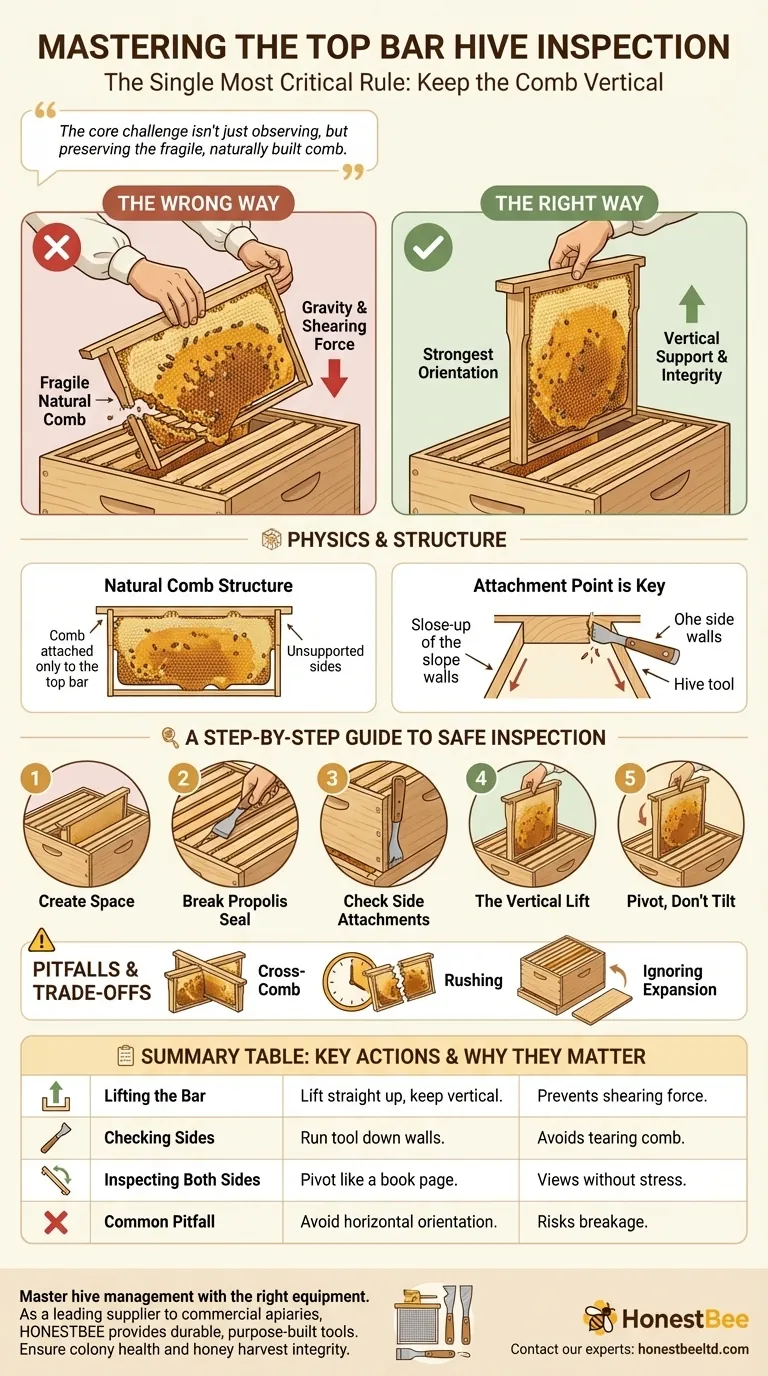
The single most critical rule for inspecting a top bar hive is to always keep the comb oriented vertically, exactly as it hangs inside the hive. When a bar is lifted, you must resist the instinct to turn it horizontally. This simple discipline prevents the delicate, naturally-drawn comb from breaking off the bar under its own weight.
The core challenge of top bar hive inspection isn't just observing the bees, but preserving the fragile, naturally built comb. Unlike in framed hives, the comb's structural integrity depends entirely on your careful handling, making a slow and deliberate technique essential for the colony's survival.

The Physics of a Top Bar Comb
To handle the comb correctly, you must first understand its structure. The method is a direct result of the hive's design.
Understanding Natural Comb Structure
A top bar hive encourages bees to build comb naturally, hanging down from a single wooden bar. This comb is not reinforced by a surrounding frame or foundation wires, making it exceptionally fragile.
The Force of Gravity
When the comb is held vertically, its weight is transferred directly up to the top bar where it is attached. This is its strongest orientation.
If you tilt the comb horizontally, gravity pulls downward on the entire face of the comb, creating a shearing force at the narrow attachment point along the bar. A heavy comb full of honey or brood will almost certainly tear away and break.
The Attachment Point is Key
The bees attach the comb to the bar and, ideally, nowhere else. The sloped sides of the hive are designed to discourage attachment to the walls, but it can still happen. A successful inspection depends on ensuring the comb is only attached to the bar you are lifting.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Inspection
A proper inspection is a calm and methodical process. Rushing is the primary cause of broken comb and agitated bees.
1. Create Working Space
Gently pry and remove the first or last bar in the hive, which is often empty or contains only light honey stores. This gives you the necessary room to maneuver the other bars without rolling bees or damaging adjacent comb.
2. Break the Propolis Seal
Bees will seal the bars together with propolis. Use your hive tool to gently pry the bar you wish to inspect loose from its neighbors on both sides.
3. Check for Side Attachments
Before lifting, slowly run your hive tool down the sides of the hive wall next to the comb. This will gently detach any small comb connections the bees may have built to the hive body. Failure to do this is a common reason for tearing comb.
4. The Vertical Lift
With both hands, lift the bar straight up, slowly and smoothly. Keep your movements deliberate. Any sudden jarring can cause the comb to sway and break.
5. Inspecting Both Sides
To see the other side of the comb, do not turn it flat. Instead, keep the bar vertical and pivot it like turning the page of a book. This allows you to view the opposite face while keeping the comb's weight safely aligned with the top bar.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While simple, the top bar design has unique challenges that you must manage during an inspection.
The Cross-Comb Challenge
Occasionally, bees will build a single comb across two or more top bars. This "cross-comb" makes a vertical lift impossible without destroying the work. This must be corrected carefully, typically by cutting the comb and realigning it.
Rushing the Process
The most common error is impatience. Trying to inspect too quickly leads to jarring movements, dropped bars, and broken comb, which can set the colony back significantly.
Ignoring Hive Expansion Needs
During your inspection, pay attention to the space near the follower board. As a rule, if the bees have drawn comb on all but one or two of the available bars, it is time to move the follower board back and add more empty bars to give them space to expand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your actions during an inspection should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is a quick health check: Gently inspect a few bars from the central brood nest to check the queen's laying pattern and look for signs of disease.
- If your primary focus is harvesting honey: Work from the back of the hive, where the heaviest combs full of cured honey are typically located.
- If your primary focus is hive expansion: Pay close attention to the space near your follower board and add new bars before the bees run out of room to build.
By mastering this deliberate handling technique, you work in partnership with the bees, ensuring the health of the colony and the integrity of their home.
Summary Table:
| Key Inspection Step | Critical Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Lifting the Bar | Lift straight up, keeping comb vertical. | Prevents shearing force from breaking the fragile comb. |
| Checking Sides | Run a hive tool down hive walls before lifting. | Detaches any comb connections to the hive body to avoid tearing. |
| Inspecting Both Sides | Pivot the bar vertically like a book page. | Allows viewing without putting stress on the comb's attachment point. |
| Common Pitfall | Avoid turning the comb horizontally. | Horizontal orientation risks the comb breaking under its own weight. |
Master the art of top bar hive management with the right equipment. As a leading supplier to commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE provides the durable, purpose-built tools you need for safe and efficient inspections. Ensure the health of your colonies and the integrity of your honey harvest. Contact our experts today to discuss your wholesale beekeeping supply needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- What are the primary functions of a stainless steel hive tool? Essential Equipment for Professional Beekeeping
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment
- Which technical challenges in hive maintenance are addressed by using a professional stainless steel hive tool?
- What is the hole in a hive tool for? A Multi-Tool for Apiary Repairs and Maintenance



















