At its core, a beehive is a man-made structure designed to house a honey bee colony. It provides a secure, organized environment that allows beekeepers to manage the bees for specific purposes, including honey production, agricultural pollination, apitherapy treatments, and the conservation of bee populations.
A beehive is more than just a box for bees; it is a sophisticated, modular tool. Its design allows a beekeeper to protect the colony from the elements, easily inspect its health, and efficiently harvest products like honey without destroying the hive itself.
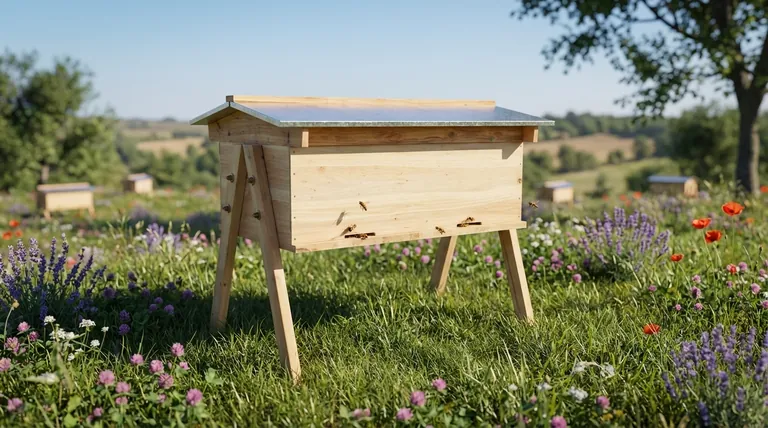

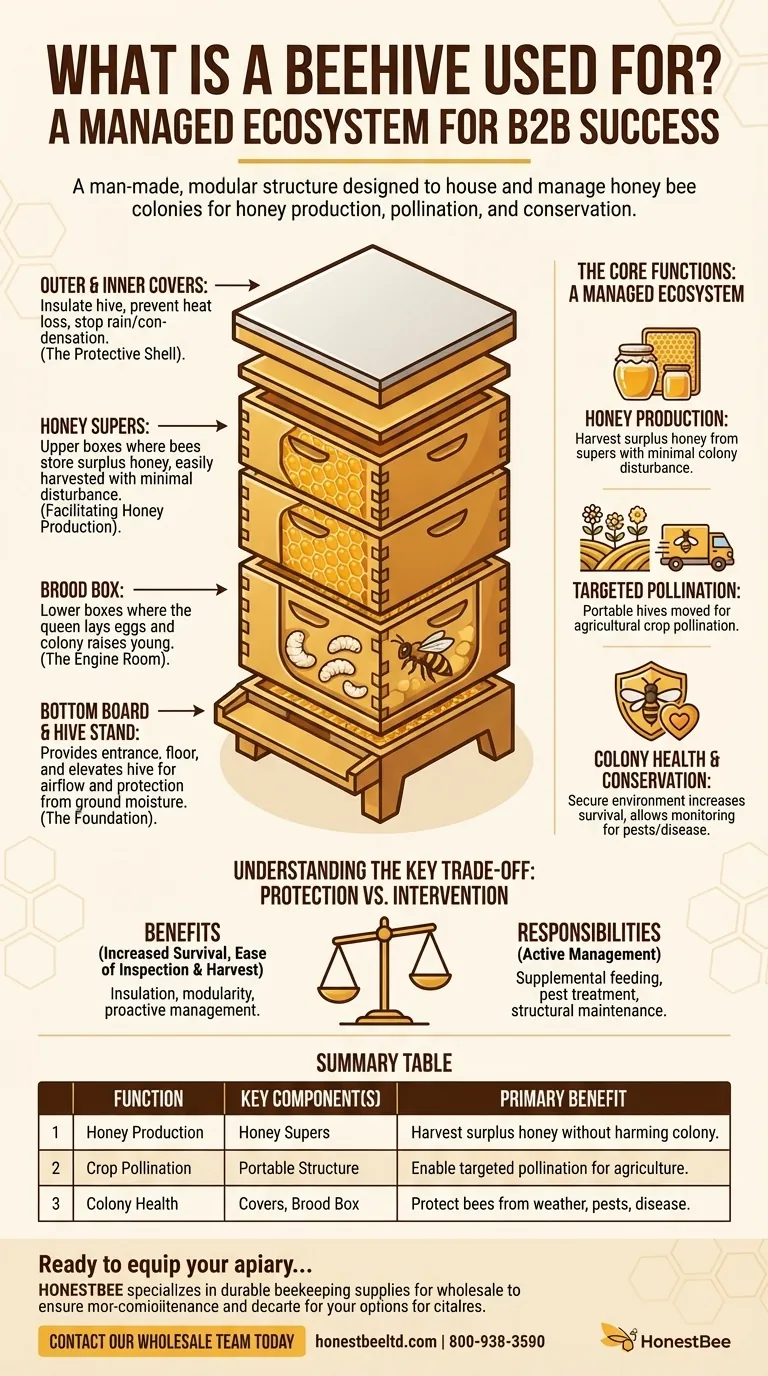
The Core Functions: A Managed Ecosystem
A modern beehive allows humans to partner with bees, directing their natural behaviors toward specific, mutually beneficial goals. It turns a wild colony into a managed resource.
Facilitating Honey Production
The hive's modular design, typically using boxes called supers, separates the queen's egg-laying area (the brood box) from the honey storage area.
This allows beekeepers to harvest surplus honey from the supers with minimal disturbance to the colony's nursery.
Enabling Targeted Pollination
Beehives are portable. This portability is critical for modern agriculture, where beekeepers transport hives across the country to pollinate specific crops as they come into bloom.
This service is essential for the production of fruits, nuts, and vegetables.
Supporting Colony Health and Conservation
By providing a secure and insulated home, a beehive significantly increases a colony's chance of surviving winter and other environmental stressors.
This managed environment helps beekeepers monitor for disease and pests, playing a crucial role in mitigating the effects of issues like Colony Collapse Disorder.
Anatomy of a Modern Beehive
A typical hive is not a single piece but a stack of interacting components, each with a specific function designed to regulate the colony's environment.
The Foundation: Bottom Board and Stand
The hive rests on a bottom board, which serves as the floor and entrance. It is often placed on a hive stand.
Elevating the hive protects the wooden components from ground moisture, improves air circulation, and keeps the entrance clear of grass and debris.
The Engine Room: Brood Box and Supers
The middle section contains the colony's living quarters. The lower boxes, or brood boxes, are where the queen lays eggs and the colony raises its young.
The upper boxes, called honey supers, are where the bees store surplus honey. This is the honey that a beekeeper typically harvests.
The Protective Shell: Inner and Outer Covers
The top of the hive consists of an inner cover and a telescoping outer cover.
These components are critical for environmental control. They insulate the hive, prevent heat loss, and most importantly, stop rainwater and condensation from dripping onto the bees, which can be fatal in cold weather.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Protection vs. Intervention
Using a man-made hive is fundamentally different from leaving a colony to its own devices in the wild. This intervention comes with significant advantages but also responsibilities.
Benefit: Increased Survival and Productivity
A well-managed hive dramatically increases a colony's survival rate. The insulated covers help the bees thermoregulate, saving them energy and leading to larger, more productive colonies come springtime.
Benefit: Ease of Inspection and Harvest
The modular frame system allows a beekeeper to easily remove and inspect combs for signs of disease, check the queen's health, and assess food stores. This makes proactive management possible.
The Responsibility: Active Management
Unlike a wild colony, a managed colony often relies on the beekeeper. This can include providing supplemental food during shortages, treating for pests like Varroa mites, and ensuring the hive structure remains sound and protective.
Applying This to Your Goal
The way you manage a hive depends entirely on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is honey production: Your goal will be to grow a large, strong colony and add honey supers at the right time to capture the nectar flow.
- If your primary focus is garden pollination: You can maintain a smaller, single-box hive, focusing on colony health and stability rather than maximizing honey surplus.
- If your primary focus is bee conservation: Your management will prioritize minimal intervention, ensuring the bees have a safe, weatherproof home and sufficient food stores to thrive naturally.
Ultimately, the beehive is the essential interface that makes the partnership between humans and honey bees possible.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Component(s) | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Honey Production | Honey Supers | Harvest surplus honey without harming the colony. |
| Crop Pollination | Portable Hive Structure | Enable targeted pollination for agriculture. |
| Colony Health & Conservation | Insulated Covers, Brood Box | Protect bees from weather, pests, and disease. |
Ready to equip your apiary or supply your customers with reliable beekeeping equipment?
As HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying durable, high-performance beehives and beekeeping supplies to commercial apiaries and equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. Partner with us to get the tools you need for successful honey production, effective pollination services, and robust colony health management.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs and request a catalog!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
- Professional Insulated Winter Hive Wrap for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a top bar hive? Simpler, Bee-Centric Beekeeping for All
- What is a horizontal top bar hive? Discover Natural and Ergonomic Beekeeping Benefits
- What are the most popular types of hives besides the Langstroth? Top Bar & Horizontal Hives Explained
- How does the design of a top bar hive benefit beekeepers? Ergonomic & Natural Beekeeping for Hobbyists
- What are the benefits of the top bar hive? A Guide to Ergonomic, Natural Beekeeping



















