus is colony health: Ensure your peaked roof effectively prevents all moisture from entering the hive, as a dry environment is critical for preventing disease.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Regularly inspect and repaint your roof to protect the wood, ensuring it continues to shed water effectively for years.
- If your primary focus is security in a high-wind area: Always place a heavy weight on your roof to guarantee it remains in place during severe weather events.
Ultimately, a well-maintained peaked roof is a simple and powerful tool for protecting your most valuable beekeeping asset: the colony itself.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit of Peaked Design |
|---|---|
| Rain Runoff | Angled slopes create a natural watershed, directing water away from the hive body and entrance to prevent moisture intrusion and rot. |
| Wind Resistance | Aerodynamic shape and ability to hold added weight (e.g., a brick) provide crucial stability, preventing the hive from being disturbed or toppled. |
| Colony Health | Maintains a dry, secure internal environment, protecting against chilled brood, mold, and compromised honey stores. |
Protect your investment and ensure your colonies thrive in any weather. The right equipment is fundamental to successful beekeeping. HONESTBEE supplies durable, well-designed beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. Let us help you build a more resilient operation.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our equipment can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Insulated Winter Hive Wrap for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Stainless Steel J-Hook Hive Tool
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What is the function of dark-colored hive coverings in regions with significant winter sunshine? Boost Colony Survival
- What key factors should a beekeeper consider before wrapping a beehive? 3 Essentials for Winter Survival
- Why are insulation wraps critical for outdoor honey bee wintering? Maximize Colony Survival & Energy Efficiency
- Why is it critical to keep beehive covers closed during the winter months? Protect Your Colony's Thermal Energy
- What is the critical function of top insulation covers in a winterized beehive? Maximize Colony Survival with Heat Trapping



















